Abstract
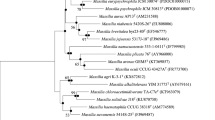
A formaldehyde-degrading bacterium strain, FD3, was isolated from contaminated soil and identified as Paracoccus sp. based on partial 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. In batch culture, the bacterium metabolized 5,000 and 8,000 mg/L formaldehyde completely within 16 and 18 h, respectively, at 30°C (pH 7.0) with agitation at 150 rpm. The degradation kinetics was found to follow a first-order model at all initial formaldehyde concentrations with regression values greater than 0.99. Formaldehyde degradation rates increased from 532.37 to 2283.04 mg/L/h as the initial concentration of formaldehyde was increased from 1,000 to 8,000 mg/L. The growth of strain FD3 on formaldehyde as a sole carbon and energy source was well described by the Luong model with a maximal specific growth rate of 0.1754/h, a half-saturation constant of 309.02 mg/L, and a maximum substrate concentration of 3875.53 mg/L. Due to its high tolerance and degradation capacity to formaldehyde, Paracoccus sp., FD3 is considered an excellent candidate for use in degrading formaldehyde in wastewaters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, G., Y. Shi, S. J. Sturla, J. R. Jalas, E. J. McIntee, P. W. Villalta, M. Wang, and S. S. Hecht (2003) Reactions of formaldehyde plus acetaldehyde with deoxyguanosine and DNA: Formation of cyclic deoxyguanosine adducts and formaldehyde cross-links. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 16: 145–152.
Marsh, G. M. (1982) Proportional mortality patterns among chemical plant workers exposed to formaldehyde. Br. J. Ind. Med. 39: 313–322.
Grafstrom, R. C., R. D. Curren, and C. C. Harris (1985) Genotoxicity of formaldehyde in cultured human bronchial fibroblasts. Sci. 228: 89–91.
Casteel, S. W., R. J. Vernon, and E. M. Bailery (1987) Formaldehyde: Toxicology and hazards. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 29: 31–33.
Zoutberg, G. R. and P. de Been (1997) The BiobedR EGSB (expanded granular sludge bed) system covers shortcomings of the up flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor in the chemical industry. Water Sci. Technol. 35: 183–188.
Kaszycki, P., M. Tyszka, P. Malec, and H. Kołoczek (2001) Formaldehyde and methanol biodegradation with the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha. An application to real wastewater treatment. Biodegradation 12: 169–177.
Shinagawa, E., H. Toyama, K. Matsushita, P. Tuitemwong, G. Theeragool, and O. Adachi (2008) Formaldehyde elimination with formaldehyde and formate oxidase in membrane of acetic acid bacteria. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 105: 292–295.
Kondo, T., Y. Morikawa, N. Hayashi, and N. Kitamoto (2002) Purification and characterization of formate oxidase from a formaldehyde-resistant fungus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 214: 137–142.
Kato, N., N. Miyawaki, and C. Sakazawa (1982) Oxidation of formaldehyde by the resistant yeasts Debaryomyces vanriji and Trichosporon penicillatum. Agric. Biol. Chem. 46: 655–661.
Gutheil, W. G., E. Kasimoglu, and P. C. Nicholson (1997) Induction of glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity in Escherichia coli and Hemophilus influenza. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 238: 693–696.
Azachi, M., Y. Henis, A. Oren, P. Gurevich, and S. Sarig (1995) Transformation of formaldehyde by a Halomonas sp. Can. J. Microbiol. 41: 548–553.
Mirdamadi, S., A. Rajabi, P. Khalilzadeh, N. Norozian, A. Akbarzadeh, and F. A. Mohseni (2005) Isolation of bacteria able to metabolize high concentrations of formaldehyde. World J. Microb. Biot. 21: 1299–1301.
Adroer, N., C. Casas, C. de Mas, and C. Solà (1990) Mechanism of formaldehyde biodegradation by Pseudomonas putida. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33: 217–220.
Doronina, N. V., V. A. Ezhov, and Y.. A. Trotsenko (1997) Aerobic biodegradation of formaldehyde, methanol and methylamine by immobilized Methylobacterium extorquens cells. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 33: 138–141.
Hidalgo, A., A. Lopategi, M. Prieto, J. L. Serra, and M. J. Llama (2002) Formaldehyde removal in synthetic and industrial wastewater by Rhodococcus erythropolis UPV-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 58: 260–263.
Sawada, A., R. Ikeda, E. Tamiya, T. Yoshida, T. Oyabu, and H. Nanto (2006) A novel formaldehyde-degrading fungus, Trichoderma virens: Isolation and some properties. IEICE Trans. Electron. 89: 1786–1791.
Oliveira, S. V. W. B., E. M. Moraes, M. A. T. Adorno, M. B. A. Varesche, E. Foresti, and M. Zaiat (2004) Formaldehyde degradation in an anaerobic packed-bed bioreactor. Water Res. 38: 1685–1694.
Qu, M. and S. K. Bhattacharya (1997) Toxicity and biodegradation of formaldehyde in anaerobic methanogenic culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 55: 727–736.
Nash, T. (1953) The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem. J. 55: 416–421.
Gonzalez-Gil, G., R. Kleerbezem, and G. Lettinga (2002) Conversion and toxicity characteristics of formaldehyde in acetoclastic methanogenic sludge. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 79: 314–322.
Pereira, N. S. and M. Zaiat (2009) Degradation of formaldehyde in anaerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor (ASBBR). J. Hazard. Mater. 163: 777–782.
Luong, J. H. T. (1987) Generalization of Monod kinetics for analysis of growth data with substrate inhibition. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29: 242–248.
Alagappan, G. and R. Cowan (2003) Substrate inhibition kinetics for toluene and benzene degrading pure cultures and a method for collection and analysis of respirometric data for strongly inhibited cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 83: 798–809.
Emanuelsson, M. A. E., M. B. Osuna, R. M. F. Jorge, and P. M. L. Castro (2009) Isolation of a Xanthobacter sp. degrading dichloromethane and characterization of the gene involved in the degradation. Biodegradation 20: 235–244.
Baptista, I. I. R., N. Y. Zhou, R. A. C. Emanuelsson, L. G. Peeva, and D. J. Leak (2007) Evidence of species succession during chlorobenzene biodegradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 99: 68–74.
Carvalho, M. F., C. C. Alves, M. I. Ferreira, P. De Marco, and P. M. L. Castro (2002) Isolation and initial characterization of bacterial consortia able to mineralize fluorobenzene. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68: 102–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Geng, Y., Fan, J. et al. Isolation and identification of Paracoccus sp. FD3 and evaluation of its formaldehyde degradation kinetics. Biotechnol Bioproc E 18, 300–305 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0449-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0449-8