Abstract
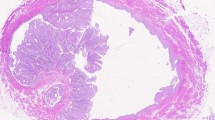
The current protocol for reporting urinary bladder cancer in radical cystectomies may exhibit limitations in the diagnostic accuracy, such as a risk of understaging, especially in cases with prostatic involvement. Difficulty can arise in the verification of stage pT0, and the assessment of surgical margins is suboptimal. We have developed a daily gross dissection protocol practice where radical cystectomies are totally embedded and evaluated histologically in whole-mount sections. We report here on the first 138 consecutive specimens from 2008 to the first quarter of 2012 inclusive. The incidence of the cancer stages was compared with data on 15,586 radical cystectomies from the literature. The differences were analyzed with the one-sample z-test (p < 0.05). The following emerged from and our series and the literature data: pT0 8.7 % and 6.1 %; pTa 0.7 % and 2.9 %; pTis 2.9 % and 6 %; pT1 15.2 % and 15.5 %; pT2 21 % and 23.3 %; pT3 34.8 % and 34.3 %; and pT4 16.7 % and 11 %, respectively. Our findings closely reflected the means of the published statistical data based on a large number of cases. The differences were due to the more detailed processing: the case numbers in groups from pTis to pT2 were comparatively low, while those in groups pT3 and pT4 were higher. The difference in group pT4 was significant (p = 0.0494). With this method, only those samples were regarded as pT0 in which the granulomatous area and the hemosiderin deposition indicative of the earlier intervention were observable and the entire preparation was tumor-free.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM (2008) The global burden of urinary bladder cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl (218)42:12–20
Cheng L, Montironi R, Davidson DD, Lopez-Beltran A (2009) Staging and reporting of urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Mod Pathol 22(Suppl 2):S70–S95
Herr HW (1992) Staging invasive bladder tumors. J Surg Oncol 51:217–220
Shariat SF, Palapattu GS, Karakiewicz PI, Rogers CG, Vazina A, Bastian PJ et al (2007) Discrepancy between clinical and pathologic stage: impact on prognosis after radical cystectomy. Eur Urol 51:137–149, discussion 149-151
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R, Groshen S, Feng AC, Boyd S et al (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19:666–675
Teloh HA (1957) Methods in surgical pathology. Thomas Chapter 26, Springfield, IL, pp 80–82
Lopez-Beltran A, Bassi PF, Pavone-Macaluso M, Montironi R (2004) Handling and pathology reporting of specimens with carcinoma of the urinary bladder, ureter, and renal pelvis. A joint proposal of the European Society of Uropathology and the Uropathology Working Group. Virchows Arch 445:103–110
(2011) Rosai and Ackerman’s surgical pathology, 10th edn. In: Rosai J. Mosby, St. Louis, MO, pp 2913–2914
van Dijk PR, Ploeg M, Aben KK, Weijerman PC, Karthaus HF, van Berkel JT et al (2011) Downstaging of TURBT-based muscle-invasive bladder cancer by radical cystectomy predicts better survival. ISRN Urol 2011:458930
Hautmann RE, de Petriconi RC, Pfeiffer C, Volkmer BG (2012) Radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder without neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy: long-term results in 1100 patients. Eur Urol 61:1039–1047
Herrmann E, Stoter E, van Ophoven A, Bierer S, Bolenz C, Hertle L et al (2008) The prognostic impact of pelvic lymph node metastasis and lymphovascular invasion on bladder cancer. Int J Urol 15:607–611
Madersbacher S, Hochreiter W, Burkhard F, Thalmann GN, Danuser H, Markwalder R et al (2003) Radical cystectomy for bladder cancer today–a homogeneous series without neoadjuvant therapy. J Clin Oncol 21:690–696
Mallen Mateo E, Gil Martinez P, Gil Sanz MJ, Sancho Serrano C, Pascual Regueriro D, Rioja Sanz LA (2006) Stage pT0 bladder tumors after radical cystectomy: a review of our series. Actas Urol Esp 30:763–771
May M, Bastian PJ, Burger M, Bolenz C, Trojan L, Herrmann E et al (2011) Multicenter evaluation of the prognostic value of pT0 stage after radical cystectomy due to urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. BJU Int 108:E278–E283
Roupret M, Drouin SJ, Larre S, Neuzillet Y, Botto H, Hitier M et al (2011) Oncologic outcomes and survival in pT0 tumors after radical cystectomy in patients without neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results from a large multicentre collaborative study. Ann Surg Oncol 18:3833–3838
Rink M, Ehdaie B, Cha EK, Green DA, Karakiewicz PI, Babjuk M et al (2012) Stage-specific impact of tumor location on oncologic outcomes in patients with upper and lower tract urothelial carcinoma following radical surgery. Eur Urol 62(4):677–684
Rodriguez Faba O, Palou J, Rosales A, Breda A, Algaba F, Urdaneta G et al (2011) Clinical predictive factors of poor outcome in patients with stage pT0 disease at radical cystectomy. J Urol 186:442–447
Takahashi A, Tsukamoto T, Tobisu K, Shinohara N, Sato K, Tomita Y et al (2004) Radical cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer: results of multi-institutional pooled analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 34:14–19
Tilki D, Reich O, Svatek RS, Karakiewicz PI, Kassouf W, Novara G et al (2010) Characteristics and outcomes of patients with clinical carcinoma in situ only treated with radical cystectomy: an international study of 243 patients. J Urol 183:1757–1763
Tollefson MK, Boorjian SA, Farmer SA, Frank I (2012) Downstaging to non-invasive urothelial carcinoma is associated with improved outcome following radical cystectomy for patients with cT2 disease. World J Urol 30(6):795–799
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Kattan MW, Gonen M, Scardino PT, Milowsky MI et al (2009) Clinical benefits of a multivariate prediction model for bladder cancer: a decision analytic approach. Cancer 115:5460–5469
Yu RJ, Stein JP, Cai J, Miranda G, Groshen S, Skinner DG (2006) Superficial (pT2a) and deep (pT2b) muscle invasion in pathological staging of bladder cancer following radical cystectomy. J Urol 176:493–498, discussion 498-499
Greene FL, Page DL, Flemming ID et al (2002) American joint committee on cancer staging manual. Springer, New York
Soto EA, Friedell GH, Tiltman AJ (1977) Bladder cancer as seen in giant Histologic sections. Cancer 39:447–455
Jewett HJ (1977) The historical development of the staging of bladder tumors: personal reminiscences. Urol Surv 27:37–40
Boudreaux KJ Jr, Clark PE, Lowrance WT, Rumohr JA, Barocas DA, Cookson MS et al (2009) Comparison of american joint committee on cancer pathological stage T2a versus T2b urothelial carcinoma: analysis of patient outcomes in organ confined bladder cancer. J Urol 181:540–545, discussion 546
Tilki D, Reich O, Karakiewicz PI, Novara G, Kassouf W, Ergun S et al (2010) Validation of the AJCC TNM substaging of pT2 bladder cancer: deep muscle invasion is associated with significantly worse outcome. Eur Urol 58:112–117
Scosyrev E, Yao J, Messing E (2010) Microscopic invasion of perivesical fat by urothelial carcinoma: implications for prognosis and pathology practice. Urology 76:908–913, discussion 914
Donat SM, Genega EM, Herr HW, Reuter VE (2001) Mechanisms of prostatic stromal invasion in patients with bladder cancer: clinical significance. J Urol 165:1117–1120
Shen SS, Lerner SP, Muezzinoglu B, Truong LD, Amiel G, Wheeler TM (2006) Prostatic involvement by transitional cell carcinoma in patients with bladder cancer and its prognostic significance. Hum Pathol 37:726–734
Montironi R, Cheng L, Mazzucchelli R, Scarpelli M, Kirkali Z, Montorsi F et al (2009) Critical evaluation of the prostate from cystoprostatectomies for bladder cancer: insights from a complete sampling with the whole mount technique. Eur Urol 55:1305–1309
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mihály Dezső for the photography and graphical work, and Dr. Tibor Nyári for help with the statistical analyses. Supported by TÁMOP-4.2.2.A-11/1/KONV-2012-0035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 67 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sükösd, F., Iványi, B. & Pajor, L. Accurate Determination of the Pathological Stage with Gross Dissection Protocol for Radical Cystectomy. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 677–685 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9748-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9748-z