Abstract
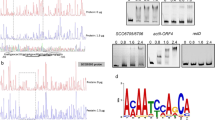
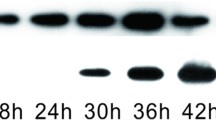
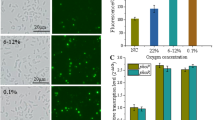
In this study, transcriptional analyses by using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), DNA chip, and quantitative real time-PCR were performed to investigate effects of acidic pH shock on two-component systems in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Two-component systems of cseC/cseB and vanS/vanR known to be closely linked with self-protection against cell wall hydrolysis caused by external stimuli were upregulated by the pH shock. The chiS/chiR, afsQ2/afsQ1, ecrA2/ecrA1, bldM, ramC/ramR, and ragK/ragR known to be positively associated with the initiation of secondary metabolism were also upregulated. The cutS/cutR known to be negatively related to the secondary metabolism was, however, slightly downregulated. Upregulation or downregulation by the acidic pH shock of these two-component regulator systems might have contributed in a concerted manner to the enhancement of secondary metabolite production, at least, in this particular case of actinorhodin production in S. coelicolor A3(2).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beppu, T. (1995) Signal transduction and secondary metabolism: prospects for controlling productivity. Trends Biotechnol. 13: 264–269.
Hayes, A., G. Hobbs, C. P. Smith, S. G. Oliver, and P. R. Butler (1997) Environmental signals triggering methylenomycin production by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 179: 5511–5515.
Horinouchi, S. (2003) AfsR as an integrator of signals that are sensed by multiple serine/threonine kinase in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30: 462–467.
Horiouchi, S. and T. Beppu (1992) Regulatin of secondary metabolism and cell differentiation in Streptomyces: A-factor as a microbial hormone and the AfsR protein as a component of a two-component regulatory system. Gene 115: 167–172.
Mikilik, K., Q. Khanh-Hoang, P. Halada, S. Bezoouskova, O. Benada, and V. Behal (1999) Expression of the Csp protein family upon cold shock and production of tetracycline in Streptomyces aureofaciens. Biochem. Biophysic. Res. Comm. 265: 305–310.
Sevcikova, B. and J. Kormanec (2004) Differential prodcution of two antibiotics of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), actinorhodin and undecylprodigiosin, upon salt stress conditions. Arch. Microbiol. 181: 384–389.
Kim, C. J., Y. K. Chang, G. T. Chun, Y. H. Jeong, and S. J. Lee (2001) Continuous culture of immobilized Streptomyces cells for kasugamycin production. Biotechnol. Prog. 17: 453–461.
Kim, C. J., Y. K. Chang, and G. T. Chun (2000) Enhancement of kasugamycin production by pH shock in batch cultures of Streptomyces kasugaensis. Biotechnol. Prog. 16: 548–552.
Kim, Y. J., J. Y. Song, M. H. Moon, C. P. Smith, S. K. Hong, and Y. K. Chang (2007) pH shock induces overexpression of regulatory and biosynthetic genes for actinorhodin production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76: 1119–1130.
Hoch, J. A. and T. J. Silhavy (1995) Two-Component Signal Transduction. ASM Press, Washington, DC, USA.
Stephenson, K. and J. A. Hoch (2002) Virulence- and antibiotic resistance-associated two-component systems of Gram-positive pathogenic bacteria as targets for antimicrobial therapy. Pharm. Therap. 93: 293–305.
Ninfa, A. J. and B. Magasanik (1986) Covalent modification of the glnG product, NRI, by the glnL product, NRII, regulates the transcription of the glnALG operon in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83: 5909–5913.
Kieser, T., M. J. Bibb, M. J. Buttner, K. F. Chater, and D. A. Hopwood (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich, UK.
Hong, H. J., M. S. B. Paget, and M. J. Buttner (2002) A systems in Streptomyces coelicolor that activates the expression of a putative cell wall glycan operon in response to vancomycin and other cell wall-specific antibiotics. Mol. Microbiol. 44: 1199–1211.
Hong, H. J., M. I. Hutchings, J. M. Neu, G. D. Wright, M. S. B. Paget, and M. J. Buttner (2004) Characterization of an inducible vancomycin resistance system in Streptomyces coelicolor reveals a novel gene (vanK) required for drug resistance. Mol. Microbiol. 52: 1107–1121.
Hutchings, M. I., H. J. Hong, and M. J. Buttner (2006) The vancomycin resistance VanRS two-component signal transduction system of Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol. Microbiol. 59: 923–935.
Homerová, D., R. Knirschová, and J. Kormanec (2002) Response regulator ChiR regulates expression of chitinase gene, chiC, in Streptomyces coelicolor. Folia Microbiol. 47: 499–505.
Tsujibo, H., N. Hatano, T. Okamoto, H. Endo, K. Miyamoto, and Y. Inamori (1999) Synthesis of chitinase in Streptomyces thermoviolaceus is regulated by a two-component sensor-regulator system. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 181: 83–90.
Ishizuka, H., S. Horinouchi, H. M. Kieser, D. A. Hopwood, and T. Beppu (1992) A putative two-component regulatory system involved in secondary metabolism in Streptomyces spp. J. Bacteriol. 17423: 7585–7594.
LI, Y. Q., P. L. Cen, S. F. Chen, D. Wu, and J. Zheng (2004) A pair of two-component regulatory genes ecrA1/A2 in S. coelicolor. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 5: 173–179.
Huang, J. L., C. J. Lih, K. H. Pan, and S. N. Cohen (2001) Global analysis of growth phase responsive gene expression and regulation of antibiotic biosynthetic pathways in Streptomyces coelicolor using DNA microarrays. Genes Dev. 15: 3183–3192.
Chang, H. M., M. Y. Chen, T. T. Shieh, M. J. Bibb, and C. W. Chen (1996) The cutRS systems of Streptomyces lividans represses the biosynthesis of the polyketide antibiotic actinorhodin. Mol. Microbiol. 21: 1075–1085.
Chater, K. F. and G. Chandra (2006) The evolution of development in Streptomyces analysed by genome comparisons. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 30: 651–672.
Paolo, S. S., J. Huang, S. N. Cohen, and C. J. Thompson (2006) Rag genes: novel components of the RamR regulon that trigger morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol. Microbiol. 61: 1167–1186.
Nguyen, K. T., J. M. Willey, L. D. Nguyen, L. T. Nguyen, P. H. Viollier, and C. J. Thompson (2002) A central regulator of morphological differentiation in the multicellular bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol. Microbiol. 46: 1223–1238.
Bibb, M. J., V. Molle, and M. J. Buttner (2000) σBldN, an extracytoplasmic function RNA polymerase sigma factor required for aerial mycelium formation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J. Bacteriol. 182: 4606–4616.
Kodani, S., M. E. Hudson, M. C. Durrant, M. J. Butter, J. R. Nodwell, and J. M. Willey (2004) The SapB morphogen is a lantibiotic-like peptide derived from the product of the developmental gene rams in Streptomyces coelicolor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101: 11448–11453.
O’connor, T. J., P. Kanellis, and J. R. Nodwell (2002) The ramC gene is required for morphogenesis in Streptomyces coelicolor and expressed in a cell type-specific manner under the direct control of RamR. Mol. Microbiol. 45: 45–57.
Hopwood, D. A., K. F. Chater, and M. J. Bibb (1995) Genetics of antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), a model streptomycete. Biotechnol. 28: 65–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y.J., Moon, A.N., Song, J.Y. et al. Gene-expression analysis of acidic pH shock effects on two-component systems in Streptomyces coelicolor . Biotechnol Bioproc E 14, 584–590 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-008-0260-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-008-0260-8