Abstract
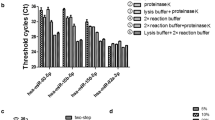
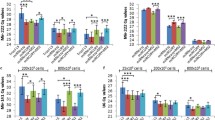
MiRNA remain stable for detection and PCR-based amplification in FFPE tissue samples. Several miRNA extraction kits are available, however miRNA fraction, as part of total RNA can be isolated using total RNA purification methods, as well. Our primary aim was to compare four different miRNA and total RNA isolation methods from FFPE tissues. Further purposes were to evaluate quantitatively and qualitatively the yield of the isolated miRNA. MiRNAs were isolated from normal colorectal cancer FFPE specimens from the same patients. Two miRNA isolation kits (High Pure miRNA Isolation Kit, miRCURY™ RNA Isolation Kit) and two total RNA isolation kits were compared (High Pure RNA Paraffin Kit, MagNA Pure 96 Cellular RNA LV Kit). Quantity and quality were determined, expression analysis was performed by real-time PCR using qPCR Human Panel I + II (Exiqon) method detecting 742 human miRNAs in parallel. The yield of total RNA was found to be higher than miRNA purification protocols (in CRC: Ex: 0203 ± 0021 μg; HPm: 1,45 ± 0,8 μg; HPp: 21,36 ± 4,98 μg; MP: 8,6 ± 5,1 μg). MiRNAs were detected in lower relative quantity of total RNA compared to the miRNA kits. Higher number of miRNAs could be detected by the miRNA isolation kits in comparison to the total RNA isolation methods. (Ex: 497 ± 16; HPm: 542 ± 11; HPp: 332 ± 36; MP: 295 ± 74). Colon specific miRNAs (miR-21-5p;-34-5p) give satisfying results by miRNA isolation kits. Although miRNA can be detected also after total RNA isolation methods, for reliable and reproducible miRNA expression profiling the use of miRNA isolation kits are more suitable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120(1):15–20. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.035
Aslam MI, Taylor K, Pringle JH, Jameson JS (2009) MicroRNAs are novel biomarkers of colorectal cancer. The British Journal of Surgery 96(7):702–710. doi:10.1002/bjs.6628
Agostini M, Pucciarelli S, Calore F, Bedin C, Enzo M, Nitti D (2010) MiRNAs in colon and rectal cancer: a consensus for their true clinical value. Clinica Chimica Acta; International Journal of Clinical Chemistry 411(17–18):1181–1186. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2010.05.002
Wang CJ, Zhou ZG, Wang L, Yang L, Zhou B, Gu J, Chen HY, Sun XF (2009) Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-31,-143 and-145 expression in colorectal cancer. Dis Markers 26(1):27–34. doi:10.3233/Dma-2009-0601
Kalmar A, Peterfia B, Wichmann B, Patai AV, Bartak BK, Nagy ZB, Furi I, Tulassay Z, Molnar B (2015) Comparison of automated and manual DNA isolation methods for DNA methylation analysis of biopsy, fresh frozen, and formalin-fixed. Paraffin-Embedded Colorectal Cancer Samples Journal of Laboratory Automation. doi:10.1177/2211068214565903
Godfrey TE, Kim SH, Chavira M, Ruff DW, Warren RS, Gray JW, Jensen RH (2000) Quantitative mRNA expression analysis from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues using 5 ' nuclease quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. J Mol Diagn 2(2):84–91. doi:10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60621-6
Cronin M, Pho M, Dutta D, Stephans JC, Shak S, Kiefer MC, Esteban JM, Baker JB (2004) Measurement of gene expression in archival paraffin-embedded tissues - development and performance of a 92-gene reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay. Am J Pathol 164(1):35–42. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63093-3
Kalmar A, Wichmann B, Galamb O, Spisak S, Toth K, Leiszter K, Tulassay Z, Molnar B (2013) Gene expression analysis of normal and colorectal cancer tissue samples from fresh frozen and matched formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens after manual and automated RNA isolation. Methods 59(1):S16–S19. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.09.011
Li J, Smyth P, Flavin R, Cahill S, Denning K, Aherne S, Guenther SM, O'Leary JJ, Sheils O (2007) Comparison of miRNA expression patterns using total RNA extracted from matched samples of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cells and snap frozen cells. BMC Biotechnol 7:36. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-7-36
Bovell L, Shanmugam C, Katkoori VR, Zhang B, Vogtmann E, Grizzle WE, Manne U (2012) MiRNAs are stable in colorectal cancer archival tissue blocks. Front Biosci 4:1937–1940
Podolska A, Kaczkowski B, Litman T, Fredholm M, Cirera S (2011) How the RNA isolation method can affect microRNA microarray results. Acta Biochim Pol 58(4):535–540
Monleau M, Bonnel S, Gostan T, Blanchard D, Courgnaud V, Lecellier CH (2014) Comparison of different extraction techniques to profile microRNAs from human sera and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. BMC Genomics 15:395. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-395
Guo Y, Bosompem A, Zhong X, Clark T, Shyr Y, Kim AS (2014) A comparison of microRNA sequencing reproducibility and noise reduction using mirVana and TRIzol isolation methods. Int J Comput Biol Drug Des 7(2–3):102–112. doi:10.1504/IJCBDD.2014.061642
Oue N, Anami K, Schetter AJ, Moehler M, Okayama H, Khan MA, Bowman ED, Mueller A, Schad A, Shimomura M, Hinoi T, Aoyagi K, Sasaki H, Okajima M, Ohdan H, Galle PR, Yasui W, Harris CC (2014) High miR-21 expression from FFPE tissues is associated with poor survival and response to adjuvant chemotherapy in colon cancer. Int J Cancer 134(8):1926–1934. doi:10.1002/Ijc.28522
Schetter AJ, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Mathe EA, Yuen ST, Hawkes JE, Croce CM, Leung SY, Harris CC (2009) Association of inflammation-related and microRNA gene expression with cancer-specific mortality of colon adenocarcinoma. Clin Can Res: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 15(18):5878–5887. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0627
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, Zanetti KA, Bowman ED, Yanaihara N, Yuen ST, Chan TL, Kwong DL, Au GK, Liu CG, Calin GA, Croce CM, Harris CC (2008) MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA 299(4):425–436. doi:10.1001/jama.299.4.425
Wang L, Yu J, Xu J, Zheng C, Li X, Du J (2015) The analysis of microRNA-34 family expression in human cancer studies comparing cancer tissues with corresponding pericarcinous tissues. Gene 554(1):1–8. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2014.10.032
Hiyoshi Y, Schetter AJ, Okayama H, Inamura K, Anami K, Nguyen GH, Horikawa I, Hawkes JE, Bowman ED, Leung SY, Harris CC (2015) Increased MicroRNA-34b and-34c predominantly expressed in stromal tissues is associated with poor prognosis in human colon cancer. PLoS One 10(4). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0124899
Ach RA, Wang H, Curry B (2008) Measuring microRNAs: comparisons of microarray and quantitative PCR measurements, and of different total RNA prep methods. BMC Biotechnol 8:69. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-8-69
Jung M, Schaefer A, Steiner I, Kempkensteffen C, Stephan C, Erbersdobler A, Jung K (2010) Robust microRNA stability in degraded RNA preparations from human tissue and cell samples. Clin Chem 56(6):998–1006. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2009.141580
Kotorashvili A, Ramnauth A, Liu C, Lin J, Ye K, Kim R, Hazan R, Rohan T, Fineberg S, Loudig O (2012) Effective DNA/RNA Co-extraction for analysis of MicroRNAs, mRNAs, and genomic DNA from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens. PLoS One 7(4). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034683
Ellis-Connell AL, Iempridee T, Xu I, Mertz JE (2010) Cellular MicroRNAs 200b and 429 regulate the Epstein-Barr virus switch between latency and lytic replication. J Virol 84(19):10329–10343. doi:10.1128/Jvi.00923-10
Ulivi P, Foschi G, Mengozzi M, Scarpi E, Silvestrini R, Amadori D, Zoli W (2013) Peripheral blood miR-328 expression as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of NSCLC. Int J Mol Sci 14(5):10332–10342. doi:10.3390/ijms140510332
Gao J, Li N, Dong Y, Li S, Xu L, Li X, Li Y, Li Z, Ng SS, Sung JJ, Shen L, Yu J (2014) miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II/III colorectal cancer. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.348
Acknowledgement
Conflict of Interest
The Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, Z.B., Wichmann, B., Kalmár, A. et al. miRNA Isolation from FFPET Specimen: A Technical Comparison of miRNA and Total RNA Isolation Methods. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 22, 505–513 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0027-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-015-0027-4