Abstract
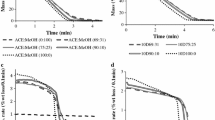
In this study, peptide-loaded microparticles were prepared using an aerosol solvent extraction system (ASES) by employing supercritical carbon dioxide as an antisolvent. The effects of the molecular weight of poly(Llactide) (PLLA), poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG), the block length of methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide) (mPEG-PLLA), the blending of PLLA and PEG, and the drug-to-polymer feed ratio on the formation of leuprolide acetate (LA)-loaded microparticles and their release characteristics were investigated. Scanning electron microscope observations showed that the LA-loaded polymer particles had a spherical morphology with a smooth surface. The entrapment efficiency of LA in the ASES-processed microparticles was found to be extremely high (about 99%), whereas the initial release rate of the LA-loaded microparticles was very low for PLLA. The release rate of LA was observed to increase as the PEG block length of mPEG-PLLA and/or the drug content in the microparticles increased. When PLLA was blended with PEG, the release rate of LA from the PLLA/PEG microparticles was significantly faster compared with the corresponding mPEG-PLLA copolymer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharifi, R., L. D. Knoll, J. Smith, and E. Kramolowsky (1998) Leuprolide acetate (30-mg depot every four months) in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Urol. 51: 271–276.
Inada, K., T. Tominaga, M. Toi, Y. Yamamoto, M. Abe, J. Yamashita, and M. Ogawa (1996) Protective effect of leuprolide acetate on 7,12-dimehtylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary carcinogenesis in rats. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 22: 583–587.
Covens, A., G. Thomas, P. Shaw, I. Ackerman, R. Osborne, H. Lukka, M. Carey, E. Franssen, and K. Roche (1997) A phase II study of leuprolide in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 64: 126–129.
Lee, P. A. and J. G. Page (1989) Effects of leuprolide in the treatment of central precocious puberty. J. Pediatr. 114: 321–324.
Wilson, A. C., S. V. Meethal, R. L. Bowen, and C. S. Atwood (2007) Leuprolide acetate:A drug of diverse clinical application. Experti. Opin. Investig. Drugs 16: 1–13.
Qiu, Y., H. W. Johnson, T. L. Reiland, and M. -Y. F. Lu (1999) Sublingual absorption of leuprolide: comparison between human and animal models. Int. J. Pharm. 179: 27–36.
Okada, H. (1997) One- and three-month release injectable microspheres of the LH-RH superagonist leuprorelin acetate. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 28: 43–70.
Woo, B. H., J. W. Kostanski, S. Gebrekidan, B. A. Dani, B. C. Thanoo, and P. P. DeLuca (2001) Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of 120-day poly(d,l-lactide) leuprolide microspheres. J. Control. Rel. 75: 307–315.
Ravivarapu, H. B., K. Burton, and P. P. DeLuca (2000) Polymer and microsphere blending to alter the release of a peptide from PLGA microspheres. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 50: 263–270.
Alcock, R., J. A. Blair, D. J. O’Mahony, A. Raoof, and A. V. Quirk (2002) Modifying the release of leuprolide from spray dried OED microparticles. J. Control. Rel. 82: 429–440.
Gref, R., A. Domb, P. Quellec, T. Blunk, R. H. Miiller, J. M. Verbavatz, and R. Langer (1995) The controlled intravenous delivery of drugs using PEG-coated sterically stabilized nanospheres. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 16: 215–233.
Stolnik, S., S. E. Dunn, M. C. Garnett, M. C. Davies, A. G. A. Coombes, D. C. Taylor, M. P. Irving, S. C. Purkiss, T. F. Tadros, S. S. Davis, and L. Illum (1994) Surface modification of poly-(lactide-co-glycolide) nanospheres by biodegradable poly(lactide)-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymer. Pharm. Res. 11: 1800–1808.
Robio, M., R. Gref, A. Sanchez, R. Langer, and M. J. Alonso (1998) Stealth PLA-PEG nanoparticles as protein carriers for nasal administration. Pharm. Res. 15: 270–275.
Owens III, D. E. and N. A. Peppas (2006) Opsonization, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics of polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 307: 93–102.
Li, Y. -P., Y. -Y. Pei, X. -Y. Zhang, Z. -H. Gu, Z. -H. Zhou, W. -F. Yuan, J. -J. Zhou, J. -H. Zhu, and X. -J. Gao (2001) PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles as protein carriers: Synthesis, preparation and biodistribution in rats. J. Control. Rel. 71: 203–211.
Yeo, Y., N. Baek, and K. Park (2001) Microencapsulation methods for delivery of protein drugs. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 6: 213–230.
Yeo, S. D. and E. Kiran (2005) Formation of polymer particles with supercritical fluids: A review. J. Supercrit. Fluids 34: 287–308.
Fages, J., H. T. Lochard, J. -J. Letourneau, M. Sauceau, and E. Rodier (2004) Particle generation for pharmaceutical applications using supercritical fluid technology. Powder Technol. 141: 219–226.
Reverchon, E. (1999) Supercritical antisolvent precipitation of micro- and nano-particles. J. Supercrit. Fluids 15: 1–21.
Huang, C., S. -H. Tsai, and C. -M. Chen (2006) Isothermal crystallization behavior of poly(L-lactide) in poly(L-lactide)-blockpoly( ethylene glycol) diblock copolymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys. 44: 2438–2448.
Kaihara, S., S. Matsumura, A. G. Mikos, and J. P. Fisher (2007) Synthesis of poly(L-lactide) and polyglycolide by ring-opening polymerization. Nat. Protoc. 2: 2767–2771.
Gourgouillon, D. and M. Nunes da Ponte (1999) High pressure phase equilibria for poly(ethylene glycol)s + CO2: experimental results and modeling. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1: 5369–5375.
Elvassore, N., A. Bertucco, and P. Caliceti (2001) Production of insulin-loaded poly(ethylene glycol)/poly(l-lactide) (PEG/PLA) nanoparticles by gas antisolvent techniques. J. Pharm. Sci. 90: 1628–1636.
International Conferences on Harmonization (1997) Impurities-Guidelines for residual solvents, Q3C. Federal Register. 62: 67377–67388.
Jacobson, G. B., R. Shinde, C. H. Contag, and R. N. Zare (2008) Sustained release of drugs dispersed in polymer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47: 7880–7882.
Kang, Y., C. Yang, P. Ouyang, G. Yin, Z. Huang, Y. Yao, and X. Liao (2009) The preparation of BSA-PLLA microparticles in a batch supercritical anti-solvent process. Carbohydr. Polym. 77: 244–249.
Dong, Y. and S. -S. Feng (2004) Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactide) (MPEG-PLA) nanoparticles for controlled delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 25: 2843–2849.
Elvassor, N. and A. Bertucco (2001) Production of protein-loaded polymeric microcapsules by compressed CO2 in a mixed solvent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 40: 795–800.
Mehta, R. C., B. C. Thanoo, and P. P. DeLuca (1996) Peptide containing microspheres from low molecular weight and hydrophilic poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide). J. Control. Rel. 41: 249–257.
Hyvönen, S., L. Peltonen, M. Karjalainen, and J. Hirvonen (2005) Effect of nanoprecipitation on the physicochemical properties of low molecular weight poly([scl]-lactic acid) nanoparticles loaded with salbutamol sulphate and beclomethasone dipronate, Int. J. Pharm. 295: 269–281.
Wichert, B. and P. Rohdewald (1990) A new method for the preparation of drug containing polylactic acid microparticles without using organic solvents. J. Control. Rel. 14: 269–283.
Palade, L. -I., H. J. Lehermeier, and J. R. Dorgan (2001) Melt rheology of high L-content poly(lactic acid). Macromol. 34: 1384–1390.
López-Periago, A., C. A. García-González, and C. Domingo (2009) Solvent- and thermal-induced crystallization of poly-Llactic acid in supercritical CO2 medium. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 111: 291–300.
Westerman, D., S. P. Nalawade, G. A. Leeke, D. W. Grijpma, and R. C. D. Santos (2008) Analysis of melting point depression in biodegradable polymers using supercritical carbon dioxide by golden gate IR and high pressure DSC. Proceedings of 11th European Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. May 4–7, Barcelona, Spain.
Martin, A., F. Mattea, L. Gutierrez, F. Miguel, and M. J. Cocero (2007) Co-precipitation of carotenoids and bio-polymers with the supercritical anti-solvent process. J. Supercr. Fluids 41: 138–147.
Choi, Y., S. Y. Kim, M. -H. Moon, S. H. Kim, K. -S. Lee, and Y. Byun (2001) Poly(ethylene glycol)}poly(l-lactide) diblock copolymer prevents aggregation of poly(l-lactide) microspheres during ethylene oxide gas sterilization. Biomaterials 22: 995–1004.
Lee, B. -C. and Y. -M. Kuk (2002) Phase behavior of poly(l-lactide) in supercritical mixtures of dichloromethane and carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 47: 367–370.
Huang, Y. -Y., T. -W. Chung, and T. -W. Tzeng (1997) Drug release from PLA/PEG microparticulates. Int. J. Pharm. 156: 9–15.
Caliceti, P., S. Salmaso, N. Elvassore, and A. Bertucco (2004) Effective protein release from PEG/PLA nano-particles produced by compressed gas anti-solvent precipitation techniques. J. Control. Rel. 94: 195–205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, II., Haam, S., Lim, G. et al. Preparation of peptide-loaded polymer microparticles using supercritical carbon dioxide. Biotechnol Bioproc E 17, 185–194 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0241-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0241-1