Abstract
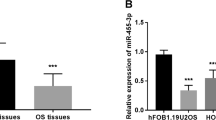
Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary malignant bone tumor with two peaks of incidence, in early adolescence and the elderly. Patients affected with this malignancy often present metastatic disease at diagnosis, and despite multimodality therapy, survival has not improved substantially over the past 3 decades. Recently, miR-138-5p, proposed as a crucial intracellular mediator of invasion, has been recognized to target the Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 (ROCK2). Dysregulation of ROCK1 and ROCK2 was also described in OS, being associated to higher metastasis incidence and worse prognosis. Nonetheless, the specific roles of miR-138-5p in pediatric and young adult OS and its ability to modulate these kinases remain to be established. Thus, in the present study, the expression levels miR-138-5p were evaluated in a consecutive cohort of exclusively pediatric and young adult primary OS samples. In contrast to previous reports that included adult tissues, our results showed upregulation of miR-138-5p associated with reduced event-free survival and relapsed cases. In parallel, ROCK1 mRNA levels were significantly reduced in tumor samples and negatively correlated with miR-138-5p. Similar correlations were observed after studying the profiles of ROCK1 and ROCK2 by immunohistochemistry. Our data present miR-138-5p as a consistent prognostic factor in pediatric and young adult OS, reinforcing its participation in the post-transcriptional regulation of ROCK kinases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benjamin RS (2015) Osteosarcoma: better treatment through better trial design. Lancet Oncol 16(1):12–13
Ottaviani G, Jaffe N (2009) The etiology of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res 152:15–32
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ, Savage SA (2009) Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004. Cancer 115:1531–1543
Gorlick R, Khanna C (2010) Osteosarcoma. J Bone Miner Res 25:683–691
Harting MT, Blakely ML (2006) Management of osteosarcoma pulmonary metastases. Semin Pediatr Surg 15:25–29
Isakoff MS, Bielack SS, Meltzer P, Gorlick R (2015) Osteosarcoma: current treatment and a collaborative pathway to success. J Clin Oncol 33:3029–3035
Massagué J, Obenauf AC (2016) Metastatic colonization by circulating tumour cells. Nature 529:298–306
Liu X, Choy E, Hornicek FJ, Yang S, Yang C, Harmon D, Mankin H, Duan Z (2011) ROCK1 as a potential therapeutic target in osteosarcoma. J Orthop Res 29:1259–1266
Wang W, Zhou X, Wei M (2015) MicroRNA-144 suppresses osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by targeting ROCK1 and ROCK2. Oncotarget 6:10297–10308
Fusella F, Ferretti R, Recupero D, Rocca S, Di Savino A, Tornillo G, Silengo L, Turco E, Cabodi S, Provero P, Pandolfi PP, Sapino A, Tarone G, Brancaccio M (2014) Morgana acts as a proto-oncogene through inhibition of a ROCK-PTEN pathway. J Pathol 234(2):152–163
Lochhead PA, Wickman G, Mezna M, Olson MF (2010) Activating ROCK1 somatic mutations in human cancer. Oncogene 29:2591–2598
Zucchini C, Manara MC, Pinca RS, De Sanctis P, Guerzoni C, Sciandra M, Lollini P-L, Cenacchi G, Picci P, Valvassori L, Scotlandi K (2014) CD99 suppresses osteosarcoma cell migration through inhibition of ROCK2 activity. Oncogene 33:1912–1921
Tan Y, Hu H, Tan W, Jin L, Liu J, Zhou H (2016) MicroRNA-138 inhibits migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting LIMK1. Mol Med Rep 14:4422–4428
Zhang J, Liu D, Feng Z, Mao J, Zhang C, Lu Y, Li J, Zhang Q, Li Q, Li L (2016) MicroRNA-138 modulates metastasis and EMT in breast cancer cells by targeting vimentin. Biomed Pharmacother 77:135–141
Jiang L, Liu X, Kolokythas A, Yu J, Wang A, Heidbreder CE, Shi F, Zhou X (2010) Downregulation of the Rho GTPase signaling pathway is involved in the microRNA-138-mediated inhibition of cell migration and invasion in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 127:505–512
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Varghese F, Bukhari AB, Malhotra R, De A (2014) IHC profiler: an open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples. PLoS One 9:e96801
Li B, Yang X-X, Wang D, Ji H-K (2016) MicroRNA-138 inhibits proliferation of cervical cancer cells by targeting c-Met. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:1109–1114
Liu X, Jiang L, Wang A, Yu J, Shi F, Zhou X (2009) MicroRNA-138 suppresses invasion and promotes apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett 286:217–222
Long L, Huang G, Zhu H, Guo Y, Liu Y, Huo J (2013) Down-regulation of miR-138 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via directly targeting TWIST2. J Transl Med 11:275
Mitomo S, Maesawa C, Ogasawara S, Iwaya T, Shibazaki M, Yashima-Abo A, Kotani K, Oikawa H, Sakurai E, Izutsu N, Kato K, Komatsu H, Ikeda K, Wakabayashi G, Masuda T (2008) Downregulation of miR-138 is associated with overexpression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase protein in human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Sci 99:280–286
Sun D-K, Wang J-M, Zhang P, Wang Y-Q (2015) MicroRNA-138 regulates metastatic potential of bladder Cancer through ZEB2. Cell Physiol Biochem 37:2366–2374
Xiao L, Zhou H, Li X-P, Chen J, Fang C, Mao C-X, Cui J-J, Zhang W, Zhou H-H, Yin J-Y, Liu Z-Q (2016) MicroRNA-138 acts as a tumor suppressor in non small cell lung cancer via targeting YAP1. Oncotarget 7:40038–40046
Yu C, Wang M, Li Z, Xiao J, Peng F, Guo X, Deng Y, Jiang J, Sun C (2015) MicroRNA-138-5p regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth through targeting FOXC1. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 38:173–181
Wang Q, Tang H, Yin S, Dong C (2013) Downregulation of microRNA-138 enhances the proliferation, migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the upregulation of RhoC/p-ERK/MMP-2/MMP-9. Oncol Rep 29:2046–2052
Yeh Y-M, Chuang C-M, Chao K-C, Wang L-H (2013) MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α. Int J Cancer 133:867–878
Jiang B, Mu W, Wang J, Lu J, Jiang S, Li L, Xu H, Tian H (2016) MicroRNA-138 functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma by targeting differentiated embryonic chondrocyte gene 2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:69
Lane J, Martin TA, Watkins G, Mansel RE, Jiang WG (2008) The expression and prognostic value of ROCK I and ROCK II and their role in human breast cancer. Int J Oncol 33:585–593
Mertsch S, Thanos S (2014) Opposing signaling of ROCK1 and ROCK2 determines the switching of substrate specificity and the mode of migration of glioblastoma cells. Mol Neurobiol 49:900–915
Wu Y, Tang Y, Li Z, Li Z, Zhao Y, Wu Z, Su Q (2014) Expression and significance of Rac1, Pak1 and Rock1 in gastric carcinoma. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 10:e33–e39
Takeba Y, Matsumoto N, Watanabe M, Takenoshita-Nakaya S, Ohta Y, Kumai T, Takagi M, Koizumi S, Asakura T, Otsubo T (2012) The rho kinase inhibitor fasudil is involved in p53-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:1545–1555
Yang X, Di J, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Lu J, Liu J, Shi W (2012) The rho-kinase inhibitor inhibits proliferation and metastasis of small cell lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 66:221–227
Storey JD, Madeoy J, Strout JL, Wurfel M, Ronald J, Akey JM (2007) Gene-expression variation within and among human populations. Am J Hum Genet 80:502–509
Zhang W, Dolan ME (2008) Ancestry-related differences in gene expression: findings may enhance understanding of health disparities between populations. Pharmacogenomics 9:489–492
Scotting PJ, Walker DA, Perilongo G (2005) Opinion: childhood solid tumours: a developmental disorder. Nat Rev Cancer 5:481–488
Boissel N, Auclerc MF, Lhéritier V, Perel Y, Thomas X, Leblanc T, Rousselot P, Cayuela JM, Gabert J, Fegueux N, Piguet C, Huguet-Rigal F, Berthou C, Boiron JM, Pautas C, Michel G, Fière D, Leverger G, Dombret H, Baruchel A (2003) Should adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia be treated as old children or young adults? Comparison of the French FRALLE-93 and LALA-94 trials. J Clin Oncol 21(5):774–780
Korshunov A, Remke M, Werft W, Benner A, Ryzhova M, Witt H, Sturm D, Wittmann A, Schöttler A, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Rutkowski S, Scheurlen W, Kulozik AE, von Deimling A, Lichter P, Pfister S (2010) Adult and pediatric Medulloblastomas are genetically distinct and require different algorithms for molecular risk stratification. J Clin Oncol 28:3054–3060
Northcott PA, Hielscher T, Dubuc A, Mack S, Shih D, Remke M, Al-Halabi H, Albrecht S, Jabado N, Eberhart CG, Grajkowska W, Weiss WA, Clifford SC, Bouffet E, Rutka JT, Korshunov A, Pfister S, Taylor MD (2011) Pediatric and adult sonic hedgehog medulloblastomas are clinically and molecularly distinct. Acta Neuropathol 122:231–240
Paugh BS, Qu C, Jones C, Liu Z, Adamowicz-Brice M, Zhang J, Bax DA, Coyle B, Barrow J, Hargrave D, Lowe J, Gajjar A, Zhao W, Broniscer A, Ellison DW, Grundy RG, Baker SJ (2010) Integrated molecular genetic profiling of pediatric high-grade gliomas reveals key differences with the adult disease. J Clin Oncol 28:3061–3068
Sultan I, Qaddoumi I, Yaser S, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Ferrari A (2009) Comparing adult and pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program, 1973 to 2005: an analysis of 2,600 patients. J Clin Oncol 27:3391–3397
Akagi EM, Lavorato-Rocha AM, Maia B d M, Rodrigues IS, Carvalho KC, Stiepcich MM, Baiocchi G, Sato-Kuwabara Y, Rogatto SR, Soares FA, Rocha RM (2014) ROCK1 as a novel prognostic marker in vulvar cancer. BMC Cancer 14:822
Dourado MR, de Oliveira CE, Sawazaki-Calone I, Sundquist E, Coletta RD, Salo T (2017) Clinicopathologic significance of ROCK2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinomas. J Oral Pathol Med 47:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1111/jop.12651
Amaya CN, Mitchell DC, Bryan BA (2017) Rho kinase proteins display aberrant upregulation in vascular tumors and contribute to vascular tumor growth. BMC Cancer 17:485
Islam M, Datta J, Lang JC, Teknos TN (2014) Down regulation of RhoC by microRNA-138 results in de-activation of FAK, Src and Erk1/2 signaling pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol 50:448–456
Funding
FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo): Grant 2014/03877–3 and LEAD and GMV fellowships, 2014/07117–3 and 2014/07118–0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that they had no conflict of interest that could be perceived to impair the impartiality of the research reported.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberto, G.M., Lira, R.C., Delsin, L.E. et al. microRNA-138-5p as a Worse Prognosis Biomarker in Pediatric, Adolescent, and Young Adult Osteosarcoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 877–883 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00633-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00633-0