Abstract
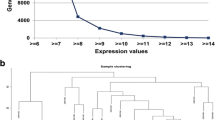
Osteosarcoma is the most common malignant bone-tumor with a peak manifestation during the second and third decade of life. In order to explore the influence of genetic factors on the mechanism of osteosarcoma by analyzing the inter relationship between osteosarcoma and its related genes, and then provide potential genetic references for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of osteosarcoma, we collected osteosarcoma related gene sequences in Genebank of National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and local alignment analysis for a pair of sequences was carried out to identify the measurement association among related sequences. Then fuzzy clustering method was used for clustering analysis so as to contact the unknown genes through the consistent osteosarcoma related genes in one class. From the result of fuzzy clustering analysis, we could classify the osteosarcoma related genes into two groups and deduced that the genes clustered into one group had similar function. Based on this knowledge, we found more genes related to the pathogenesis of osteosarcoma and these genes could exert similar function as Runx2, a risk factor confirmed in osteosarcoma, this study may help better understand the genetic mechanism and provide new molecular markers and therapies for osteosarcoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G, Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M, Winkelmann W (2002) Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: an analysis of 1,702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J Clin Oncol 20:776–790
Fletcher C.D, Unni K.K, Mertens F (2002) Pathology & genetics: tumours of soft tissue and bone, World Health Organization
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper review for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Kansara M, Thomas DM (2007) Molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol 26:1–18
Sjin RTT, Naspinski J, Birsner A, Li C, Chan R, Lo K, Gillies S, Zurakowski D, Folkman J, Samulski J (2006) Endostatin therapy reveals a U-shaped curve for antitumor activity. Cancer Gene Ther 13:619–627
Mohammed RAA, Green A, El-Shikh S, Paish E, Ellis I, Martin S (2007) Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial cell growth factors-A,-C and-D in breast cancer and their relationship with angio-and lymphangiogenesis. Br J Cancer 96:1092–1100
IIDA K, NOBORI T, MATSUMINE A, ISAKA A, Seto M, Shiraishi T, Uchida A (2003) Effect of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene expression on chemosensitivity of human osteosarcoma cell lines. Oncol Rep 10:1961–1965
Ek ET, Dass CR, Contreras KG, Choong PF (2007) Inhibition of orthotopic osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by multitargeted antitumor activities of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Clinical Exp Metastasis 24:93–106
Stricker S, Fundele R, Vortkamp A, Mundlos S (2002) Role of Runx genes in chondrocyte differentiation. Dev Biol 245:95–108
Pratap J, Galindo M, Zaidi SK, Vradii D, Bhat BM, Robinson JA, Choi J-Y, Komori T, Stein JL, Lian JB (2003) Cell growth regulatory role of Runx2 during proliferative expansion of preosteoblasts. Cancer Res 63:5357–5362
Choi J-Y, Pratap J, Javed A, Zaidi SK, Xing L, Balint E, Dalamangas S, Boyce B, Van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB (2001) Subnuclear targeting of Runx/Cbfa/AML factors is essential for tissue-specific differentiation during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:8650–8655
Ping G, Liangtian S, Shilun L, Lei S (1996) A theoretical study of the effect of porous media on the dew point pressure of a gas condensate, in, SPE Gas Technology Symposium
Saeidi, L. Handy (1974) Flow and phase behavior of gas condensate and volatile oils in porous media, in, SPE California Regional Meeting
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Casey R (2005) Blast sequences aid in genomics and proteomics. Business Intelligence Network
Gustafson DE, Kessel WC (1978) Fuzzy clustering with a fuzzy covariance matrix, in, Decision and Control including the 17th Symposium on Adaptive Processes, 1978 I.E. Conference on, IEEE, pp. 761–766
Dembele D, Kastner P (2003) Fuzzy C-means method for clustering microarray data. Bioinformatics 19:973–980
Pickert L, Reuter I, Klawonn F, Wingender E (1998) Transcription regulatory region analysis using signal detection and fuzzy clustering. Bioinformatics 14:244–251
Bezdek JC (1981) Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithms, Kluwer Academic Publishers
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:14863–14868
Banerjee C, Javed A, Choi J-Y, Green J, Rosen V, Van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Lian JB, Stein GS (2001) Differential regulation of the two principal Runx2/Cbfa1 n-terminal isoforms in response to bone morphogenetic protein-2 during development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocrinology 142:4026–4039
Stein GS, Lian JB (1993) Molecular mechanisms mediating proliferation/differentiation interrelationships during progressive development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocr Rev 14:424–442
Stewart M, Terry A, Hu M, O’hara M, Blyth K, Baxter E, Cameron E, Onions D, Neil J (1997) Proviral insertions induce the expression of bone-specific isoforms of PEBP2αA (CBFA1): evidence for a new myc collaborating oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94:8646–8651
Langdon C, Kerr C, Hassen M, Hara T, Arsenault AL, Richards CD (2000) Murine oncostatin m stimulates mouse synovial fibroblasts in vitro and induces inflammation and destruction in mouse joints in vivo. Am J Pathol 157:1187–1196
Horn D, Fitzpatrick WC, Gompper PT, Ochs V, Bolton-Hansen M, Zarling J, Malik N, Todaro GJ, Linsley PS (1990) Regulation of cell growth by recombinant oncostatin M. Growth Factors 2:157–165
Grant SL, Begley CG (1999) The oncostatin M signalling pathway: reversing the neoplastic phenotype? Molecular Med Today 5:406–412
Klausen P, Pedersen L, Jurlander J, Baumann H (2000) Oncostatin M and interleukin 6 inhibit cell cycle progression by prevention of p27kip1 degradation in HepG2 cells. Oncogene 19:3675
Halfter H, Lotfi R, Westermann R, Young P, Ringelstein EB, Stögbauer FT (1998) Inhibition of growth and induction of differentiation of glioma cell lines by oncostatin M (OSM). Growth Factors 15:135–147
Bellido T, Borba VZ, Roberson P, Manolagas SC (1997) Activation of the Janus kinase/STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) signal transduction pathway by interleukin-6-type cytokines promotes osteoblast differentiation. Endocrinology 138:3666–3676
de Hooge AS, van de Loo FA, Bennink MB, de Jong DS, Arntz OJ, Lubberts E, Richards CD, van den Berg WB (2002) Adenoviral transfer of murine oncostatin M elicits periosteal bone apposition in knee joints of mice, despite synovial inflammation and up-regulated expression of interleukin-6 and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand. Am J Pathol 160:1733–1743
Liu F, Aubin J, Malaval L (2002) Expression of leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)/interleukin-6 family cytokines and receptors during in vitro osteogenesis: differential regulation by dexamethasone and LIF. Bone 31:212
Wang Z-Q, Ovitt C, Grigoriadis AE, Möhle-Steinlein U, Rüther U, Wagner EF (1992) Bone and haematopoietic defects in mice lacking c-fos
Grigoriadis AE, Wang Z-Q, Cecchini MG, Hofstetter W, Felix R, Fleisch HA, Wagner EF (1994) c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science 266:443–448
Grigoriadis AE, Wang Z-Q, Wagner EF (1995) Fos and bone cell development: lessons from a nuclear oncogene. Trends Genet 11:436–441
Chambers T, Fuller K (1985) Bone cells predispose bone surfaces to resorption by exposure of mineral to osteoclastic contact. J Cell Sci 76:155–165
Fuller K, Gallagher A, Chambers T (1991) Osteoclast resorption—stimulating activity is associated with the osteoblast cell surface and/or the extracellular matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:67–73
Rozen N, Ish-Shalom S, Rachmiel A, Stein H, Lewinson D (2000) Interleukin-6 modulates trabecular and endochondral bone turnover in the nude mouse by stimulating osteoclast differentiation. Bone 26:469–474
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no any conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kai Chen and Dajiang Wu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, K., Wu, D., Bai, Y. et al. Fuzzy Clustering Analysis of Osteosarcoma Related Genes. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 20, 535–539 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9725-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-013-9725-y