Abstract
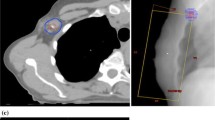
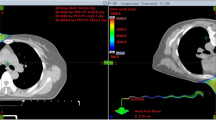
To analyse the displacement of surgical clips in prone (Pr) position and assess the consequences on target volumes and integral dose of partial breast irradiation (PBI). 30 post-lumpectomy breast cancer patients underwent CT imaging in supine (Su) and Pr. Clip displacements were measured by the distances from the clips to a common fix bony reference point. On each dataset, the tumour bed (TB = clips ± seroma), clinical target volume (CTV = TB + 1.5 cm) and planning target volumes (PTV = CTV + 1 cm) for PBI were determined and the volume pairs were compared. Furthermore estimation of integral dose ratio (IDR) within the breast from tangential treatment was performed as the ratio of the irradiated breast volume and the volume encompassing all clips. Clips close to the chest wall (CW) in Su showed significantly less displacement in Pr. The mean volumes of seroma, CTV and PTV were significantly higher in Pr than in Su. The PTV volume difference (Pr-Su) was significantly higher in patients with presence of seroma, deep clips and TB location in the superior-internal-quadrant (SIQ) and at the junction of superior quadrants (jSQ). In a multivariate analysis two factors remained significant: seroma and TB localization in SIQ-jSQ. The IDR was significantly larger in Su than in Pr (7.6 vs. 4.1 p < 0.01). Clip displacements varied considerably with respect to their relative position to the CW. In selected patients Pr position potentially leads to a significant increase in target volumes of PBI. Tangential beam arrangement for PBI should be avoided, not only in Su but in Pr as well in case of clip-based target volume definition.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darby S, McGale P, Correa C, Taylor C, Arriagada R, Clarke M et al (2011) Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 378:1707–1716. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61629-2
Kovacs A, Lakosi F, Liposits G, Toller G, Hadjiev J, Vandulek C et al (2011) 3-D conformal photon boost in the treatment of early stage breast cancer: four year follow up results. Pathol Oncol Res 17:17–23. doi:10.1007/s12253-010-9264-8
Polgár C, Van Limbergen E, Pötter R, Kovács G, Polo A, Lyczek J et al (2010) Patient selection for accelerated partial-breast irradiation (APBI) after breast-conserving surgery: recommendations of the Groupe Européen de Curiethérapie-European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (GEC-ESTRO) breast cancer working group ba. Radiother Oncol 94:264–273. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2010.01.014
Smith BD, Arthur DW, Buchholz TA, Haffty BG, Hahn CA, Hardenbergh PH et al (2009) Accelerated partial breast irradiation consensus statement from the American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:987–1001. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.031
Polgár C, Fodor J, Major T, Sulyok Z, Kásler M (2013) Breast-conserving therapy with partial or whole breast irradiation: ten-year results of the Budapest randomized trial. Radiother Oncol 108:197–202. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.05.008
Mózsa E, Mészáros N, Major T, Fröhlich G, Stelczer G, Sulyok Z et al (2014) Accelerated partial breast irradiation with external beam three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy : five-year results of a prospective phase II clinical study. Strahlenther Onkol 444–450. doi:10.1007/s00066-014-0633-1
Formenti SC, Hsu H, Fenton-Kerimian M, Roses D, Guth A, Jozsef G et al (2012) Prone accelerated partial breast irradiation after breast-conserving surgery: five-year results of 100 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.01.039
Kirby AM, Evans PM, Donovan EM, Convery HM, Haviland JS, Yarnold JR (2010) Prone versus supine positioning for whole and partial-breast radiotherapy: a comparison of non-target tissue dosimetry. Radiother Oncol 96:178–184. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2010.05.014
Coles CE, Wilson CB, Cumming J, Benson JR, Forouhi P, Wilkinson JS et al (2009) Titanium clip placement to allow accurate tumour bed localisation following breast conserving surgery: audit on behalf of the IMPORT Trial Management Group. Eur J Surg Oncol 35:578–582. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2008.09.005
Major T, Fröhlich G, Lövey K, Fodor J, Polgár C (2009) Dosimetric experience with accelerated partial breast irradiation using image-guided interstitial brachytherapy. Radiother Oncol 90:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2007.10.027
Ahunbay EE, Robbins J, Christian R, Godley A, White J, Li XA (2012) Interfractional target variations for partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1594–1604. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.01.041
Kirby AM, Evans PM, Helyer SJ, Donovan EM, Convery HM, Yarnold JR (2011) A randomised trial of supine versus prone breast radiotherapy (SuPr study): comparing set-up errors and respiratory motion. Radiother Oncol 100:221–226. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2010.11.005
Mitchell J, Formenti SC, DeWyngaert JK (2010) Interfraction and intrafraction setup variability for prone breast radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:1571–1577. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1683
Lakosi F, Gulyban A, Janvary L, Simoni SB-M, Jansen N, Seidel L et al (2015) Respiratory motion, anterior heart displacement and heart dosimetry: comparison between prone (Pr) and supine (Su) whole breast irradiation. Pathol Oncol Res. doi:10.1007/s12253-015-9932-9
Mukesh M, Harris E, Jena R, Evans P, Coles C (2012) Relationship between irradiated breast volume and late normal tissue complications: a systematic review. Radiother Oncol 104:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2012.04.025
Leonard KL, Hepel JT, Hiatt JR, Dipetrillo TA, Price LL, Wazer DE (2013) The effect of dose-volume parameters and interfraction interval on cosmetic outcome and toxicity after 3-dimensional conformal accelerated partial breast irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 85:623–629. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.06.052
Formenti SC, DeWyngaert JK, Jozsef G, Goldberg JD (2012) Prone vs supine positioning for breast cancer radiotherapy. JAMA 308:861–863. doi:10.1001/2012.jama.10759
Mulliez T, Speleers B, Madani I, De Gersem W, Veldeman L, De Neve W (2013) Whole breast radiotherapy in prone and supine position: is there a place for multi-beam IMRT? Radiat Oncol 8:151. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-8-151
Qiu J-J, Chang Z, Horton JK, Wu Q-RJ, Yoo S, Yin F-F (2014) Dosimetric comparison of 3D conformal, IMRT, and V-MAT techniques for accelerated partial-breast irradiation (APBI). Med Dosim 39:152–158. doi:10.1016/j.meddos.2013.12.001
Fahimian B, Yu V, Horst K, Xing L, Hristov D (2013) Trajectory modulated prone breast irradiation: a LINAC-based technique combining intensity modulated delivery and motion of the couch. Radiother Oncol 109:475–481. doi:10.1016/j.radonc.2013.10.031
Vicini F, Winter K, Wong J, Pass H, Rabinovitch R, Chafe S et al (2010) Initial efficacy results of RTOG 0319: three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) confined to the region of the lumpectomy cavity for stage I/ II breast carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:1120–1127. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.067
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakosi, F., Gulyban, A., Simoni, S.BM. et al. The Influence of Treatment Position (Prone vs. Supine) on Clip Displacement, Seroma, Tumor Bed and Partial Breast Target Volumes: Comparative Study. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 22, 493–500 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0028-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0028-3