Abstract
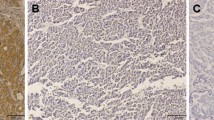
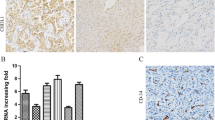
Regional hypoxia caused by accelerated cell proliferation and overgrowth is an important characteristic of neoplasm. Hypoxia can cause a series of changes in gene transcription and protein expression, thereby not only inducing tumor cell resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy but also promoting tumor invasion and metastasis. This study aimed to investigate the relationship between HIF-1α expression and cellular apoptosis, angiogenesis and clinical prognosis in rectal carcinoma. In 113 rectal carcinoma cases, cellular apoptosis was analyzed by the in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay, whereas the levels of HIF-1α expression, VEGF expression, microvessel density (MVD) and lymphatic vessel density(LVD) were examined by immunohistochemical staining. HIF-1 expression was detected in 67 of 113 rectal carcinoma cases (59.3 %). A positive correlation was found among HIF-1α expression, cellular apoptosis and angiogenesis. The 5-year survival rate in the HIF-1α-negative group was significantly higher than that in the HIF-1α-positive group (81.34 % versus 50 %, P < 0.05). According to the Cox regression analysis, HIF-1α expression, VEGF expression and cellular apoptosis index were independent risk factors for clinical prognosis in rectal carcinoma. Aberrant HIF-1α expression correlates with apoptosis inhibition, angiogenesis and poor prognosis in rectal carcinoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gupta SC, Kim JH, Prasad S et al (2010) Regulation of survival, proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and metastasis of tumor cells through modulation of inflammatory pathways by nutraceuticals. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29(3):405–434
de Krijger I, Mekenkamp LJ, Punt CJ et al (2011) MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer metastasis. J Pathol 224(4):438–447
Arvelo F, Cotte C (2009) Hypoxia in cancer malignity. Invest Clin 50(4):529–546
Greijer AE, van der Groep P, Kemming D et al (2005) Up-regulation of gene expression by hypoxia is medi-ated predominantly by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1). J Pathol 206:291–304
Belozerov VE, Van Meir EG (2005) Hypoxia inducible factor-1: a novel target for cancer therapy. Anticancer Drugs 16(9):901–909
Mucaj V, Shay JE, Simon MC (2012) Effects of hypoxia and HIFs on cancer metabolism. Int J Hematol 95(5):464–670
Semenza GL (2000) HIF-1: mediator of physiological and pathophysiological responses to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 88(4):1474–1480
Yeung SJ, Pan J, Lee MH (2008) Roles of p53, MYC and HIF-1 in regulating glycolysis - the seventh hallmark of cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(24):3981–3999
Rapisarda A, Melillo G (2012) Role of the VEGF/VEGFR axis in cancer biology and therapy. Adv Cancer Res 114:237–267
Kerbel RS (2008) Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 358(19):2039–2049
Merritt WM, Sood AK (2007) Markers of angiogenesis in ovarian cancer. Dis Markers 23(5–6):419–431
Menrad H, Werno C, Schmid T et al (2010) Roles of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) versus HIF-2alpha in the survival of hepatocellular tumor spheroids. Hepatology 51(6):2183–2192
Ardyanto TD, Osaki M, Nagahama Y et al (2008) Down-regulation of cobalt-induced HIF-1alpha expression correlates with cell proliferation and apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep 19(2):339–343
Hao X, Du M, Bishop AE et al (1998) Imbalance between proliferation and apoptosis in development of colorectal carcinoma. Virchows Arch 433:523–527
Benchabane H, Ahmed Y (2009) The adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor and Wnt signaling in the regulation of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 656:75–84
Lampropoulos P, Zizi-Sermpetzoglou A, Rizos S et al (2012) TGF-beta signalling in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett 314(1):1–7
Liu W, Shen SM, Zhao XY et al (2012) Targeted genes and interacting proteins of hypoxia inducible factor-1. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 3(2):165–178
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E et al (1999) Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 59:5830–5835
Koh MY, Spivak-Kroizman TR, Powis G (2010) HIF-1alpha and cancer therapy. Recent Results Cancer Res 180:15–34
Simiantonaki N, Taxeidis M, Jayasinghe C et al (2008) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression increases during colorectal carcinogenesis and tumor progression. BMC Cancer 8:320
Kotch LE, Iyer NV, Laughner E et al (1999) Defective vascularization of HIF-1alpha-null embryos is not associated with VEGF deficiency but with mesenchymal cell death. Dev Biol 209:254–267
Tsuzuki Y, Fukumura D, Oosthuyse B et al (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) modulation by targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha–> hypoxia re-sponse element–> VEGF cascade differentially regulates vascular response and growth rate in tumors. Cancer Res 60:6248–6252
Rey S, Semenza GL (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res 86(2):236–242
Duffy JP, Eibl G, Reber HA et al (2003) Influence of hypoxia and neoangiogenesis on the growth of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 2:12
Suzuki H, Tomida A, Tsuruo T (2001) Dephosphorylated hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha as a mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis during hypoxia. Oncogene 20(41):5779–5788
Piret JP, Mottet D, Raes M et al (2002) Is HIF-1alpha a pro- or an anti-apoptotic protein? Biochem Pharmacol 64(5–6):889–892
Price DJ, Miralem T, Jiang S et al (2001) Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the stimulation of cellular invasion and signaling of breast cancer cells. Cell Growth Differ 12(3):129–135
Bos R, van Diest PJ, van der Groep P et al (2004) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and cell cycle proteins in invasive breast cancer are estrogen receptor related. Breast Cancer Res 6(4):R450–R459
Nagy JA, Vasile E, Feng D et al (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor induces lymphangiogenesis as well as angiogenesis. J Exp Med 196(11):1497–1506
Mohammed RA, Green A, El-Shikh S et al (2007) Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial cell growth factors -A, -C and -D in breast cancer and their relationship with angio- and lymphangiogenesis. Br J Cancer 96(7):1092–1100
Gao Y, Zhong WX, Mu DB et al (2008) Distributions of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in gastrointestinal intramucosal tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 15(4):1117–1123
Lee S, Choi I, Hong YK (2010) Heterogeneity and plasticity of lymphatic endothelial cells. Semin Thromb Hemost 36(3):352–361
Acknowledgments
The work was Supported by Chongqing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.cstc2013jcyjA10057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Tao, L., Dawei, H. et al. HIF-1α Expression Correlates with Cellular Apoptosis, Angiogenesis and Clinical Prognosis in Rectal Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 603–610 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9738-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9738-6