Abstract
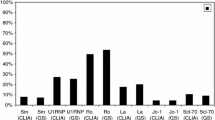
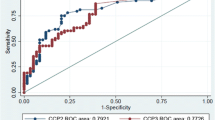
An immunoassay based on stick-type solid support (immunostick assay) was developed. To demonstrate the medical diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), cyclic-citrullinated peptide (CCP), one of specific antigens against RA autoantibodies, was immobilized on the surface of the immunostick, and a color index table was prepared for the determination of CCP-positivity of the test sera. The positivity of RA-positive (n = 31) and RA-negative (n = 20) sera was tested using the immunostick assay and a conventional enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The statistical agreement of the test results from both methods was analyzed using inter-rater coefficient kappa and Bland-Altman test. The immunostick assay with a color index table was determined to have a high statistical correlation to the conventional ELISA method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekins, R. P. (1999) Immunoassay and other ligand assays: From isotopes to luminescence. J. Clin. Ligand Assay 22: 61–77.
Gosling, J. P. (2000) Immunoassays. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Asensio, L., I. González, T. García, and R. Martín (2008) Determination of food authenticity by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Food Control. 19: 1–8.
Hurley, I. P., R. Cook, C. W. Laughton, N. A. Pickles, H. E. Ireland, and J. H. H. Williams (2009) Detection of human blood by immunoassay for applications in forensic analysis. Forensic Sci. International. 190: 91–97.
Wolfe, A. M., J. H. Kellgren, and A. T. Masi (1968) The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis: A review. II. Incidence and diagnostic criteria. Bull Rheum. Dis. 19: 524–529.
Visser, H., L. B. S. Gelinck, A. H. Kampfraath, C. Breedveld, and J. M. W. Hazes (1996) Diagnostic and prognostic characteristics of the enzyme linked immunosorbent rheumatoid factor assay in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 55: 157–161.
Harris, E. (1993) Etiology and pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. pp. 833–868. In: W. Kelley, E. Harris, S. Ruddy, and C. Sledge (eds.). Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Harris, E. (1993) Clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. pp. 874–907. In: W. Kelley, E. Harris, S. Ruddy, and C. Sledge (eds.). Kelley’s Textbook of Rheumatology. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Schellekens, G. A., H. Visser, B. A. de Jong, F. H. van den Hoogen, J. M. Hazes, F. C. Breedveld, and W. J. van Venrooij (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum. 43: 155–163.
Nakamura, R. M. (2000) Progress in the use of biochemical and biological markers for evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 14: 305–313.
Sebbag, M., M. Simon, C. Vincent, C. Masson-Bessiere, E. Girbal, J. J. Durieux, and G. Serre (1995) The antiperinuclear factor and the so-called antikeratin antibodies are the same rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J. Clin. Invest. 95: 2672–2679.
Arnett, F. C., S. M. Edworthy, and D. A. Bloch (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 31: 315–324.
Jose, J., M. Park, and J. C. Pyun (2010) Highly sensitive immunoassay based on E. coli with autodisplayed Z-domain. Analytica Chim. Acta. 667: 113–118.
Mackinnon, A. (2000) A spreadsheet for the calculation of comprehensive statistics for the assessment of diagnostic tests and inter-rater agreement. Computers in Biol. Med. 30: 127–134.
Bland, J. M. and D. G. Altman (1986) Statistical method for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. The Lancet i: 307–310.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, H., Lee, EH., Jeon, BJ. et al. Immunostick assay for medical diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Biotechnol Bioproc E 16, 1248–1253 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0106-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-011-0106-7