Abstract
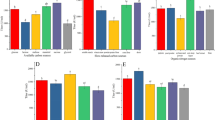
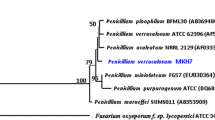
Beauvericin (BEA) is a proven and potent antibiotic compound useful for bio-control and a potential antifungal and anticancer agent for human. This study was to evaluate and optimize the nutrient medium for BEA production in mycelial liquid culture of a high BEA-producing fungus Fusarium redolens Dzf2 isolated from a medicinal plant. Among various organic and inorganic carbon and nitrogen sources, glucose and peptone were found the most favorable for the F. redolens Dzf2 mycelial growth and BEA production. Through a Plackett-Burman screening test on a basal medium, glucose, peptone, and medium pH were identified as the significant factors for mycelial growth and BEA production. These factors were optimized through central composite design of experiments and response surface methodology, as 49.0 g/L glucose, 13.0 g/L peptone and pH 6.6, yielding 198 mg/L BEA (versus 156 mg/L in the basal medium). The BEA yield was further increased to 234 mg/L by feeding 10 g/L glucose to the culture during exponential phase. The results show that F. redolens Dzf2 mycelial fermentation is a feasible and promising process for production of BEA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamill, R. L., C. E. Higgens, H. E. Boaz, and M. Gorman (1969) The structure of beauvericin, a new depsipeptide antibiotic toxic to Artemia salina. Tetrahed. Lett. 49: 4255–4258.
Bernardini, M., A. Carilli, G. Pacioni, and B. Santurbano (1975) Isolation of beauvericin from Paecilomyces fumosoroseus. Phytochemistry 14: 1865.
Grove, J. F. and M. Pople (1980) The insecticidal activity of beauvericin and the enniatin complex. Mycopathologia 70: 103–105.
Castlebury, L. A., J. B. Sutherland, L. A. Tanner, A. L. Henderson, and C. E. Cerniglia (1999) Use of a bioassay to evaluate the toxicity of beauvericin to bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 15: 119–121.
Nilanonta, C., M. Isaka, P. Kittakoop, and S. Trakulnaleamsai (2002) Precursor-directed biosynthesis of beauvericin analogs by the insect pathogenic fungus Paecilomyces tenuipes BCC 1614. Tetrahedron 58: 3355–3360.
Jow, G., C. Chou, B. Chen, and J. Tsai (2004) Beauvericin induces cytotoxic effects in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells through cytochrome c release, caspase 3 activation: the causative role of calcium. Cancer Lett. 216: 165–173.
Lin, H. I., Y. J. Lee, B. F. Chen, M. C. Tsai, J. L. Lu, C. J. Chou, and G. M. Jow (2005) Involvement of Bcl-2 family, cytochrom c, and caspase 3 in induction of apoptosis by beauvericin in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 230: 248–259.
Zhang, L., K. Yan, Y. Zhang, R. Huang, and X. Chen (2007) High-throughput synergy screening identifies microbial metabolites as combination agents for the treatment of fungal infections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104: 4606–4611.
Logrieco, A., A. Moretti, G. Castella, M. Kostecki, P. Golinski, A. Ritieni, and J. Chelkowski (1998) Beauvericin production by Fusarium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 3084–3088.
Fotso, J., J. F. Leslie, and J. S. Smith (2002) Production of beauvericin, moniliformin, fusaproliferin, and fumonisins B1, B2, and B3 by fifteen ex-type strains of Fusarium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68: 5195–5197.
Moretti, A., G. Mule, A. Ritieni, and A. Logrieco (2007) Further data on the production of beauvericin, enniatins and fusaproliferin and toxicity to Artemia salina by Fusarium species of Gibberella fujikuroi species complex. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 118: 158–163.
Lee, H. S., H. H. Song, J. H. Ahn, C. G. Shin, G. P. Lee, and C. Lee (2008) Statistical optimization of growth medium for the production of the entomopathogenic and phytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide beauvericin from Fusarium oxysporum KFCC 11363P. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18: 138–144.
Xu, L., L. Zhou, J. Zhao, J. Li, X. Li, and J. Wang (2008) Fungal endophytes from Dioscorea zingiberensis rhizomes and their antibacterial activity. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 46: 68–72.
Cheilas T., T. Stoupis, P. Christakopoulos, P. Katapodis, D. Mamma, D. G. Hatzinikolaou, D. Kekos, and B. J. Macris (2000) Hemicellulolytic activity of Fusarium oxysporum grown on sugar beet pulp. Production of extracellular arabinanase. Proc. Biochem. 35: 557–561.
Pio, T. F. and G. A. Macedo (2007) Optimizing the production of cutinase by Fusarium oxysporum using response surface methodology. Enz. Microb. Technol. 41: 613–619.
Duncan, D. B. (1955) Multiple range and multiple F tests. Biometrics 11: 1–42.
Box, G. E. P., J. S. Hunter, and W. G. Hunter (2005) Statistics for experimenters: design, innovation, and discovery. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken, NJ, USA.
Peeters, H., R. Zocher, N. Madry, and H. Kleinkauf (1983) Incorporation of radioactive precursors into beauvericin produced by Paecilomyces fumoso-roseus. Phytochem. 22: 1719–1720.
Peeters, H., R. Zocher, N. Madry, and H. Kleinkauf (1988) Synthesis of beauvericin by a multifunctional enzyme. J. Antibiot. 41: 352–359.
Lee, C., H. Gorisch, H. Kleinkauf, and R. Zocher (1992) A highly specific D-hydroxyisovalerate dehydrogenase from the enniatin producer Fusarium sambucinum. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 11741–11747.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, LJ., Liu, YS., Zhou, LG. et al. Optimization of a liquid medium for beauvericin production in Fusarium redolens Dzf2 mycelial culture. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 460–466 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3031-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3031-2