Abstract
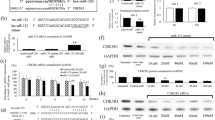
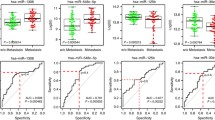
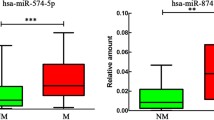
Over the last decade, the rho-associated kinases and several metastasis-associated microRNAs have emerged as important contributors of tumor invasion. However, despite prominence, our understanding of their involvement in the metastatic potential of Ewing Sarcoma (EWS) is incomplete. The expression profiles of ROCK1 or ROCK2 and miR-124-3p, miR-138-5p, miR-139-5p, miR-335-5p and miR-584-5p (all of which were previously predicted or validated to regulate these kinases) were evaluated through qRT-PCR and associated with clinical parameters. In vitro assays to evaluate colony formation and invasion/migration capacieties were performed on SK-ES-1 cells transfected with pre-miR mimics. ROCK1 expression was significantly reduced in EWS tissues, though there was no association with pathological parameters. miR-124-3p, miR-139-5p and miR-335-3p were also found significantly downregulated and positively correlated with ROCK1. Stratification indicated an association between lower levels of miR-139-5p and miR-584-5p with disease progression (p < 0.05), while reduced expression of the former and miR-124-3p were associated with reduced survival. In vitro miR-139-5p overexpression yielded inconsistent results: while mir-139-5p restoration significantly reduced invasion, the clonogenic capacity of cells was increased. Our study demonstrated that down-regulation of miR-124-3p, miR-139-5p and miR-584-5p are associated with disease progression in EWS and may serve as a risk assessment biomarkers though, as seen for mir-139-5p, their specific role remain to be elucidated for considering tailoring treatment options.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzales EHH, Betancourt GM, Martinez OQ, Cabezaz IH (2013) Sarcoma de Ewing. AMC 17:n5:623–640
Rodriguez-Galindo C, Spunt SL, Pappo AS (2003) Treatment of Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: current status and outlook for the future. Med Pediatr Oncol 40:276–287
Kim JY, Nam JK, Lee SA, Lee MS, Cho SK, Park ZY et al (2011) Proteasome inhibition causes epithelial-mesenchymal transition upon TM4SF5 expression. J Cell Biochem 112:782–792
Tseliou M, Al-Qahtani A, Alarifi S, Alkahtani SH, Stournaras C, Sourvinos G (2016) The role of RhoA, RhoB and RhoCGTPases in cell morphology, proliferation and migration in human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infected glioblastoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 38:94–109
Amano M, Nakayama M, Kaibuchi K (2010) Rho-kinase/ROCK. A key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell polarity. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 67:545–554
Kamai T, Tsujii T, Arai K, Takagi K, Asami H, Ito Y et al (2003) Significant association of rho/ROCK pathway with invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:2632–2641
Bottino J, Gelaleti GB, Maschio LB, Jardim-Perassi BV, de Campos Zuccari DA (2014) Immunoexpression of ROCK-1 and MMP-9 as prognostic markers in breast cancer. Acta Histochem 116:1367–1373
Wong CC, Wong CM, Tung EK, SL A, Lee JM, Poon RT et al (2011) The microRNA miR-139 suppresses metastasis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by down-regulating rho-kinase 2. Gastroenterology 140:322–331
Akagi EM, Lavorato-Rocha AM (2014) Maia BeM, Rodrigues IS, Carvalho KC, Stiepcich MM et al. ROCK1 as a novel prognostic marker in vulvar cancer. BMC Cancer 14:822
Raimo M, Orso F, Grassi E, Cimino D, Penna E, De Pittà C et al (2016) miR-146a exerts differential effects on melanoma growth and Metastatization. Mol Cancer Res 14:548–562
Loirand G (2015) Rho kinases in health and disease: from basic science to translational research. Pharmacol Rev 67:1074–1095
SH L, Jiang XJ, Xiao GL, Liu DY, Yuan XR (2014) miR-124a restoration inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion by suppressing IQGAP1 and β-catenin. Oncol Rep 32:2104–2110
Agirre X, Vilas-Zornoza A, Jiménez-Velasco A, Martin-Subero JI, Cordeu L, Gárate L et al (2009) Epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor microRNA Hsa-miR-124a regulates CDK6 expression and confers a poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res 69:4443–4453
Furuta M, Kozaki KI, Tanaka S, Arii S, Imoto I, Inazawa J (2010) miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 31:766–776
Pierson J, Hostager B, Fan R, Vibhakar R (2008) Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 by microRNA 124 in medulloblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 90:1–7
Wilting SM, van Boerdonk RA, Henken FE, Meijer CJ, Diosdado B, Meijer GA et al (2010) Methylation-mediated silencing and tumour suppressive function of hsa-miR-124 in cervical cancer. Mol Cancer 9:167
Chen X, He D, Dong XD, Dong F, Wang J, Wang L et al (2013) MicroRNA-124a is epigenetically regulated and acts as a tumor suppressor by controlling multiple targets in uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:2248–2256
CB H, Li QL, JF H, Zhang Q, Xie JP (2014) Deng.miR-124 inhibits growth and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting ROCK1. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:6543–6546
An L, Liu Y, Wu A, Guan Y (2013) microRNA-124 inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulating ROCK1 in glioma. PLoS One 8:e69478
Ueno K, Hirata H, Shahryari V, Chen Y, Zaman MS, Singh K et al (2011) Tumour suppressor microRNA-584 directly targets oncogene Rock-1 and decreases invasion ability in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 104:308–315
Xiang J, Wu Y, Li DS, Wang ZY, Shen Q, Sun TQ et al (2015) miR-584 suppresses invasion and cell migration of thyroid carcinoma by regulating the target oncogene ROCK1. Oncol Res Treat 38:436–440
Xue H, Guo X, Han X, Yan S, Zhang J, Xu S et al (2016) MicroRNA-584-3p, a novel tumor suppressor and prognostic marker, reduces the migration and invasion of human glioma cells by targeting hypoxia-induced ROCK1. Oncotarget 7:4785–4805
Hua W, Sa KD, Zhang X, Jia LT, Zhao J, Yang AG et al (2015) MicroRNA-139 suppresses proliferation in luminal type breast cancer cells by targeting topoisomerase II alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 463:1077–1083
Luo HN, Wang ZH, Sheng Y, Zhang Q, Yan J, Hou J et al (2014) MiR-139 targets CXCR4 and inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of laryngeal squamous carcinoma cells. Med Oncol 31:789
Song M, Yin Y, Zhang J, Zhang B, Bian Z, Quan C et al (2014) MiR-139-5p inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer by downregulating AMFR and NOTCH1. Protein Cell 5:851–861
Sun C, Sang M, Li S, Sun X, Yang C, Xi Y et al (2015) Hsa-miR-139-5p inhibits proliferation and causes apoptosis associated with down-regulation of c-met. Oncotarget 6:39756–39792
Krowiorz K, Ruschmann J, Lai C, Ngom M, Maetzig T, Martins V et al (2016) MiR-139-5p is a potent tumor suppressor in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J 6:e508
Bao W, Fu HJ, Xie QS, Wang L, Zhang R, Guo ZY et al. HER2 interacts with CD44 to up-regulate CXCR4 via epigenetic silencing of microRNA-139 in gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:2076–2087.e2076
Bühnemann C, Li S, Yu H, Branford WH, Schäfer KL, Llombart-Bosch A et al (2014) Quantification of the heterogeneity of prognostic cellular biomarkers in ewing sarcoma using automated image and random survival forest analysis. PLoS One 9:e107105
Komuro H, Saihara R, Shinya M, Takita J, Kaneko S, Kaneko M et al (2007) Identification of side population cells (stem-like cell population) in pediatric solid tumor cell lines. J Pediatr Surg 42:2040–2045
Yang M, Zhang R, Yan M, Ye Z, Liang W, Luo Z (2010) Detection and characterization of side population in Ewing's sarcoma SK-ES-1 cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391:1062–1066
Gao CF, Xie Q, Su YL, Koeman J, Khoo SK, Gustafson M et al (2005) Proliferation and invasion: plasticity in tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10528–10533
Hecht I, Natan S, Zaritsky A, Levine H, Tsarfaty I, Ben-Jacob E (2015) The motility-proliferation-metabolism interplay during metastatic invasion. Sci Rep 5:13538
Acknowledgments
FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo): Grant 2014/03877-3 and LEAD and GMV fellowships, 2014/07117-3 and 2014/07118-0.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None declared.
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
(DOCX 14 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberto, G.M., Delsin, L.E.A., Vieira, G.M. et al. ROCK1-PredictedmicroRNAs Dysregulation Contributes to Tumor Progression in Ewing Sarcoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 26, 133–139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0374-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0374-4