Abstract
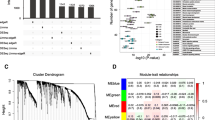
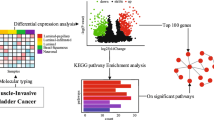
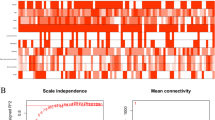
Muscle-invasive bladder urothelial carcinoma (MIBC) is characterized as a genetic heterogeneous cancer with a high percentage of recurrence and worse prognosis. Identify the prognostic potentials of novel genes for muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer could at least provide important information for early detection and clinical treatment. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) algorithm, a powerful systems biology approach, was utilized to extract co-expressed gene networks from mRNA expression dataset to construct transcriptional modules in MIBC samples, which was associated with demographic and clinical traits of MIBC patients. The potential prognostic markers of MIBC were screened out in the discovery dataset and verified in an independent external validation dataset. A total of 8 co-expression modules were detected through the WGCNA algorithm in the discovery datasets based on 401 MIBC samples. One transcriptional module enriched in cell development was observed to be correlated with the MIBC prognosis in the discovery datasets (HR = 1.48, 95%CI = 1.04–2.11) and independently verified in an external dataset (HR = 3.59, 95%CI = 1.09–11.79). High expression of hub genes including discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 2 (DDR2), PDZ and LIM domain 3 (PDLIM3), zinc finger protein 521 (ZNF521), methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 (MSRB3) were significantly associated with the unfavorable survival of MIBC patients. We identified and validated four novel potential biomarkers associated with prognosis of MIBC patients by constructing genes co-expression networks. The discovery of these genetic markers may provide a new target for the development of MIBC chemotherapeutic drugs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F (2017) Bladder Cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol 71(1):96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.010
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner SP, Malmström P-U, Choi W, Guo CC, Lotan Y, Kassouf W (2016) Bladder cancer. Lancet 388(10061):2796–2810. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(16)30512-8
Migita T, Ueda A, Ohishi T, Hatano M, Seimiya H, Horiguchi SI, Koga F, Shibasaki F (2017) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotes SOX2 and NANOG expression in bladder cancer. Lab Invest 97:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2017.17
Baumgart E, Cohen MS, Silva Neto B, Jacobs MA, Wotkowicz C, Rieger-Christ KM, Biolo A, Zeheb R, Loda M, Libertino JA, Summerhayes IC (2007) Identification and prognostic significance of an epithelial-mesenchymal transition expression profile in human bladder tumors. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American association for. Cancer Res 13(6):1685–1694. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2330
Grossman HB, Natale RB, Tangen CM, Speights VO, Vogelzang NJ, Trump DL, deVere White RW, Sarosdy MF, Wood DP Jr, Raghavan D, Crawford ED (2003) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N Engl J Med 349(9):859–866. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa022148
Amir S, Mabjeesh NJ (2017) microRNA expression profiles as decision-making biomarkers in the management of bladder cancer. Histol Histopathol 32(2):107–119. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-11-814
Dudek AM, van Kampen JGM, Witjes JA, Kiemeney L, Verhaegh GW (2018) LINC00857 expression predicts and mediates the response to platinum-based chemotherapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Med 7:3342–3350. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1570
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21442
Kiselyov A, Bunimovich-Mendrazitsky S, Startsev V (2016) Key signaling pathways in the muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma: clinical markers for disease modeling and optimized treatment. Int J Cancer 138(11):2562–2569. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29918
Masson-Lecomte A, Rava M, Real FX, Hartmann A, Allory Y, Malats N (2014) Inflammatory biomarkers and bladder cancer prognosis: a systematic review. Eur Urol 66(6):1078–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.07.033
Clarke C, Madden SF, Doolan P, Aherne ST, Joyce H, O'Driscoll L, Gallagher WM, Hennessy BT, Moriarty M, Crown J, Kennedy S, Clynes M (2013) Correlating transcriptional networks to breast cancer survival: a large-scale coexpression analysis. Carcinogenesis 34(10):2300–2308. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgt208
Oros Klein K, Oualkacha K, Lafond MH, Bhatnagar S, Tonin PN, Greenwood CM (2016) Gene Coexpression analyses differentiate networks associated with diverse cancers harboring TP53 missense or null mutations. Front Genet 7:137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2016.00137
Guo L, Zhang K, Bing Z (2017) Application of a coexpression network for the analysis of aggressive and nonaggressive breast cancer cell lines to predict the clinical outcome of patients. Mol Med Rep 16(6):7967–7978. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7608
Robertson AG, Kim J, Al-Ahmadie H, Bellmunt J, Guo G, Cherniack AD, Hinoue T, Laird PW, Hoadley KA, Akbani R, Castro MAA, Gibb EA, Kanchi RS, Gordenin DA, Shukla SA, Sanchez-Vega F, Hansel DE, Czerniak BA, Reuter VE, Su X, de Sa Carvalho B, Chagas VS, Mungall KL, Sadeghi S, Pedamallu CS, Lu Y, Klimczak LJ, Zhang J, Choo C, Ojesina AI, Bullman S, Leraas KM, Lichtenberg TM, Wu CJ, Schultz N, Getz G, Meyerson M, Mills GB, McConkey DJ, Network TR, Weinstein JN, Kwiatkowski DJ, Lerner SP (2017) Comprehensive molecular characterization of muscle-invasive bladder Cancer. Cell 171(3):540–556 e525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.007
Rebouissou S, Bernard-Pierrot I, de Reynies A, Lepage ML, Krucker C, Chapeaublanc E, Herault A, Kamoun A, Caillault A, Letouze E, Elarouci N, Neuzillet Y, Denoux Y, Molinie V, Vordos D, Laplanche A, Maille P, Soyeux P, Ofualuka K, Reyal F, Biton A, Sibony M, Paoletti X, Southgate J, Benhamou S, Lebret T, Allory Y, Radvanyi F (2014) EGFR as a potential therapeutic target for a subset of muscle-invasive bladder cancers presenting a basal-like phenotype. Sci Transl Med 6(244):244ra291. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3008970
Mak MP, Tong P, Diao L, Cardnell RJ, Gibbons DL, William WN, Skoulidis F, Parra ER, Rodriguez-Canales J, Wistuba II, Heymach JV, Weinstein JN, Coombes KR, Wang J, Byers LA (2016) A patient-derived, pan-Cancer EMT signature identifies global molecular alterations and immune target enrichment following epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res 22(3):609–620. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0876
Love MI, Huber W, Anders S (2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol 15(12):550. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
Langfelder P, Horvath S (2008) WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 9:559. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Zhang B, Horvath S (2005) A general framework for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 4:Article17. https://doi.org/10.2202/1544-6115.1128
Yuan L, Chen L, Qian K, Qian G, Wu CL, Wang X, Xiao Y (2017) Co-expression network analysis identified six hub genes in association with progression and prognosis in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Genom Data 14:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gdata.2017.10.006
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, He QY (2012) clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics : a Journal Of Integrative Biology 16(5):284–287. https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Achkar T, Parikh RA (2018) Adjuvant therapy in muscle-invasive bladder Cancer and upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Clin N Am 45(2):257–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ucl.2017.12.010
Hermans TJN, Voskuilen CS, van der Heijden MS, Schmitz-Drager BJ, Kassouf W, Seiler R, Kamat AM, Grivas P, Kiltie AE, Black PC, van Rhijn BWG (2017) Neoadjuvant treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: the past, the present, and the future. Urol Oncol 36:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.10.014
Tsai MC, Li WM, Huang CN, Ke HL, Li CC, Yeh HC, Chan TC, Liang PI, Yeh BW, Wu WJ, Lim SW, Li CF (2016) DDR2 overexpression in urothelial carcinoma indicates an unfavorable prognosis: a large cohort study. Oncotarget 7(48):78918–78931. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12912
Corsa CA, Brenot A, Grither WR, Van Hove S, Loza AJ, Zhang K, Ponik SM, Liu Y, DeNardo DG, Eliceiri KW, Keely PJ, Longmore GD (2016) The action of Discoidin domain receptor 2 in basal tumor cells and stromal Cancer-associated fibroblasts is critical for breast Cancer metastasis. Cell Rep 15(11):2510–2523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.033
Grither WR, Divine LM, Meller EH, Wilke DJ, Desai RA, Loza AJ, Zhao P, Lohrey A, Longmore GD, Fuh KC (2018) TWIST1 induces expression of discoidin domain receptor 2 to promote ovarian cancer metastasis. Oncogene 37(13):1714–1729. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-017-0043-9
Kim D, Ko P, You E, Rhee S (2014) The intracellular juxtamembrane domain of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2) is essential for receptor activation and DDR2-mediated cancer progression. Int J Cancer 135(11):2547–2557. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28901
Sasaki S, Ueda M, Iguchi T, Kaneko M, Nakayama H, Watanabe T, Sakamoto A, Mimori K (2017) DDR2 expression is associated with a high frequency of peritoneal dissemination and poor prognosis in colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res 37(5):2587–2591. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11603
Bagnall RD, Yeates L, Semsarian C (2010) Analysis of the Z-disc genes PDLIM3 and MYPN in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol 145(3):601–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.08.004
Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM, Oksvold P, Kampf C, Djureinovic D, Odeberg J, Habuka M, Tahmasebpoor S, Danielsson A, Edlund K, Asplund A, Sjostedt E, Lundberg E, Szigyarto CA, Skogs M, Takanen JO, Berling H, Tegel H, Mulder J, Nilsson P, Schwenk JM, Lindskog C, Danielsson F, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson A, von Feilitzen K, Forsberg M, Zwahlen M, Olsson I, Navani S, Huss M, Nielsen J, Ponten F, Uhlen M (2014) Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 13(2):397–406. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M113.035600
Germano G, Morello G, Aveic S, Pinazza M, Minuzzo S, Frasson C, Persano L, Bonvini P, Viola G, Bresolin S, Tregnago C, Paganin M, Pigazzi M, Indraccolo S, Basso G (2017) ZNF521 sustains the differentiation block in MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 8(16):26129–26141. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15387
Spina R, Filocamo G, Iaccino E, Scicchitano S, Lupia M, Chiarella E, Mega T, Bernaudo F, Pelaggi D, Mesuraca M, Pazzaglia S, Semenkow S, Bar EE, Kool M, Pfister S, Bond HM, Eberhart CG, Steinkuhler C, Morrone G (2013) Critical role of zinc finger protein 521 in the control of growth, clonogenicity and tumorigenic potential of medulloblastoma cells. Oncotarget 4(8):1280–1292. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.1176
Harder L, Eschenburg G, Zech A, Kriebitzsch N, Otto B, Streichert T, Behlich AS, Dierck K, Klingler B, Hansen A, Stanulla M, Zimmermann M, Kremmer E, Stocking C, Horstmann MA (2013) Aberrant ZNF423 impedes B cell differentiation and is linked to adverse outcome of ETV6-RUNX1 negative B precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Exp Med 210(11):2289–2304. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20130497
Mega T, Lupia M, Amodio N, Horton SJ, Mesuraca M, Pelaggi D, Agosti V, Grieco M, Chiarella E, Spina R, Moore MA, Schuringa JJ, Bond HM, Morrone G (2011) Zinc finger protein 521 antagonizes early B-cell factor 1 and modulates the B-lymphoid differentiation of primary hematopoietic progenitors. Cell Cycle 10(13):2129–2139. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.10.13.16045
Brot N, Weissbach L, Werth J, Weissbach H (1981) Enzymatic reduction of protein-bound methionine sulfoxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78(4):2155–2158
Kim HY, Gladyshev VN (2004) Methionine sulfoxide reduction in mammals: characterization of methionine-R-sulfoxide reductases. Mol Biol Cell 15(3):1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-08-0629
Kwak GH, Kim HY (2017) MsrB3 deficiency induces cancer cell apoptosis through p53-independent and ER stress-dependent pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys 621:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2017.04.001
Kwak GH, Kim TH, Kim HY (2017) Down-regulation of MsrB3 induces cancer cell apoptosis through reactive oxygen species production and intrinsic mitochondrial pathway activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 483(1):468–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.12.120
Lee E, Kwak GH, Kamble K, Kim HY (2014) Methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 deficiency inhibits cell growth through the activation of p53-p21 and p27 pathways. Arch Biochem Biophys 547:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2014.02.008
Morel AP, Ginestier C, Pommier RM, Cabaud O, Ruiz E, Wicinski J, Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Combaret V, Finetti P, Chassot C, Pinatel C, Fauvet F, Saintigny P, Thomas E, Moyret-Lalle C, Lachuer J, Despras E, Jauffret JL, Bertucci F, Guitton J, Wierinckx A, Wang Q, Radosevic-Robin N, Penault-Llorca F, Cox DG, Hollande F, Ansieau S, Caramel J, Birnbaum D, Vigneron AM, Tissier A, Charafe-Jauffret E, Puisieux A (2017) A stemness-related ZEB1-MSRB3 axis governs cellular pliancy and breast cancer genome stability. Nat Med 23(5):568–578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4323
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J, Weinberg RA (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133(4):704–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.027
Polyak K, Weinberg RA (2009) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 9(4):265–273. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2620
Manzotti G, Torricelli F, Benedetta D, Lococo F, Sancisi V, Rossi G, Piana S, Ciarrocchi A (2018) An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transcriptional switch triggers evolution of pulmonary Sarcomatoid carcinoma (PSC) and identifies Dasatinib as new therapeutic option. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2364
Xie B, Lin W, Ye J, Wang X, Zhang B, Xiong S, Li H, Tan G (2015) DDR2 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis via activating ERK signaling and stabilizing SNAIL1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res : CR 34:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-015-0218-6
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author would like to thank all the co-workers for collecting, managing, maintaining and interpreting the data used in this analysis. We also appreciate Soochow University for providing the financial support to conduct the present study.
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific Research Foundation for Talented Scholars in Soochow University, China (Q413900215).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Yueyi Feng, Xiaochen Shu.
Financial support: Xiaochen Shu.
Collection and assembly of data: Yueyi Feng.
Data analysis and interpretation: Yueyi Feng, Yiqing Jiang, Tao Wen, Fang Meng, Xiaochen Shu.
Manuscript writing: Yueyi Feng, Xiaochen Shu.
Final approval of manuscript: Yueyi Feng, Yiqing Jiang, Tao Wen, Fang Meng, and Xiaochen Shu.
Xiaochen Shu will be responsible for the overall content as guarantor of this work.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No potential conflict of interests was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Jiang, Y., Wen, T. et al. Identifying Potential Prognostic Markers for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 1063–1072 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00657-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00657-6