Abstract
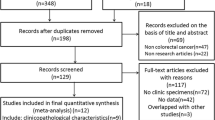
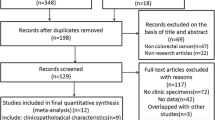
Progranulin (PGRN) has been characterized as an autocrine growth and survival factor and is known to stimulate tumorigenesis and proliferation of several types of cancer cell. However, little is known about the prognostic role of PGRN in colorectal cancer (CRC). A retrospective analysis was performed for patients with colorectal cancer who underwent curative resection between May 2013 and June 2015. PGRN expression in tumor cells was semi-quantitatively categorized (no expression, 0; weak/focal, 1+; moderate/focal or diffuse, 2+; strong/diffuse, 3+), and high expression was considered for tumors graded ≥2+ staining intensity. A total of 109 patients (28 stage I, 32 stage II, and 49 stage III) were analyzed. Thirty-eight patients (35%) had tumors with high PGRN expression, and there was a trend of elevated pre-operative CEA and CA19–9 levels in patients with high PGRN-expressing tumors compared to those with low PGRN-expressing tumors (CEA, 49% vs. 21%; CA19–9, 21% vs. 7%). The 3–year recurrence-free survival (3Y–RFS) and overall survival rates were 83.7% (95% CI, 76.8–90.6) and 96.0% (95% CI, 92.3–99.7), respectively. Patients with high PGRN-expressing tumors had a worse rate of 3Y–RFS (66.8%) compared to those with low PGRN-expressing tumors (92.4%; p = 0.010). Multivariate analysis showed that high PGRN expression, age (>66 years), stage (III), and perineural invasion (+) were independent prognostic factors associated with poor RFS after adjusting for confounding factors including sex, MSI, tumor location, KRAS, and lympho-vascular invasion. PGRN overexpression was significantly associated with poor RFS in patients with CRC who have undergone curative resection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Ciombor KK, Bekaii-Saab T (2018) A comprehensive review of sequencing and combination strategies of targeted agents in metastatic colorectal Cancer. Oncologist 23:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0203
Serrero G (2003) Autocrine growth factor revisited: PC-cell-derived growth factor (progranulin), a critical player in breast cancer tumorigenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 308:409–413
Yang D, Wang LL, Dong TT, Shen YH, Guo XS, Liu CY, Liu J, Zhang P, Li J, Sun YP (2015) Progranulin promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and angiogenesis through TNFR2/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Am J Cancer Res 5:3085–3097
Lee KW, Park SK, Yang HJ, Jung YS, Choi KY, Kim KE, Jung KU, Kim HO, Kim H, Chun HK, Park DI (2016) Microsatellite instability status of interval colorectal cancers in a Korean population. Gut Liver 10:781–785. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl15376
Lee J, Jang KT, Ki CS, Lim T, Park YS, Lim HY, Choi DW, Kang WK, Park K, Park JO (2007) Impact of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase mutations, EGFR gene amplifications, and KRAS mutations on survival of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 109:1561–1569. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22559
Kim JH, Do IG, Kim K, Sohn JH, Kim HJ, Jeon WK, Lee SR, Son BH, Shin JH, Nam H, Kwon HJ, Kim MS, Hong HP, Serrero G, Koo DH (2016) Progranulin as a predictive factor of response to chemotherapy in advanced biliary tract carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 78:1085–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-016-3170-z
Serrero G, Hawkins DM, Yue B, Ioffe O, Bejarano P, Phillips JT, Head JF, Elliott RL, Tkaczuk KR, Godwin AK, Weaver J, Kim WE (2012) Progranulin (GP88) tumor tissue expression is associated with increased risk of recurrence in breast cancer patients diagnosed with estrogen receptor positive invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res 14:R26. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3111
Arechavaleta-Velasco F, Perez-Juarez CE, Gerton GL, Diaz-Cueto L (2017) Progranulin and its biological effects in cancer. Med Oncol 34:194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-017-1054-7
Serrero G, Ioffe OB (2003) Expression of PC-cell-derived growth factor in benign and malignant human breast epithelium. Hum Pathol 34:1148–1154
Davidson B, Alejandro E, Florenes VA, Goderstad JM, Risberg B, Kristensen GB, Trope CG, Kohn EC (2004) Granulin-epithelin precursor is a novel prognostic marker in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Cancer 100:2139–2147. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20219
Ho JC, Ip YC, Cheung ST, Lee YT, Chan KF, Wong SY, Fan ST (2008) Granulin-epithelin precursor as a therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47:1524–1532. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22191
Wang H, Sun Y, Liu S, Yu H, Li W, Zeng J, Chen C, Jia J (2011) Upregulation of progranulin by helicobacter pylori in human gastric epithelial cells via p38MAPK and MEK1/2 signaling pathway: role in epithelial cell proliferation and migration. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 63:82–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00833.x
Edelman MJ, Feliciano J, Yue B, Bejarano P, Ioffe O, Reisman D, Hawkins D, Gai Q, Hicks D, Serrero G (2014) GP88 (progranulin): a novel tissue and circulating biomarker for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Hum Pathol 45:1893–1899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2014.05.011
Elkabets M, Gifford AM, Scheel C, Nilsson B, Reinhardt F, Bray MA, Carpenter AE, Jirstrom K, Magnusson K, Ebert BL, Ponten F, Weinberg RA, McAllister SS (2011) Human tumors instigate granulin-expressing hematopoietic cells that promote malignancy by activating stromal fibroblasts in mice. J Clin Invest 121:784–799. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci43757
Koo DH, Park CY, Lee ES, Ro J, Oh SW (2012) Progranulin as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer recurrence in patients who had hormone receptor-positive tumors: a cohort study. PLoS One 7:e39880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039880
Han JJ, Yu M, Houston N, Steinberg SM, Kohn EC (2011) Progranulin is a potential prognostic biomarker in advanced epithelial ovarian cancers. Gynecol Oncol 120:5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2010.09.006
Cheung ST, Cheung PF, Cheng CK, Wong NC, Fan ST (2011) Granulin-epithelin precursor and ATP-dependent binding cassette (ABC)B5 regulate liver cancer cell chemoresistance. Gastroenterology 140:344–355. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.07.049
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, Bergenstal RM, Gapstur SM, Habel LA, Pollak M, Regensteiner JG, Yee D (2010) Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin 60:207–221. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20078
Matsubara T, Mita A, Minami K, Hosooka T, Kitazawa S, Takahashi K, Tamori Y, Yokoi N, Watanabe M, Matsuo E, Nishimura O, Seino S (2012) PGRN is a key adipokine mediating high fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity through IL-6 in adipose tissue. Cell Metab 15:38–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.12.002
Tang W, Lu Y, Tian QY, Zhang Y, Guo FJ, Liu GY, Syed NM, Lai Y, Lin EA, Kong L, Su J, Yin F, Ding AH, Zanin-Zhorov A, Dustin ML, Tao J, Craft J, Yin Z, Feng JQ, Abramson SB, Yu XP, Liu CJ (2011) The growth factor progranulin binds to TNF receptors and is therapeutic against inflammatory arthritis in mice. Science 332:478–484. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1199214
Song Z, Zhang X, Zhang L, Xu F, Tao X, Zhang H, Lin X, Kang L, Xiang Y, Lai X, Zhang Q, Huang K, Dai Y, Yin Y, Cao J (2016) Progranulin plays a central role in host defense during Sepsis by promoting macrophage recruitment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 194:1219–1232. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201601-0056OC
Limburg PJ, Vierkant RA, Fredericksen ZS, Leibson CL, Rizza RA, Gupta AK, Ahlquist DA, Melton LJ 3rd, Sellers TA, Cerhan JR (2006) Clinically confirmed type 2 diabetes mellitus and colorectal cancer risk: a population-based, retrospective cohort study. Am J Gastroenterol 101:1872–1879. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00725.x
Shebl FM, Andreotti G, Meyer TE, Gao YT, Rashid A, Yu K, Shen MC, Wang BS, Han TQ, Zhang BH, Stanczyk FZ, Hsing AW (2011) Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in relation to biliary tract cancer and stone risks: a population-based study in Shanghai, China. Br J Cancer 105:1424–1429. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.363
Peairs KS, Barone BB, Snyder CF, Yeh HC, Stein KB, Derr RL, Brancati FL, Wolff AC (2011) Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 29:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.27.3011
Lee JY, Jeon I, Kim JW, Song YS, Yoon JM, Park SM (2013) Diabetes mellitus and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int J Gynecol Cancer 23:402–412. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0b013e31828189b2
Turati F, Polesel J, Di Maso M, Montella M, Libra M, Grimaldi M, Tavani A, Serraino D, La Vecchia C, Bosetti C (2015) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of bladder cancer: an Italian case-control study. Br J Cancer 113:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2015.178
Buraschi S, Xu SQ, Stefanello M, Moskalev I, Morcavallo A, Genua M, Tanimoto R, Birbe R, Peiper SC, Gomella LG, Belfiore A, Black PC, Iozzo RV, Morrione A (2016) Suppression of progranulin expression inhibits bladder cancer growth and sensitizes cancer cells to cisplatin. Oncotarget 7:39980–39995. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9556
Qu H, Deng H, Hu Z (2013) Plasma progranulin concentrations are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity and correlated with insulin resistance. Mediat Inflamm 2013:360190. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/360190
Funding
This work was supported by the Medical Research Funds from Kangbuk Samsung Hospital (Seoul, Korea).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare, except of GS who is an employee of A&G Pharmaceutical.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koo, DH., Do, IG., Oh, S. et al. Prognostic Value of Progranulin in Patients with Colorectal Cancer Treated with Curative Resection. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 397–404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0520-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-018-0520-7