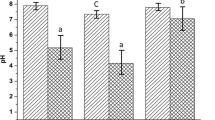
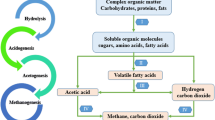
Abstract
Anaerobic co-digestion is effective and environmentally attractive technology for energy recovery from organic waste. Organic, agricultural and industrial wastes are good substrates for anaerobic co-digestion because they contain high levels of easily biodegradable materials. In this paper enhancement of biogas production from codigestion of whey and cow manure was investigated in a series of batch experiments. The influence of whey ratio on specific biogas production in a mixture with cow manure was analyzed at 35 and 55°C, for different initial pH values and for different concentrations of supplemental bicarbonate in experiments carried out over 12 days. Good biogas production (6.6 dm3/dm3), methane content (79.4%) in a biogas mixture and removal efficiencies for total solids (16%) were achieved at optimum process conditions (temperature of 55°C, 10% v/v of whey and 5 g/dm3 NaHCO3 in the initial mixture). In order to validate optimized conditions for co-digestion of whey and cow manure in the one-stage batch process, the experiments were performed within 45 days. The high biogas production (21.8 dm3/dm3), a good methane content (78.7%) in a biogas mixture as well as maximum removal efficiencies for total solids (32.3%), and chemical oxygen demand (56.3%), respectively indicate that whey could be efficiently degraded to biogas in a onestage batch process when co-digested with cow manure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kothari, R., V. V. Tyagi, and A. Pathak (2010) Waste-to-energy: A way from renewable energy sources to sustainable development. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 14: 3164–3170.
Ward, A. J., P. J. Hobbs, P. J. Holliman, and D. L. Jones (2008) Optimisation of the anaerobic digestion of agricultural resources. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 7928–7940.
Saddoud, A., I. Hassaïri, and S. Sayadi (2007) Anaerobic membrane reactor with phase separation for the treatment of cheese whey. Bioresour. Technol. 98: 2102–2108.
Álvarez, J. A., L. Otero, and J. M. Lema (2010) A methodology for optimising feed composition for anaerobic co-digestion of agro-industrial wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 1153–1158.
Mata-Alvarez, J., S. Macé, and P. Llabrés (2000) Anaerobic digestion of organic solid wastes: An overview of research achievements and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 74: 3–16.
Mshandete, A., A. Kivaisi, A. Rubindamayugi, and B. Mattiason (2004) Anaerobic digestion of sisal pulp and fish wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 95: 19–24.
Dareioti, M. A., S. N. Dokianakis, K. Stamatelatou, C. Zafiri, and M. Kornaros (2010) Exploitation of olive mill wastewater and liquid cow manure for biogas production. Waste Manage. 30: 1841–1848.
Gannoun, H., E. Khelifi, H. Bouallagui, Y. Touhami, and M. Hamdi (2008) Ecological clarification of cheese whey prior to anaerobic digestion in upflow anaerobic filter. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 6105–6111.
Demirel, B., O. Yenigun, and T. T. Onay (2005) Anaerobic treatment of dairy wastewaters: a review. Proc. Biochem. 40: 2583–2595.
Tango, M. S. A. and A. E. Ghaly (1999) Effect of temperature on lactic acid production from cheese whey using Lactobacillus helveticus under batch conditions. Biomass Bioenerg. 16: 61–78.
Vasala, A., J. Panula, and P. Neubauer (2005) Efficient lactic acid production from high salt containing dairy by-products by Lactobacillus salivarius ssp. salicinius with pre-treatment by proteolytic microorganisms. J. Biotechnol. 117: 421–431.
Mawson, A. J. (1994) Bioconversion for whey utilization and waste abatement. Bioresour. Technol. 47: 195–203.
Galegenis, J., D. Georgakakis, I. Angelidaki, and V. Mavris (2007) Optimization of biogas production by co-digesting whey with diluted poultry manure. Renew. Energ. 32: 2147–2160.
Ergüder, T. H., U. Tezel, E. Güven, and G. N. Damirer (2001) Anaerobic biotransformation and methane generation potential of cheese whey in batch and UASB reactors. Waste Manage. 21: 643–650.
Mockaitis, G., S. M. Ratusznei, J. A. D. Rodrigues, M. Zaiat, and E. Foresti (2006) Anaerobic whey treatment by a stirred sequencing batch reactor (ASBR): Effect of organic loading and supplemented alkalinity. J. Environ. Manage. 79: 198–206.
Malaspina, F., C. M. Cellamare, L. Stante, and A. Tilche (1996) Anaerobic treatment of cheese whey with a downflow-upflow hybrid reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 55: 131–139.
Ratusznei, S. M., J. A. D. Rodrigues, and M. Zaiat (2003) Operating feasibility of anaerobic whey treatment in a stirred sequencing batch reactor containing immobilized biomass. Water Sci. Technol. 48: 179–186.
Yang, K., Y. Yu, and S. Hwang (2003) Selective optimization in thermophilic acidogenesis of cheese-whey wastewater to acetic and butyric acids: Partial acidification and methanation. Water Res. 37: 2467–2477.
Frigon, J. -C., J. Breton, T. Bruneau, R. Moletta, and S. R. Guiot (2009) The treatment of cheese whey wastewater by sequential anaerobic and aerobic steps in a single digester at pilot scale. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 4156–4163.
Handajani, M. (2004) Degradation of Whey in an Anaerobic Fixed Bed (AnFB) Reactor. Dissertation. Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Fakultät für Bauingenieur-, Geo- und Umweltwissenschaften, Karlsruhe, Germany.
Tabatabaei, M., R. A. Rahim, N. Abdullah, A. -D. G. Wright, Y. Shirai, K. Sakai, A. Sulaiman, and M. A. Hassan (2010) Importance of the methanogenic archaea populations in anaerobic wastewater treatments. Proc. Biochem. 45: 1214–1225.
Göblös, S., P. Portör, D. Bordás, M. Kálmán, and I. Kiss (2008) Comparison of the effectivities of two-phase and single-phase anaerobic sequencing batch reactors during dairy wastewater treatment. Renew. Energ. 33: 960–965.
Rico, C., H. García, and J. L. Rico (2011) Physical-anaerobicchemical process for treatment of dairy cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 2143–2150.
Labatut, R. A., L. T. Angenent, and N. R. Scott (2011) Biochemical methane potential and biodegradability of complex organic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 102: 2255–2264.
Ogejo, J. A. and L. Li (2010) Enhancing biomethane production from flush dairy manure with turkey processing wastewater. Appl. Energ. 87: 3171–3177.
Al Seadi, T. (2001) Good practice in quality management of AD residues from biogas production. IEA Bioenergy. Task 24 Energy from Biological Conversion of Organic Waste.
Kavacik, B. and B. Topaloglu (2010) Biogas production from codigestion of a mixture of cheese whey and dairy manure. Biomass Bioenerg. 34: 1321–1329.
Amon, T., B. Amon, V. Kryvoruchko, W. Zollitsch, K. Mayer, and L. Gruber (2007) Biogas production from maize and dairy cattle manure — Influence of biomass composition on the methane yield. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 118: 173–182.
Hartmann, H. and B. K. Ahring (2005) Anaerobic digestion of the organic fraction of municipal solid waste: Influence of codigestion with manure. Water Res. 39: 1543–1552.
Karim, K., K. T. Klasson, R. Hoffmann, S. R. Drescher, D. W. DePaoli, and M. H. Al-Dahhan (2005) Anaerobic digestion of animal waste: Effect of mixing. Bioresour. Technol. 96: 1607–1612.
American Public Health Association (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 20th ed., American Public Health Association. Washington D. C., USA.
ISO 14235 (1998) Soil quality — Determination of organic carbon by sulfochromic oxidation.
Chen, Y., J. J. Cheng, and K. S. Creamer (2008) Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 4044–4064.
Yadvika, Santosh, T. R. Sreekrishnan, S. Kohli, and V. Rana (2004) Enhancement of biogas production from solid substrates using different techniques — a review. Bioresour. Technol. 95: 1–10.
Venetsaneas, N., G. Antonopoulou, K. Stamatelatou, M. Kornaros, and G. Lyberatos (2009) Using cheese whey for hydrogen and methane generation in a two-stage continuous process with alternative pH controlling approaches. Bioresour. Technol. 100: 3713–3717.
Kim, M., C. Y. Gomec, Y. Ahn, and R. E. Speece (2003) Hydrolysis and acidogenesis of particulate organic material in mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Environ. Technol. 24: 1183–1190.
Kizilkaya, R. and B. Bayrakli (2005) Effects of N-enriched sewage sludge on soil enzyme activities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 30: 192–202.
Kaparaju, P., I. Buendia, L. Ellegaard, and I. Angelidakia (2008) Effects of mixing on methane production during thermophilic anaerobic digestion of manure: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 4919–4928.
Vavilin, V. A., B. Fernandez, J. Palatsi, and X. Flotats (2008) Hydrolysis kinetics in anaerobic degradation of particulate organic material: An overview. Waste Manage. 28: 939–951.
Spachos, T. and A. Stamatis (2011) Thermal analysis and optimization of an anaerobic treatment system of whey. Renew. Energ. 36: 2097–2105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hublin, A., Zokić, T.I. & Zelić, B. Optimization of biogas production from co-digestion of whey and cow manure. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 1284–1293 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0044-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-012-0044-z