Abstract
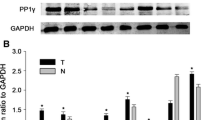
Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common malignant cancers, whose molecular mechanisms is remains largely. PTPN9 has recently been reported to play a critical role in breast cancer development. However, the role of PTPN9 in human HCC remains elusive. The present study aimed at investigating the potential role of PTPN9 in HCC. Western blot and immunohistochemistry were used to examine the expression of PTPN9 protein in HCC and adjacent non-tumorous tissues in 45 patients. Furthermore, Cell Counting Kit-8, flow cytometry and RNA interference experiments were performed to analyze the role of PTPN9 in the regulation of HCC cell proliferation. We showed that the expression level of PTPN9 was significantly reduced in HCC, compared with adjacent non-tumorous tissues. PTPN9 expression was inversely associated with Tumor size (P = 0.014), serum AFP level (P = 0.004) and Ki-67 expression. Low expression of PTPN9 predicted poor survival in HCC patients. Moreover, PTPN9 interference assay that PTPN9 inhibited cell proliferation in HepG2 cells. Cell apoptosis assay revealed that, silencing of PTPN9 expression significantly reduced cell apoptosis, compared with control ShRNA treatment group. Our results suggested that PTPN9 expression was down-regulated in HCC tumor tissues, and reduced PTPN9 expression was associated with worsened overall survival in HCC patients. Depletion of PTPN9 inhibits the apoptosis and promotes the proliferation of HCC cells.







Similar content being viewed by others

References
Wenzh El-Serag HB (2011) Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 365:1118–1127
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL (2007) Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 132:2557–2576
But D-Y-K, Lai C-L, Yuen M-F (2008) Natural history of hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 14:1652–1656
Poon RT, Ng IO, Fan ST, Lai EC, Lo CM, Liu CL et al (2001) Clinicopathologic features of long-term survivors and disease-free survivors after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a study of a prospective cohort. J Clin Oncol 19:3037–3044
Frau M, Biasi F, Feo F et al (2010) Prognostic markers and putative therapeutic targets for hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Asp Med 31:179–193
Tonks NK (2006) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:833–846
den Hertog J, Ostman A, Bohmer FD (2008) Protein tyrosine phosphatases:regulatory mechanisms. FEBS J 275:831–847
Glondu-Lassis M, Dromard M, Lacroix-Triki M, Nirde P, Puech C, Knani D, Chalbos D, Freiss G (2010) PTPL1/PTPN13 regulates breast cancer cell aggressiveness through direct inactivation of Src kinase. Cancer Res 70:5116–5126
Aoki N, Matsuda T (2002) A nuclear protein tyrosine phosphatase TC-PTP is a potential negative regulator of the PRL-mediated signaling pathway: dephosphorylation and deactivation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5a and 5b by TC-PTP in nucleus. Mol Endocrinol 16:58–69
Johnson KJ, Peck AR, Liu C, Tran TH, Utama FE, Sjolund AB, Schaber JD, Witkiewicz AK, Rui H (2010) PTP1B suppresses prolactin activation of Stat5 in breast cancer cells. Am J Pathol
Lu X, Malumbres R, Shields B, Jiang X, Sarosiek KA, Natkunam Y, Tiganis T, Lossos IS (2008) PTP1B is a negative regulator of interleukin 4-induced STAT6 signaling. Blood 112:4098–4108
Tebbutt NC, Giraud AS, Inglese M, Jenkins B, Waring P, Clay FJ, Malki S, Alderman BM, Grail D, Hollande F, Heath JK, Ernst M (2002) Reciprocal regulation of gastrointestinal homeostasis by SHP2 and STAT-mediated trefoil gene activation in gp130 mutant mice. Nat Med 8:1089–1097
Baron M, Davignon JL (2008) Inhibition of IFN-gamma-induced STAT1 tyrosine phosphorylation by human CMV is mediated by SHP2. J Immunol 181:5530–5536
Tsai CC, Kai JI, Huang WC, Wang CY, Wang Y, Chen CL, Fang YT, Lin YS, Anderson R, Chen SH, Tsao CW, Lin CF (2009) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta facilitates IFN-gamma-induced STAT1 activation by regulating Src homology-2 domain-containing phosphatase 2. J Immunol 183:856–864
ten Hoeve J, de Jesus I-SM, Fu Y, Zhu W, Tremblay M, David M, Shuai K (2002) Identification of a nuclear Stat1 protein tyrosine phosphatase. Mol Cell Biol 22:5662–5668
Meyer T, Hendry L, Begitt A, John S, Vinkemeier U (2004) A single residue modulates tyrosine dephosphorylation, oligomerization, and nuclear accumulation of stat transcription factors. J Biol Chem 279:18998–19007
Huynh H, Bottini N, Williams S, Cherepanov V, Musumeci L, Saito K, Bruckner S, Vachon E, Wang X, Kruger J, Chow CW, Pellecchia M, Monosov E, Greer PA, Trimble W, Downey GP, Mustelin T (2004) Nat Cell Biol 6:831–839
Xu MJ, Sui X, Zhao R, Dai C, Krantz SB, Zhao ZJ (2003) Blood 102:4354–4360
Wang Y, Vachon E, Zhang J, Cherepanov V, Kruger J, Li J, Saito K, Shannon P, Bottini N, Huynh H, Ni H, Yang H, McKerlie C, Quaggin S, Zhao ZJ, Marsden PA, Mustelin T, Siminovitch KA, Downey GP (2005) J Exp Med 202:1587–1597
Furth PA, Nakles RE, Millman S, Diaz-Cruz ES, Cabrera MC (2011) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 as a key signaling pathway in normal mammary gland developmental biology and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 13:220
Yuan T, Wang Y, Zhao ZJ, Gu H (2010) Protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN9 negatively regulates ErbB2 and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 285:14861–14870
Su F, Ren F et al (2012) Protein tyrosine phosphatase Meg2 dephosphorylates signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and suppresses tumor growth in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. doi:10.1186/bcr3134
Xu X, Yamamoto H, Sakon M et al (2003) Overexpression of CDC25A phosphatase is associated with hypergrowth activity and poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 9:1764–1772
Yu C, Chen K, Zheng H et al (2009) Overexpression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) progression and pathogenesis. Carcinogenesis 30:894–901
Xue Q, Lv L, Wan C, Chen B, Li M, Ni T et al (2013) Expression and clinical role of small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-containing protein alpha (SGTA) as a novel cell cycle protein in NSCLC. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139(9):1539–1549. doi:10.1007/s00432-013-1474-5
Wan C, Hou S, Shen A et al (2015) MIF4G domain containing protein regulates cell cycle and hepatic carcinogenesis by antagonizing CDK2-dependent p27 stability. Oncogene 34(2):237–245. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.536
Sun T, Aceto N, Meerbrey KL, Kessler JD, Zhou C, Migliaccio I, Nguyen DX, Pavlova NN, Botero M, Huang J, Bernardi RJ, Schmitt E, Hu G, Li MZ, Dephoure N, Gygi SP, Rao M, Creighton CJ, Hilsenbeck SG, Shaw CA, Muzny D, Gibbs RA, Wheeler DA, Osborne CK, Schiff R, Bentires-Alj M, Elledge SJ, Westbrook TF (2011) Activation of multiple proto-oncogenic tyrosinekinases in breast cancer via loss of the PTPN12 phosphatase. Cell 144:703–718
Julien SG, Dube N, Hardy S, Tremblay ML (2010) Inside the human cancer tyrosine phosphatome. Nat Rev Cancer 11:35–49
Hu TH, Huang CC, Lin PR et al (2003) Expression and prognostic role of tumor suppressor gene PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 97:1929–1940
Sánchez A, Nagy P, Thorgeirsson SS (2003) STAT-3 activity in chemically-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 39:2093–2098
Fuke H, Shiraki K, Sugimoto K, Tanaka J, Beppu T, Yoneda K, Yamamoto N, Ito K, Masuya M, Takei Y (2007) Jak inhibitor induces S phase cell-cycle arrest and augments TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 363:738–744
Leslie K, Lang C, Devgan G, Azare J, Berishaj M, Gerald W, Kim YB, Paz K, Darnell JE, Albanese C, Sakamaki T, Pestell R, Bromberg J (2006) Cyclin D1 is transcriptionally regulated by and required for transformation by activated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res 66:2544–2552
Bowman T, Broome MA, Sinibaldi D, Wharton W, Pledger WJ, Sedivy JM, Irby R, Yeatman T, Courtneidge SA, Jove R (2001) Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:7319–7324
Yue P, Turkson J (2009) Targeting STAT3 in cancer: how successful are we? Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18:45–56
Du WW, Fang L, Yang BB et al (2013) MicroRNA miR-24 enhances tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting PTPN9 and PTPRF to promote EGF signaling. J Cell Sci 126(6):1440–1453. doi:10.1242/jcs.118299
Huang X, Gschweng E, Witte ON et al (2011) Regulated expression of microRNAs-126/126* inhibits erythropoiesis from human embryonic stem cells. Blood 117(7):2157–2165. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-08-302711
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (no. 81401985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
We investigated 45 cases of liver cancer provided by Surgery Department of Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University. All liver cancer tissues were collected using protocols approved by Ethics Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, and written informed consent was obtained from every patient.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest
Additional information
Baoying Hu and Xia Yan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, B., Yan, X., Liu, F. et al. Downregulated Expression of PTPN9 Contributes to Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Progression. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 22, 555–565 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0038-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0038-1