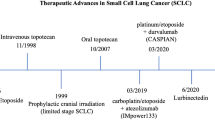
For years interest in developing new treatment strategies in SCLC has lagged behind the efforts addressing NSCLC. This trend could easily be followed during the ASCO 2009 meeting. Fifty-two abstracts relating to SCLC were exhibited, whereas 392 abstracts covered NSCLC research topics. None of the presentations dealing with SCLC showed successful phase III results no results were presented in the lung cancer oral presentation session. We are left with efforts in challenging the first-line standard regimen of etoposide/platinum (EP) with the irinotecan/platinum (IP) regimen as an alternative treatment choice with comparable results but different toxicity. Randomised phase II results with amrubicin seem to support the use of second-line treatment in an otherwise chemo-resistant and desperate disease. In various trials most of the investigated new targeting agents did not lead to a reproducible improvement in the outcome of SCLC patients. After ASCO 2009 it seems that progress in the treatment of SCLC requires not only a tailored medical approach, which is difficult to achieve, but also changes in therapeutical strategies in radiotherapy and surgery for LD-SCLC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Govindan R, Page N and Morgensztern D et al(2006). Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24(28): 4539–4544
Lara PN, Natale R and Crowley J et al (2009). Phase III trial of irinotecan/cisplatin compared with etoposide/cisplatin in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: clinical and pharmacogenomic results from SWOG S0124. J Clin Oncol 27(15): 2530–2535
Hanna N, Bunn PA Jr and Langer C et al (2006). Randomized phase III trial comparing irinotecan/cisplatin with etoposide/cisplatin in patients with previously untreated extensive-stage disease small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 24(13): 2038–2043
Noda K, Nishiwaki Y and Kawahara M et al (2002). Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346(2): 85–91
Lara PN, Jr., Chansky K, Shibata T, et al. Cisplatin + irinotecan versus cisplatin + etoposide in extensive stage small cell lung cancer (E-SCLC): Final “common arm”: comparative outcomes analysis of JCOG 9511 and SWOG 0124. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8027, 2009.
Sasse EC, Lima JP, Santos LV, et al. Irinotecan plus platinum analog (IP) compared to etoposide plus platinum analog (EP) in extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC): systematic review with meta- analysis. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8105, 2009.
Schmittel AH, Sebastian M, Fischer von Weikersthal L, et al. Irinotecan plus carboplatin versus etoposide plus carboplatin in extensive disease small cell lung cancer: results of the German randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8029, 2009.
Ettinger DS (2007). Amrubicin for the treatment of small cell lung cancer: does effectiveness cross the Pacific?. J Thorac Oncol 2(2): 160–165
Spigel D, Shah C, Lorigan P, et al. Amrubicin (AMR) and cardiotoxicity in second-line treatment of small cell lung cancer (SCLC): a pooled analysis of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) in two phase II trials. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e19019, 2009.
Yoh K, Nishiwaki Y, Kemmotsu H, et al. Interstitial lung disease associated with amrubicin in the treatment of patients with small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e19018, 2009.
Jotte R, Conkling P, Reynolds C, et al. Results of a randomized phase II trial of amrubicin (AMR) versus topotecan (Topo) in patients with extensive-disease small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC) sensitive to firstline platinum-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8028, 2009.
Ettinger DS, Jotte R, Lorigan P, et al. Results of a phase II trial of single-agent amrubicin (AMR) in patients with extensive disease small cell lung cancer (ED-SCLC) refractory to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy: an update. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8103, 2009.
Kotsakis AP, Tarhini A, Petro D, et al. Phase II study of RAD001 (everolimus) in previously treated small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8107, 2009.
Kudo K, Ohyanagi F, Horiike A, et al. A phase II study of S-1 for previously treated small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e19074, 2009.
Heist RS, Fain J, Chinnasami B, et al. A phase I/II (P1/P2) study of AT 101 in combination with topotecan (T) in patients with relapsed or refractory small cell lung cancer (SCLC) after prior platinum-containing first-line chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8106, 2009.
Chiappori A, Schreeder MT, Moezi MM, et al. A phase Ib trial of Bcl-2 inhibitor obatoclax in combination with carboplatin and etoposide for previously untreated patients with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 3576, 2009.
Gandhi L, Chu QS, Stephenson J, et al. An open label phase II trial of the Plk1 inhibitor BI 2536, in patients with sensitive relapse small cell lung cancer (SCLC). J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8108, 2009.
Batus M, Myint R, Coon J, et al. N-cadherin, E-cadherin, ERCC1, and c-kit expression in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and potential for new therapeutic targets. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e22157, 2009.
Chang M, Won Y, Han J, et al. Prognostic role of insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 (IGFR-1) and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) expression in small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e22155, 2009.
Canadas I, Arumi M, Lema L, et al. MET in small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC): effects of a MET inhibitor in SCLC cell lines and prognostic role of MET status in patients. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e14617, 2009.
Hennemann M, Sostruznik MH, Gaiger AM, et al. ERCC1 expression and survival in small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr e19080, 2009.
Seto T, Yamanaka T, Masuda N, et al. Topoisomerase II, carbonyl reductase I, and chemosensitivity for amrubicin in the treatment of patients with small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol, 27(Suppl 15s): abstr 8104, 2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ploner, F. SCLC – ASCO 2009. memo 2, 218–220 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-009-0166-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12254-009-0166-y