Summary
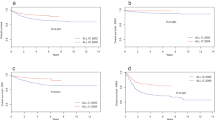
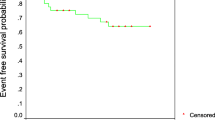
Treatment and long-term outcome in Slovenian children and adolescents, treated for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) were evaluated, mainly considering differences between treatment regimens being evolved during time. From year 1967 through 2004, 394 patients (pts) were treated and six therapeutic schemes had been used. Retrospectively 5-year overall survival ± standard error (5yOS), relapse rate (RR) and second neoplasm (SN) were estimated according to treatment regimen, age, and where recorded, also according to BFM risk group, white blood cell count and disease subtype. For treatment regimens used after year 1992, 5-year event-free survival ± standard error (5yEFS) was added to our observations. Among 75 pts enrolled in pre-POG treatment regimen, the probability of 5yOS was 25.3 ± 5.0%, while no data for RR and SN analysis were available. For 91 pts treated according to POG derived treatment, the probability of 5yOS was 61.6 ± 5.1%, with 64% RR and 5.5% occurrence of SN. Probability of 5yOS of 74.3 ± 7.4%, RR of 37% and 8.5% occurrence of SN were reached for 35 pts enrolled in ALL-BFM 83 protocol. ALL-BFM 86 protocol included 62 pts with 69.4 ± 5.9% probability of 5yOS, 33% RR and 3.2% occurrence of SN. For ALL-BFM 90 protocol the 5yEFS and 5yOS for 71 pts was 77.3 ± 5.2% and 81.8 ± 4.8%, respectively, with 17% RR and 1.5% occurrence of SN. Fifty-six patients enrolled in ALL-BFM 95 protocol reached 83.0 ± 5.2% 5yEFS and 92.6 ± 3.6% 5yOS, with 16% RR and 1.7% occurrence of SN. Stepwise rise of OS, decline in RR, reducing occurrence of SN and, for ALL-BFM 90 and ALL-BFM 95 protocol, improvements in EFS, were observed through time according to different treatment regimens. General improvement regarding OS, RR and occurrence of SN was most obvious after the application of BFM regimen with evident continuous rise in OS and decline in RR and occurrence of SN thereafter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farber S, Diamond LK, Mercer RD, Sylvester RF, Wolff JA. Temporary remissions in acute leukemia in children produced by folic acid antagonist 4-Aminopteroyl-glutamic acid (Aminopterin). New Engl J Med, 238: 787, 1948
Neglia JP, Robinson L. Epidemiology of the childhood leukemias. Ped Clin North Am, 35: 675–692, 1988
Pui CH. Childhood leukemias. New Engl J Med, 323: 1618–1629, 1995
Rhiem H, Reiter A, Schrappe M, Berthold F, Dopfer R, Gerein V, Ludwig R, Ritter J, Stollmann B, Henze G. Die corticosteroid-abhängige dezimierung der leukämiezellzahl im blut als prognosefaktor bei der akuten lymphoblastschen vleukämie im kindersalter (Therapiestudie ALL-BFM 83). Klin Pädiat, 199: 151–160, 1986.
Schrappe M, Reiter A, Ludwig WD, et al. Improved outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia despite reduced use of anthracyclines and cranial radiotherapy: results of trial ALL-BFM 90. Blood, 95: 3310–3322, 2000
Moricke A, Reiter A, Zimmermann M, Gadner H, Stanulla M, et al. Risk adjusted therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia can decrease treatment burden and improve survival: treatment results of 2169 unselected pediatric and adolescent patients enrolled in the trial ALL-BFM 95. Blood, 111(9): 4477–4489, 2008
Möricke A, Zimmermann M, Reiter A, et al. Long-term results of five consecutive trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 2000. Leukemia, 24(2): 265–284, 2010
Simone JV, Aur RJ, Hustu O, et al. Combined modality therapy of acute lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer, 35(1): 25–35, 1975
Reiter A, Schrappe M, Ludwig WD, et al. Favorable outcome of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood: a report of three consecutive studies of the BFM group. Blood, 80(10): 2471–2478, 1992
Perme MP, Jereb B. Treatment in survival after childhood cancer in Slovenia between 1957 and 2007. Pediatr Hematol Oncol, 26(4): 240–251, 2009
Jazbec J, Ecimovic P, Jereb B. Second neoplasms after treatment of childhood cancer in Slovenia. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 42(7): 574–581, 2004
Rajic V, Aplenc R, Debeljak M, et al. Influence of the polymorphism in candidate genes on late cardiac damage in patients treated due to acute leukemia in childhood. Leuk Lymphoma, 50(10): 1693–1698, 2009
Velensek V, Mazic U, Krzisnik C, et al. Cardiac damage after treatment of childhood cancer: a long term follow-up. BMC Cancer, 20(8): 141, 2008
Medical Research Council. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia-effect of 'prophylactic' therapy against central nervous system leukemia. Br Med J, 2: 381–384, 1973
Riehm H, Gadner H, Henze G, et al. Results and significance of six randomized trials in four consecutive ALL-BFM studies. Haematol Blood Transfus, 33: 439–450, 1990
Reiter A, Schrappe M, Ludwig WD, et al. Chemotherapy in 998 unselected childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Results and conclusions of the multicenter trial ALL-BFM 86. Blood, 84: 3122–3133, 1994
Schrappe M, Reiter A, Zimmermann M, et al. Long-term results of four consecutive trials in childhood ALL performed by the ALL-BFM study group from 1981 to 1995. Leukemia, 14(12): 2205–2222, 2000
Sallan SE. Myths and lessons from adult/pediatric interface in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology, 128–132, 2006
Afvani AS, Hunger SP, Burnett AK. Acute leukemia in adolescents and yound adults. Semin Oncol, 36(3): 213–226, 2009
Ng AK, Kenney LB, Gilbert ES, Travis LB. Secondary malignancies across the age spectrum. Semin Radiat Oncol, 20(1): 67–78, 2010
Bhatia S, Sather HN, Pabustan OB, et al. Low incidence of second neoplasms among children diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after 1983. Blood, 99(12): 4257–4264, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avcin, S., Prelog, T., Kavcic, M. et al. History of treatment and long-term outcome of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Slovenia. memo 4, 178–183 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-011-0278-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-011-0278-z