Abstract
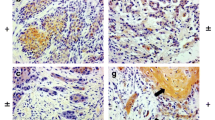
Cyclin D1 and E-cadherin are important factors in the progression and metastasis of cancers. Their role in laryngeal carcinoma has been studied with conflicting results. To define the frequency of cyclin D1 and E-cadherin expression and its correlation with both the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). Tumor tissue samples from 75 patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma were examined for cyclin D1 and E-cadherin expression by immunohistochemistry. The relationship between the expression of both molecules and the age and sex of the patient, tumor site, tumor differentiation, lymph node metastasis, tumor invasiveness, TNM stages, tumor recurrence and overall survival was analyzed. Cyclin D1 was found to be a significant independent prognostic factor of lymph node metastasis (p = 0.000). The multivariate analysis revealed that cyclin D1 and E-cadherin expression wasn’t an independent prognostic factor of local recurrence free survival (LRFS) in patients with LSCC (P = 0.56 and 0.28) respectively. However, the univariate analysis revealed a significant association between them and LRFS (p = 0.003 and 0.000) respectively. Also, the group of high cyclin D1 /low E-cadherin expression had the poorest prognosis, so they might serve as potential predictors of the prognosis of the patients with LSCC. E-cadherin was found to affect the overall survival (OAS) significantly by the univariate analysis (p = 0.01). However, by the multivariate analysis the TNM stage was the only independent prognostic factor of OAS (p < 0.05). Cyclin D1 can be used as an independent prognostic marker of lymph node metastasis in patients with LSCC and can help to identify those patients with clinically negative lymph nodes but with considerable risk for occult metastasis. Detection of cyclin D1 and E-cadherin status in LSCC may contribute to the identification of patients with high risk factors of local recurrence. However, they don’t appear to be better prognostic predictors than other established markers in LSCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luke CG, Yeoh E, Roder DM (2008) Exploring trends in laryngeal cancer incidence, mortality and survival: implications for research and cancer control. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 9(3):397–402
Freedman LS, Edwards BK, Ries LAG et al (2006) Cancer incidence in four member countries (Cyprus, Egypt, Israel, and Jordan) of the Middle East Cancer Consortium (MECC) compared with US SEER. National Cancer Institute. NIH Pub. No. 06–5873. Bethesda, MD. Chapter title; Overview and Summary Data; (1): pp 1–27. Edited by Freedman LS, Edwards BK, Ries LAG, et al
Torrente MC, Rodrigo JP, Haigentz M et al (2011) Human papillomavirus infections in laryngeal cancer. Head Neck 33(4):581–586
Krecicki T, Smigiel R, Fraczek M et al (2004) Studies of the cell cycle regulatory proteins, P16, cyclinD1and retinoblastoma protein in laryngeal carcinoma tissue. J Laryngol Otol 118(9):676–680
Cristóbal E, Arribas B, Tardio J et al (2000) Analysis of the cyclin D1/p16/pRb pathway in parathyroid adenomas. Endocr Pathol 11(3):259–266
vanDiest PJ, Michalides RJAM, Jannink I et al (1997) Cyclin D1 expression in invasive breast cancer: correlations and prognostic value. Am J Pathol 150(2):705–711
Ishikawa T, Furihata M, Ohtsuki Y et al (1998) Cyclin D1 overexpression related to retinoblastoma protein expression as a prognostic marker in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 77(1):92–97
Wangefjord S, Manjer J, Gaber A et al (2011) Cyclin D1 expression in colorectal cancer is a favourable prognostic factor in men but not in women in a prospective, population-based cohort study. Biol Sex Differ 2:10
Ito Y, Matsuura N, Sakon M et al (1999) Expression and prognostic roles of the G1-S modulators in hepatocellular carcinoma: p27 independently predicts the recurrence. Hepatology 30(1):90–99
Fracchiolla NS, Pruneri G, Pignataro L et al (1997) Molecular and immunohistochemical analysis of the bcl-1/cyclin D1 gene in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas: correlation of protein expression with lymph node metastases and advanced clinical stage. Cancer 79(6):1114–1121
Do NY, Park SY, Lim SC (2004) The role of E-cadherin/B2-catenin complex and cyclin D1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat 36(1):72–78
Berx G, Staes K, van Hengel J et al (1995) Cloning and characterization of the human invasion suppressor gene E-cadherin (CDH1). Genomics 26(2):281–289
Kashibuchi K, Tomita K, Schalken JA et al (2006) The prognostic value of E-cadherin, alpha-, beta-, and gamma-catenin in urothelial cancer of the upper urinary tract. Eur Urol 49(5):839–845
Loddo M, Kingsbury SR, Rashid M et al (2009) Cell-cycle-phase progression analysis identifies unique phenotypes of major prognostic and predictive significance in breast cancer. Br J Cancer 100(6):959–970
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart PA et al (2005) World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumors of the head and neck. Lyon: IARC. Squamous cell carcinoma in; Hypopharynx, larynx and trachea; (3): p p121. Edited by Cardesa A, Gale N, Nadal A et al
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC et al (2010) Larynx. In: AJCC cancer staging manual, 7th edn. Springer, New York, pp 57–62
Larizadeh MH, Damghani MA, Tabrizchi H et al (2009) Expression of E-cadherin in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and its correlation with clinicopathological features. J Med Sci 9(1):41–45
Leon X, Lopez M, Garcia J et al (2008) Recurrent laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: rTNM versus composite laryngeal recurrence staging system. Proposal for a modification of the CLRSS to improve patient classification. Head Neck 30(7):939–945
Awada A, Lalami Y (2005) Molecular markers, molecular-targeted therapies and taxanes: how to integrate the progress into clinical research and practice for the management of head and neck cancers. Curr Opin Oncol 17(3):209–211
Zhang Y, Xu Z, Jun-Xi Wang J et al (2012) G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 might be a prognostic biomarker for patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 13(5):2133–2137
Pignataro L, Sambataro G, Pagani D et al (2005) Clinico-prognostic value of D-type cyclins and p27 in laryngeal cancer patients: a review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 25(2):75–85
Vielba R, Eng JBC, Ispizua A et al (2003) Cyclin D1 as prognostic factors in squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx. Laryngoscope 113(1):167–172
Galera-Ruiz H, Ríos-Moreno MJ, González-Cámpora R (2012) The cadherin-catenin complex in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269(4):1183–1188
Li JJ, Zhang GH, Yang XM et al (2012) Reduced E-cadherin expression is associated with lymph node metastases in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 39(2):186–192
Paksoy M, Hardal U, Caglar C (2011) Expression of cathepsin D and E-cadherin in primary laryngeal cancers correlation with neck lymph node involvement. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(9):1371–1377
Rodrigo JP, Domínguez F, Alvarez C et al (2002) Expression of E-cadherin in squamous cell carcinomas of the supraglottic larynx with correlations to clinicopathological features. Eur J Cancer 38(8):1059–1064
Rodrigo JP, Dominguez F, Suárez V et al (2007) Focal adhesion kinase and E-cadherin as markers for nodal metastasis in laryngeal cancer. Arch Otolaryngol 133(2):145–150
Michalides RJAM, van Veelen NMJ, Kristel PMP et al (1997) Overexpression of cyclin D1 indicates a poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123(5):497–502
Pignataro L, Capaccio P, Pruneri G et al (1996) P53 and cyclin D1 protein expression in glottic laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas involving the anterior commissure (pT1bN0M0). Int J Oncol 3(9):553–557
Snow GB, Patel P, Leemans CR et al (1992) Management of cervical lymph nodes in patients with head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 249:187–194
Zou J, Yang H, Chen F et al (2010) Prognostic significance of fascin-1 and E-cadherin expression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cancer Prev 19(1):11–17
Pruneri G, Pignataro L, Valentini S et al (2005) Cyclin D3 immunoreactivity is an independent predictor of survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 11(1):242–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, R.A., Shawky, A.EA. & Hamed, R.H. Prognostic Significance of Cyclin D1 and E-cadherin Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 625–633 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9741-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-014-9741-6