Abstract
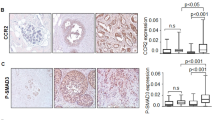
C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CXCR-7) is an atypical receptor for chemokines whose role in different stages of carcinogenesis has been evaluated in breast cancer cell lines and animal models. Moreover, it has been demonstrated to be a target of regulation by the tumor suppressor microRNA (miR)-100. In the present study, we assessed CXCR-7 expression in 60 breast cancer patients in association with clinicopathological and demographic data of patients. We also extracted the results of our previous work on miR-100 expression in the same cohort of patients to assess the correlation between miR-100 and CXCR-7 expression levels. Transcript levels of CXCR-7 were significantly higher in tumoral tissues compared with adjacent non-cancerous tissues (ANCTs) (Tumoral vs. ANCTs: 3.64 ± 1.8 vs. 0.73 ± 1.3, P = 0.000). A significant negative correlation was detected between CXCR-7 protein and miR-100 transcript levels (r = −0.526, P < 0.05). High CXCR-7 mRNA levels were significantly associated with tumor size (P = 0.01). Besides, high protein levels were more prevalent in higher TNM stages (P = 0.000). Moreover, high CXCR-7 protein levels were significantly associated with ER (P = 0.005) and PR (P = 0.02) status. The present work provides further evidence for the role of CXCR-7 in breast cancer and proposes the elimination of inhibitory effects of miR-100 on CXCR-7 expression as a mechanism for its up-regulation in breast cancer tissues.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns JM et al (2006) A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med 203:2201–2213. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20052144
Tarnowski M et al (2010) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is secreted by rhabdomyosarcoma cells, modulates tumor metastasis by binding to CXCR4 and CXCR7 receptors and inhibits recruitment of Cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer Res 8:1328–1343. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0288
Salazar N et al (2014) The chemokine receptor CXCR7 interacts with EGFR to promote breast cancer cell proliferation. Mol Cancer 13, Artn 198. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-198
Miao Z et al (2007) CXCR7 (RDC1) promotes breast and lung tumor growth in vivo and is expressed on tumor-associated vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:15735–15740. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610444104
Muir S. et al. (AACR, 2008)
Hernandez L, Magalhaes MAO, Coniglio SJ, Condeelis JS, Segall JE (2011) Opposing roles of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res 13, Artn R128. https://doi.org/10.1186/Bcr3074
Qian TT et al (2018) CXCR7 regulates breast tumor metastasis and angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Mol Med Rep 17:3633–3639. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8286
Compton C et al (2010) AJCC cancer staging manual. Chapter 14:143–164
Barrett T, Edgar R (2006) Gene expression omnibus: microarray data storage, submission, retrieval, and analysis. Method Enzymol 411:352–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(06)11019-8
Tasharrofi B et al (2016) Comparative expression analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha and its natural occurring antisense in breast cancer tissues and adjacent noncancerous tissues. Cell Biochem Funct 34:572–578. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.3230
Cao Y et al (2018) MicroRNA-100 suppresses human gastric cancer cell proliferation by targeting CXCR7. Oncol Lett 15:453–458
Zhou S-M et al (2016) miR-100 suppresses the proliferation and tumor growth of esophageal squamous cancer cells via targeting CXCR7. Oncol Rep 35:3453–3459
Zhou WH, Wu X, Hu WD, Du MR (2015) Co-expression of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in human endometrial stromal cells is modulated by steroid hormones. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:2449–2460
Kerdivel G, Boudot A, Pakdel F (2013) Estrogen represses CXCR7 gene expression by inhibiting the recruitment of NFκB transcription factor at the CXCR7 promoter in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431:729–733
Boudot A et al (2011) Differential estrogen-regulation of CXCL12 chemokine receptors, CXCR4 and CXCR7, contributes to the growth effect of estrogens in breast cancer cells. PLoS One 6:e20898
Liu Y, Beyer A, Aebersold R (2016) On the dependency of cellular protein levels on mRNA abundance. Cell 165:535–550
Acknowledgements
This article has been extracted from the thesis written by Roshanak Shamsi in School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
The present work was financially supported by “Research Department of the School of Medicine Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MSA and RS performed the experiments. MB supervised the protein experiments. MDO provided the technical support. SGH designed the study, supervised it and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the ethical committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1396.152). Informed consent was obtained from the patients.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shams, R., Seifi-Alan, M., Bandehpour, M. et al. C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 (CXCR-7) Expression in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast in Association with Clinicopathological Features. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 1015–1020 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00649-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00649-6