Abstract
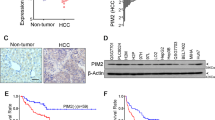
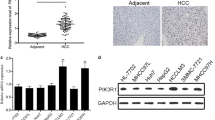
Pim-2 is proved to be relevant to the tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but the mechanism is unclear. We studied the relationship among Pim-2, NF-κB and API-5. In our experiment, expression level of the three factors and phosphorylation level of API-5, as well as NF-κB activity, were detected in HCC tissues and the nontumorous controls. Then Pim-2 gene was transfected into nontumorous liver cells L02, and Pim-2 SiRNA was transfected into hepatoblastoma cell line HepG2. Parthenolide was added as NF-κB inhibitor. The same detections as above were repeated in the cells, along with the apoptosis analysis. We found the levels of Pim-2, NF-κB and API-5, as well as NF-κB activity, were significantly higher in HCC tissues. Pim-2 level was increased in L02 cells after the transfection of Pim-2 gene, but decreased in HepG2 cells after the transfection of Pim-2 SiRNA. The levels of NF-κB and API-5, as well as NF-κB activity and API-5 phosphorylation level, were in accordance with Pim-2 level, but could be reversed by Parthenolide. Cell apoptosis rates were negatively correlated with API-5 phosphorylation level. Therefore, we infer that Pim-2 could activate API-5 to inhibit the apoptosis of liver cells, and NF-κB is the key regulator.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Pim:
-
Proviral integration of Monoley virus
- HCC:
-
hepatocellular carcinoma
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa B
- Bcl-2:
-
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2
- Bad:
-
Bcl2-antagonist of cell death
- API-5:
-
apoptosis inhibitor 5
- PNL:
-
paired noncancerous liver tissues
- NL:
-
normal liver tissues
- DEPC:
-
diethyl pyrocarbonate
- SDS-PAGE:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electropheresis
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- eI4B:
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4B
- Myc:
-
myelocytomatosis
References
Breuer ML, Cuypers HT, Berns A (1989) Evidence for the involvement of pim-2, a new common proviral insertion site, in progression of lymphomas. EMBO J 8(3):743–7488
Ren K, Shi YJ, Gong JP (2007) The research on the mechanism of Pim-2 suppressing the apoptosis of tumor cell. Prog Physiol Sci 38(2):136–139
Chen JL, Limnander A, Rothman PB (2008) Pim-1 and Pim-2 kinases are required for efficient pre-B-cell transformation by v-Abl oncogene. Blood 111(3):1677–1685
Dai H, Li R, Wheeler T et al (2005) Pim-2 upregulation: biological implications associated with disease progression and perinueral invasion in prostate cancer. Prostate 65(3):276–286
Gong J, Wang J, Ren K et al (2008) Serine/Threonine Kinase Pim-2 Promotes Liver Tumorigenesis Induction through Mediating Survival and Preventing Apoptosis of Liver Cell. J Surg Res. Apr 22. [Epub ahead of print]
Li B, Ye T, Li DH (2008) Expression of Pim-2 in normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Chinese J Hepatol 16(12):950–951
Hammerman PS, Fox CJ, Cinalli RM et al (2004) Lymphocyte Transformation by Pim-2 Is Dependent on Nuclear Factor-κB Activation. Cancer Res 64:8341–8348
Aghajanian C, Soignet S, Dizon DS et al (2002) A phase I trial of the novel proteasome inhibitor PS341 in advanced solid tumor malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 8:2505–2511
White E (2003) The pims and outs of survival signaling: role for the Pim-2 protein kinase in the suppression of apoptosis by cytokines. Genes Dev 17:1813–1816
Macdonald A, Campbell DG, Toth R et al (2006) Pim kinases phosphorylate multiple sites on Bad and promote14–3–3 binding and dissociation from Bcl-XL. BMC Cell Biol 7:1186–1471
Peng C, Knebel A, Morrice NA et al (2007) Pim kinase substrate identification and specificity. J Biochem 141(3):353–62
Wang Y, Lee AT, Ma JZ et al (2008) Profiling microRNA expression in hepatocellular carcinoma reveals microRNA-224 up-regulation and apoptosis inhibitor-5 as a microRNA-224 specific target. J Biol Chem 283(19):13205–15
Hehner SP, Hofmann TG, Dröge W et al (1999) The antiinflammatory sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide inhibits NF-kappa B by targeting the I kappa B kinase complex. J Immunol 163(10):5617–23
Li W, Lei P, Yu B et al (2008) Screening and identification of a novel target specific for hepatoma cell line HepG2 from the FliTrx bacterial peptide library. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 40(5):443–51
Guzman ML, Rossi RM, Karnischky L et al (2005) The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide induces apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Blood 105(11):4163–9
Jiang JX, Mikami K, Venugopal S et al (2009) Apoptotic body engulfment by hepatic stellate cells promotes their survival by the JAK/STAT and Akt/NF-kappaB-dependent pathways. J Hepatol 51(1):139–48
Hoffmann F, Sass G, Zillies J et al (2009) A novel technique for selective NF-kappaB inhibition in Kupffer cells - contrary effects in fulminant hepatitis and ischemia/reperfusion. Gut May 25. [Epub ahead of print]
Kuboki S, Sakai N, Clarke C et al (2009) The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase, Pin1, facilitates NF-kappaB binding in hepatocytes and protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Hepatol May 24. [Epub ahead of print]
Pelengaris S, Khan M, Evan G (2002) c-Myc: more than just a matter of life and death. Nature Reviews. Cancer 2(10):764–776
Hammerman PS, Fox CJ, Cinalli RM et al (2004) Lymphocyte Transformation by Pim-2 Is Dependent on Nuclear Factor-κB Activation. Cancer Res 64:8341–8348
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Li X et al (2008) Pim kinase-dependent inhibition of c-Myc degradation. Oncogene 27(35):4809–19
Bachmann M, Moroy T (2005) The serine/threonine kinase Pim-1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:726–730
Fujii C, Nakamoto Y, Lu P et al (2005) Aberrant expression of serine/threonine kinase Pim-3 in hepatocellular carcinoma development and its role in the proliferation of human hepatoma cell lines. Int J Cancer 114(2):209–218
Qian K, Wang L, Cywin CL et al (2009) Hit to lead account of the discovery of a new class of inhibitors of Pim kinases and crystallographic studies revealing an unusual kinase binding mode. J Med Chem 52(7):1814–27
Xia Z, Knaak C, Ma J et al (2009) Synthesis and evaluation of novel inhibitors of Pim-1 and Pim-2 protein kinases. J Med Chem 52(1):74–86
Tong Y, Stewart KD, Thomas S et al (2008) Isoxazolo [3, 4-b] quinoline-3, 4 (1H, 9H) -diones as unique, potent and selective inhibitors for Pim-1 and Pim-2 kinases: chemistry, biological activities, and molecular modeling. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18(19):5206–5208
Acknowledgement
This research is supported by National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 30400424).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, K., Zhang, W., Shi, Y. et al. Pim-2 Activates API-5 to Inhibit the Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Through NF-κB Pathway. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 229–237 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9215-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9215-4