Abstract
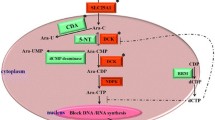
Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide (FC) chemotherapy is the basis of treatment protocols used in management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In some patients, response to therapy may be affected by aberrant function of genes involved in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drugs. The aim of this research was to assess the impact of pharmacogenetic variability, namely expression of SLC28A3 gene and the presence of CYP2B6*6 variant allele, on the FC treatment efficacy. Forty-four CLL patients with functional TP53 gene at the time of FC initiation were enrolled in this study. CYP2B6 genotyping was performed by polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing. SLC28A3 expression was measured by quantitative reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. Significantly higher pretreatment levels of SLC28A3 mRNA were detected in patients who failed to respond to FC in comparison to patients who achieved complete and partial response (p = 0.01). SLC28A3 high-expressing cases were almost ten times more likely not to respond to FC than low-expressing cases (OR = 9.8; p = 0.046). However, association of SLC28A3 expression with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was not observed. CYP2B6*6 allele, detected in 24 patients (54.6%), exerted no association with the attainment of response to FC, as well as with PFS and OS. The results of this study demonstrate that SLC28A3 expression is a significant predictor of FC efficacy in CLL patients with intact TP53. Elevated SLC28A3 mRNA levels are associated with inferior short-term response to FC, suggesting that, if validated on larger cohorts, SLC28A3 expression may become a biomarker useful for pretreatment stratification of patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, Caligaris-Cappio F, Dighiero G, Dohner H, Hillmen P, Keating MJ, Montserrat E, Rai KR, Kipps TJ International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic L (2008) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the international workshop on chronic lymphocytic leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-working group 1996 guidelines. Blood 111(12):5446–5456. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-06-093906
Grever MR, Lucas DM, Dewald GW, Neuberg DS, Reed JC, Kitada S, Flinn IW, Tallman MS, Appelbaum FR, Larson RA, Paietta E, Jelinek DF, Gribben JG, Byrd JC (2007) Comprehensive assessment of genetic and molecular features predicting outcome in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results from the US intergroup phase III trial E2997. J Clin Oncol 25(7):799–804. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.08.3089
Catovsky D, Richards S, Matutes E, Oscier D, Dyer M, Bezares RF, Pettitt AR, Hamblin T, Milligan DW, Child JA, Hamilton MS, Dearden CE, Smith AG, Bosanquet AG, Davis Z, Brito-Babapulle V, Else M, Wade R, Hillmen P, Group UKNCRIHOCS, Group NCLLW (2007) Assessment of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (the LRF CLL4 trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 370(9583):230–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61125-8
Eichhorst BF, Busch R, Hopfinger G, Pasold R, Hensel M, Steinbrecher C, Siehl S, Jager U, Bergmann M, Stilgenbauer S, Schweighofer C, Wendtner CM, Dohner H, Brittinger G, Emmerich B, Hallek M, German CLLSG (2006) Fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide versus fludarabine alone in first-line therapy of younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 107(3):885–891. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-06-2395
Hallek M, Fischer K, Fingerle-Rowson G, Fink AM, Busch R, Mayer J, Hensel M, Hopfinger G, Hess G, von Grunhagen U, Bergmann M, Catalano J, Zinzani PL, Caligaris-Cappio F, Seymour JF, Berrebi A, Jager U, Cazin B, Trneny M, Westermann A, Wendtner CM, Eichhorst BF, Staib P, Buhler A, Winkler D, Zenz T, Bottcher S, Ritgen M, Mendila M, Kneba M, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, International Group of I, German Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia Study G (2010) Addition of rituximab to fludarabine and cyclophosphamide in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 376(9747):1164–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61381-5
Ghielmini M, Vitolo U, Kimby E, Montoto S, Walewski J, Pfreundschuh M, Federico M, Hoskin P, McNamara C, Caligaris-Cappio F, Stilgenbauer S, Marcus R, Trneny M, Dreger P, Montserrat E, Dreyling M, Panel Members of the 1st ECCoML (2013) ESMO guidelines consensus conference on malignant lymphoma 2011 part 1: diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), follicular lymphoma (FL) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Ann Oncol 24(3):561–576. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mds517
Committee EG (2017) Appendix 4: chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: eUpdate published online 27 June 2017 (www.esmo.org/Guidelines/Haematological-Malignancies). Ann Oncol 28 (suppl_4):iv149-iv152. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx242
Flinn IW, Neuberg DS, Grever MR, Dewald GW, Bennett JM, Paietta EM, Hussein MA, Appelbaum FR, Larson RA, Moore DF Jr, Tallman MS (2007) Phase III trial of fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide compared with fludarabine for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: US intergroup trial E2997. J Clin Oncol 25(7):793–798. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.08.0762
Robak T, Dmoszynska A, Solal-Celigny P, Warzocha K, Loscertales J, Catalano J, Afanasiev BV, Larratt L, Geisler CH, Montillo M, Zyuzgin I, Ganly PS, Dartigeas C, Rosta A, Maurer J, Mendila M, Saville MW, Valente N, Wenger MK, Moiseev SI (2010) Rituximab plus fludarabine and cyclophosphamide prolongs progression-free survival compared with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide alone in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 28(10):1756–1765. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.26.4556
Edelmann J, Gribben JG (2017) Managing patients with TP53-deficient chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Oncol Pract 13(6):371–377. https://doi.org/10.1200/JOP.2017.023291
Zenz T, Eichhorst B, Busch R, Denzel T, Habe S, Winkler D, Buhler A, Edelmann J, Bergmann M, Hopfinger G, Hensel M, Hallek M, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S (2010) TP53 mutation and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 28(29):4473–4479. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2009.27.8762
Rossi D, Cerri M, Deambrogi C, Sozzi E, Cresta S, Rasi S, De Paoli L, Spina V, Gattei V, Capello D, Forconi F, Lauria F, Gaidano G (2009) The prognostic value of TP53 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is independent of Del17p13: implications for overall survival and chemorefractoriness. Clin Cancer Res 15(3):995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1630
Malcikova J, Smardova J, Rocnova L, Tichy B, Kuglik P, Vranova V, Cejkova S, Svitakova M, Skuhrova Francova H, Brychtova Y, Doubek M, Brejcha M, Klabusay M, Mayer J, Pospisilova S, Trbusek M (2009) Monoallelic and biallelic inactivation of TP53 gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: selection, impact on survival, and response to DNA damage. Blood 114(26):5307–5314. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-07-234708
Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Krober A, Bullinger L, Dohner K, Bentz M, Lichter P (2000) Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 343(26):1910–1916. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200012283432602
Zenz T, Habe S, Denzel T, Mohr J, Winkler D, Buhler A, Sarno A, Groner S, Mertens D, Busch R, Hallek M, Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S (2009) Detailed analysis of p53 pathway defects in fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): dissecting the contribution of 17p deletion, TP53 mutation, p53-p21 dysfunction, and miR34a in a prospective clinical trial. Blood 114(13):2589–2597. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-05-224071
Landau DA, Tausch E, Taylor-Weiner AN, Stewart C, Reiter JG, Bahlo J, Kluth S, Bozic I, Lawrence M, Bottcher S, Carter SL, Cibulskis K, Mertens D, Sougnez CL, Rosenberg M, Hess JM, Edelmann J, Kless S, Kneba M, Ritgen M, Fink A, Fischer K, Gabriel S, Lander ES, Nowak MA, Dohner H, Hallek M, Neuberg D, Getz G, Stilgenbauer S, Wu CJ (2015) Mutations driving CLL and their evolution in progression and relapse. Nature 526(7574):525–530. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15395
Galmarini CM, Mackey JR, Dumontet C (2001) Nucleoside analogues: mechanisms of drug resistance and reversal strategies. Leukemia 15(6):875–890
Emadi A, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA (2009) Cyclophosphamide and cancer: golden anniversary. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(11):638–647. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.146
Young JD (2016) The SLC28 (CNT) and SLC29 (ENT) nucleoside transporter families: a 30-year collaborative odyssey. Biochem Soc Trans 44(3):869–876. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160038
Molina-Arcas M, Bellosillo B, Casado FJ, Montserrat E, Gil J, Colomer D, Pastor-Anglada M (2003) Fludarabine uptake mechanisms in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 101(6):2328–2334. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-07-2236
Mackey JR, Galmarini CM, Graham KA, Joy AA, Delmer A, Dabbagh L, Glubrecht D, Jewell LD, Lai R, Lang T, Hanson J, Young JD, Merle-Beral H, Binet JL, Cass CE, Dumontet C (2005) Quantitative analysis of nucleoside transporter and metabolism gene expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): identification of fludarabine-sensitive and -insensitive populations. Blood 105(2):767–774. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-03-1046
Roy P, Yu LJ, Crespi CL, Waxman DJ (1999) Development of a substrate-activity based approach to identify the major human liver P-450 catalysts of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide activation based on cDNA-expressed activities and liver microsomal P-450 profiles. Drug Metab Dispos 27(6):655–666
Zanger UM, Klein K (2013) Pharmacogenetics of cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6): advances on polymorphisms, mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Front Genet 4:24. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2013.00024
Desta Z, Saussele T, Ward B, Blievernicht J, Li L, Klein K, Flockhart DA, Zanger UM (2007) Impact of CYP2B6 polymorphism on hepatic efavirenz metabolism in vitro. Pharmacogenomics 8(6):547–558. https://doi.org/10.2217/14622416.8.6.547
Hofmann MH, Blievernicht JK, Klein K, Saussele T, Schaeffeler E, Schwab M, Zanger UM (2008) Aberrant splicing caused by single nucleotide polymorphism c.516G>T [Q172H], a marker of CYP2B6*6, is responsible for decreased expression and activity of CYP2B6 in liver. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325(1):284–292. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.107.133306
Tsuchiya K, Gatanaga H, Tachikawa N, Teruya K, Kikuchi Y, Yoshino M, Kuwahara T, Shirasaka T, Kimura S, Oka S (2004) Homozygous CYP2B6 *6 (Q172H and K262R) correlates with high plasma efavirenz concentrations in HIV-1 patients treated with standard efavirenz-containing regimens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319(4):1322–1326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.116
Lang T, Klein K, Fischer J, Nussler AK, Neuhaus P, Hofmann U, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Zanger UM (2001) Extensive genetic polymorphism in the human CYP2B6 gene with impact on expression and function in human liver. Pharmacogenetics 11(5):399–415
Zhang H, Sridar C, Kenaan C, Amunugama H, Ballou DP, Hollenberg PF (2011) Polymorphic variants of cytochrome P450 2B6 (CYP2B6.4-CYP2B6.9) exhibit altered rates of metabolism for bupropion and efavirenz: a charge-reversal mutation in the K139E variant (CYP2B6.8) impairs formation of a functional cytochrome p450-reductase complex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338(3):803–809. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.111.183111
Ariyoshi N, Ohara M, Kaneko M, Afuso S, Kumamoto T, Nakamura H, Ishii I, Ishikawa T, Kitada M (2011) Q172H replacement overcomes effects on the metabolism of cyclophosphamide and efavirenz caused by CYP2B6 variant with Arg262. Drug Metab Dispos 39(11):2045–2048. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.111.039586
Xu C, Ogburn ET, Guo Y, Desta Z (2012) Effects of the CYP2B6*6 allele on catalytic properties and inhibition of CYP2B6 in vitro: implication for the mechanism of reduced efavirenz metabolism and other CYP2B6 substrates in vivo. Drug Metab Dispos 40(4):717–725. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.111.042416
Xie HJ, Yasar U, Lundgren S, Griskevicius L, Terelius Y, Hassan M, Rane A (2003) Role of polymorphic human CYP2B6 in cyclophosphamide bioactivation. Pharmacogenomics J 3(1):53–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500157
Johnson GG, Lin K, Cox TF, Oates M, Sibson DR, Eccles R, Lloyd B, Gardiner LJ, Carr DF, Pirmohamed M, Strefford JC, Oscier DG, Gonzalez de Castro D, Else M, Catovsky D, Pettitt AR (2013) CYP2B6*6 is an independent determinant of inferior response to fludarabine plus cyclophosphamide in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 122(26):4253–4258. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-07-516666
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, Kay N, Keating MJ, O'Brien S, Rai KR (1996) National Cancer Institute-sponsored working group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 87(12):4990–4997
Pospisilova S, Gonzalez D, Malcikova J, Trbusek M, Rossi D, Kater AP, Cymbalista F, Eichhorst B, Hallek M, Dohner H, Hillmen P, van Oers M, Gribben J, Ghia P, Montserrat E, Stilgenbauer S, Zenz T, European Research Initiative on CLL (2012) ERIC recommendations on TP53 mutation analysis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 26(7):1458–1461. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2012.25
Wood BL, Arroz M, Barnett D, DiGiuseppe J, Greig B, Kussick SJ, Oldaker T, Shenkin M, Stone E, Wallace P (2007) 2006 Bethesda international consensus recommendations on the immunophenotypic analysis of hematolymphoid neoplasia by flow cytometry: optimal reagents and reporting for the flow cytometric diagnosis of hematopoietic neoplasia. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 72(Suppl 1):S14–S22. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.b.20363
Davis BH, Holden JT, Bene MC, Borowitz MJ, Braylan RC, Cornfield D, Gorczyca W, Lee R, Maiese R, Orfao A, Wells D, Wood BL, Stetler-Stevenson M (2007) 2006 Bethesda international consensus recommendations on the flow cytometric immunophenotypic analysis of hematolymphoid neoplasia: medical indications. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 72 Suppl 1:S5–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.b.20365
Ghia P, Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Moreno C, Stilgenbauer S, Stevenson F, Davi F, Rosenquist R, European Research Initiative on CLL (2007) ERIC recommendations on IGHV gene mutational status analysis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 21(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2404457
Rosenquist R, Cortese D, Bhoi S, Mansouri L, Gunnarsson R (2013) Prognostic markers and their clinical applicability in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: where do we stand? Leuk Lymphoma 54(11):2351–2364. https://doi.org/10.3109/10428194.2013.783913
Stilgenbauer S (2015) Prognostic markers and standard management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2015:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2015.1.368
Montserrat E, Dreger P (2016) Treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with del(17p)/TP53 mutation: allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation or BCR-signaling inhibitors? Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 16(Suppl):S74–S81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2016.02.013
Justenhoven C, Pentimalli D, Rabstein S, Harth V, Lotz A, Pesch B, Bruning T, Dork T, Schurmann P, Bogdanova N, Park-Simon TW, Couch FJ, Olson JE, Fasching PA, Beckmann MW, Haberle L, Ekici A, Hall P, Czene K, Liu J, Li J, Baisch C, Hamann U, Ko YD, Brauch H (2014) CYP2B6*6 is associated with increased breast cancer risk. Int J Cancer 134(2):426–430. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28356
Berkoz M, Yalin S (2009) Association of CYP2B6 G15631T polymorphism with acute leukemia susceptibility. Leuk Res 33(7):919–923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2008.11.014
Yuan ZH, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Liu HX, Zhao J, Zhu P (2011) CYP2B6 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms and leukemia susceptibility. Ann Hematol 90(3):293–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-010-1085-z
Daraki A, Zachaki S, Koromila T, Diamantopoulou P, Pantelias GE, Sambani C, Aleporou V, Kollia P, Manola KN (2014) The G(5)(1)(6)T CYP2B6 germline polymorphism affects the risk of acute myeloid leukemia and is associated with specific chromosomal abnormalities. PLoS One 9(2):e88879. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088879
Daraki A, Kakosaiou K, Zachaki S, Sambani C, Aleporou-Marinou V, Kollia P, Manola KN (2016) Polymorphisms and haplotypes of the CYP2B6 detoxification gene in the predisposition of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and induction of its cytogenetic abnormalities. Cancer Genet 209(11):525–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cancergen.2016.10.004
Gandhi M, Aweeka F, Greenblatt RM, Blaschke TF (2004) Sex differences in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:499–523. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.44.101802.121453
Lamba V, Lamba J, Yasuda K, Strom S, Davila J, Hancock ML, Fackenthal JD, Rogan PK, Ring B, Wrighton SA, Schuetz EG (2003) Hepatic CYP2B6 expression: gender and ethnic differences and relationship to CYP2B6 genotype and CAR (constitutive androstane receptor) expression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307(3):906–922. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.054866
Ren S, Kalhorn TF, McDonald GB, Anasetti C, Appelbaum FR, Slattery JT (1998) Pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and its metabolites in bone marrow transplantation patients. Clin Pharmacol Ther 64(3):289–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-9236(98)90178-3
Chang TK, Yu L, Maurel P, Waxman DJ (1997) Enhanced cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide activation in primary human hepatocyte cultures: response to cytochrome P-450 inducers and autoinduction by oxazaphosphorines. Cancer Res 57(10):1946–1954
McCune JS, Salinger DH, Vicini P, Oglesby C, Blough DK, Park JR (2009) Population pharmacokinetics of cyclophosphamide and metabolites in children with neuroblastoma: a report from the Children's oncology group. J Clin Pharmacol 49(1):88–102. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091270008325928
Tsang RY, Santos C, Ghosh S, Dabbagh L, King K, Young J, Cass CE, Mackey JR, Lai R (2008) Immunohistochemistry for human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 protein predicts fludarabine sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mod Pathol 21(11):1387–1393. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2008.110
Fernandez-Calotti P, Pastor-Anglada M (2010) All-trans-retinoic acid promotes trafficking of human concentrative nucleoside transporter-3 (hCNT3) to the plasma membrane by a TGF-beta1-mediated mechanism. J Biol Chem 285(18):13589–13598. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.055673
Fernandez-Calotti PX, Lopez-Guerra M, Colomer D, Pastor-Anglada M (2012) Enhancement of fludarabine sensitivity by all-trans-retinoic acid in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Haematologica 97(6):943–951. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2011.051557
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant No. III 41004, Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vukovic, V., Karan-Djurasevic, T., Antic, D. et al. Association of SLC28A3 Gene Expression and CYP2B6*6 Allele with the Response to Fludarabine Plus Cyclophosphamide in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 743–752 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00613-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-019-00613-4