Abstract
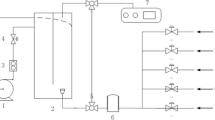
A photoautotrophic cultivation of green algae Scenedesmus cells was used for the removal of nitric oxide (NO) from a model flue gas mixture. In an attempt to improve the solubility of NO in the culture broth, the addition of Fe(II)EDTA to the cultivation was investigated. The addition of Fe(II)EDTA greatly enhanced NO-dissolution in the culture broth and subsequently increased the algal-uptake of NO. NO was assimilated as a source of nitrogen for the growth of Scenedesmus cells since there was a steady increase in cell density with no other nitrogen source in the culture except the incoming NO. 40–45% of NO removal was maintained for more than 12 days with the addition of 5 mM Fe(II)EDTA in a 1-L air-lift type photobioreactor system fed with 300 ppm of NO gas at a rate of 0.3 wm. However, the NO-dissolution-enhancing capacity of Fe(II)EDTA did not reach its full potential due to its oxidation to Fe(III)EDTA, possibly induced by molecular oxygen that evolved from algal photosynthesis, and subsequent loss of chelating capabilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fritz, A. and V. Pitchon (1997) The current state of research on automotive lean NOx catalysis. Appl. Catal. B 13: 1–25.
Cant, N. W. and I. O. Y. Liu (2000) The mechanism of the selective reduction of nitrogen oxides by hydrocarbons on zeolite catalysts. Catal. Today 63: 133–146.
Jin, Y., M. C. Veiga, and C. Kennes (2005) Bioprocesses for the removal of nitrogen oxides from polluted air. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 80: 483–494.
Nagase, H., K. I. Yoshihara, K. Eguchi, Y. Okamoto, S. Murasaki, R. Yamashita, K. Hirata, and K. Miyamoto (2001) Uptake pathway and continuous removal of nitric oxide from flue gas using microalgae. Biochem. Eng. J. 7: 241–246.
Yoshihara, K. I., H. Nagase, K. Eguchi, K. Hirata, and K. Miyamoto (1996) Biological elimination of nitric oxide and carbon dioxide from flue gas by marine microalga NOA-113 cultivated in a long tubular photobioreactor. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 82: 351–354.
Lee, J. S. and J. P. Lee (2003) Review of advances in biological CO2 mitigation technology. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 8: 354–359.
Olaizola, M. (2003) Microalgal removal of CO2 from flue gases: Changes in medium pH and flue gas composition do not appear to affect the photochemical yield of microalgal cultures. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 8: 360–367.
Wijanarko, A., Dianursanti, M. Gozan, S. M. K. Andika, P. Widiastuti, H. Hermansyah, A. B. Witarto, K. Asami, R. W. Soemantojo, K. Ohtaguchi, and S. K. Song (2006) Enhancement of carbon dioxide fixation by alteration of illumination during Chlorella vulgaris-Buintenzorg’s growth. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11: 484–488.
Negoro, M., N. Shioji, K. Miyamoto, and Y. Miura (1991) Growth of microalgae in high CO2 gas and effects of SOx and NOx. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 29: 877–886.
Melis, A. and T. Happe (2001) Hydrogen production: Green algae as a source of energy. Plant Physiol. 127: 740–748.
Hur, W. and Y. K. Chung (2006) An artificial neural network for biomass estimation from automatic pH control signal. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 11: 351–356.
van der Maas, P., T. van de Sandt, B. Klapwijk, and P. Lens (2003) Biological reduction of nitric oxide in aqueous Fe(II)EDTA solutions. Biotechnol. Prog. 19: 1323–1328.
Doucha, J., F. Straka, and K. Livansky (2005) Utilization of flue gas for cultivation of microalgae (Chlorella sp.) in an outdoor open thin-layer photobioreactor. J. Appl. Phycol. 17: 403–412.
Matsumoto, H., A. Hamasaki, and N. Sioji (1997) Influence of CO2, SO2 and NO in flue gas on microalgae productivity. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 30: 620–624.
Demmink, J. F., I. C. F. van Gils, and A. A. C. M. Beenackers (1997) Absorption of nitric oxide into aqueous solutions of ferrous chelates accompanied by instantaneous reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 36: 4914–4927.
Kleifges, K. H., G. Kreysa, and K. Juttner (1997) An indirect electrochemical process for the removal of NOx from industrial waste gases. J. Appl. Electrochem. 27: 1012–1020.
Kumaraswamy, R., U. van Dongen, J. G. Kuenen, W. Abma, M. C. M. van Loosdrecht, and G. Muyzer (2005) Characterization of microbial communities removing nitrogen oxides from flue gas: the BioDeNOx process. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71: 6345–6352.
van der Maas, P., L. Harmsen, S. Weelink, B. Klapwijk, and P. Lens (2004) Denitrification in aqueous FeEDTA solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 79: 835–841.
Roden, E. E. and D. R. Lovley (1993) Dissimilatory Fe(III) reduction by the marine microorganism Desulfu-romonas acetoxidans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 734–742.
van der Maas, P., P. van den Brink, S. Utomo, B. Klapwijk, and P. Lens (2006) NO removal in continuous BioDeNOx reactors: Fe(II)EDTA2− regeneration, biomass growth, and EDTA degradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 94: 575–584.
Andersen, R. A. (2005) Algal Culturing Techniques. pp. 439–440. Elsevier Academic Press, UK.
Jin, H. F., B. R. Lim, and K. Lee (2006) Influence of nitrate feeding on carbon dioxide fixation by microalgae. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 41: 2813–2824.
Ministry of Environment (2000) Standard Methods of Water Quality. Sections 4–12 & 4–13. The Ministry of Environment, Korea.
van der Maas, P., P. van den Bosch, B. Klapwijk, and P. Lens (2005) Nox removal from flue gas by an integrated physicochemical absorption and biological denitrification process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 90: 433–441.
Buisman, C. J. N., H. Dijkman, P. L. Verbraak, and A. J. D. Hartog (1999) Process for purifying flue gas containing nitrogen oxides. US Patent 5,891,408.
Hishinuma, Y., R. Kaji, H. Akimoto, F. Nakajima, T. Mori, T. Kamo, Y. Arikawa, and S. Nozawa (1979) Reversible binding of NO to Fe(II)EDTA. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 52: 2863–2865.
Zang, V., M. Kotowski, and R. van Eldik (1988) Kinetics and mechanism of the formation of FeII(edta)NO in the system FeII(edta)/NO/HONO/NO −2 in aqueous solutions. Inorg. Chem. 27: 3279–3283.
Hong, S. J. and C. G. Lee (2007) Evaluation of central metabolism based on a genomic database of Synechocystis PCC6803. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 12: 165–173.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, HF., Santiago, D.E.O., Park, J. et al. Enhancement of nitric oxide solubility using Fe(II)EDTA and its removal by green algae Scenedesmus sp.. Biotechnol Bioproc E 13, 48–52 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-007-0164-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-007-0164-z