Abstract
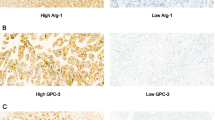
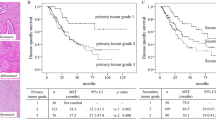
Phosphatase of regenerating liver (PRL)-3 is involved in the metastasis of various tumors, but the expression of PRL-3 and its possible role in primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) has not been reported yet. In this study, we assessed the expression levels of PRL-3 by immunohistochemistry in 102 primary ICC samples, 62 matched lymph node metastases (LNM) and 102 adjacent normal liver tissues. Then we investigated the relationship between PRL-3 expression and clinicopathologic factors. Survival analysis was performed to determine the prognostic significance of PRL-3 expression in ICC. Immunochemistry results suggested PRL-3 expression was negative or weak in non-neoplastic intrahepatic bile ducts of adjacent liver tissue. In primary lesion and LNM high PRL-3 expression was frequently detected. Furthermore, the rate of high PRL-3 expression in LNM was higher than that in primary lesion (80.6% vs. 47.1%, P < 0.05). High expression of PRL-3 in primary tumors was significantly associated with TNM (P < 0.001), T stage (P < 0.001), vascular invasion (P = 0.002), and LNM (P < 0.001). Survival analysis results with Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazard model indicated high expression of PRL-3 was correlated with decreased overall survival and was an independent prognostic marker of overall survival. Thus, our results suggested high expression of PRL-3 was correlated with progression and metastasis of ICC and indicated negative prognostic impact. PRL-3 might serve as a novel prognostic marker for patients with ICC.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PRL-3:
-
phosphatase of regenerating liver-3
- ICC:
-
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- LNM:
-
lymph node metastasis
- RR:
-
relative risk
- CI:
-
confidence interval
References
Khan SA, Thomas HC, Davidson BR, Taylor-Robinson SD (2005) Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet 366:1303–1314
Patel T (2001) Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology 33:1353–1357
Shaib Y, EI-Serag HB (2004) The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 24:115–125
Taylor-Robinson SD, Toledano MB, Arora S, Keegan TJ, Hargreaves S, Beck A, Khan SA et al (2001) Increase in mortality rates from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in England and Wales 1968–1998. Gut 48:816–820
Mouzas IA, Dimoulios P, Vlachonikolis IG, Skordilis P, Zoras O, Kouroumalis E (2002) Increasing incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in Crete 1992–2000. Anticancer Res 22:3637–3641
Okuda K, Nakanuma Y, Miyazaki M (2002) Cholangiocarcinoma: recent progress. Part 1: epidemiology and etiology. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:1049–1055
Okuda K, Nakanuma Y, Miyazaki M (2002) Cholangiocarcinoma: recent progress. Part 2: molecular pathology and treatment. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 17:1056–1063
Anderson CD, Pinson CW, Berlin J, Chari RS (2004) Diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Oncologist 9:43–57
Nakagawa T, Kamiyama T, Kurauchi N, Matsushita M, Nakanishi K, Kamachi H, Kudo T et al (2005) Number of lymph node metastases is a significant prognostic factor in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Surg 29:728–733
Yamamoto M, Takasaki K, Yoshikawa T (1999) Lymph node metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 29:147–150
Harada K, Masuda S, Hirano M, Nakanuma Y (2003) Reduced expression of syndecan-1 correlates with histologic dedifferentiation, lymph node metastasis, and poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hum Pathol 34:857–863
Shimonishi T, Miyazaki K, Kono N, Sabit H, Tuneyama K, Harada K, Hirabayashi J et al (2001) Expression of endogenous galectin-1 and galectin-3 in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hum Pathol 32:302–310
Alonso A, Sasin J, Bottini N, Friedberg I, Friedberg I, Osterman A, Godzik A et al (2004) Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 117:699–711
Stoker AW (2005) Protein tyrosine phosphatases and signalling. J Endocrinol 185:19–33
van Huijsduijnen RH, Bombrun A, Swinnen D (2002) Selecting protein tyrosine phosphatases as drug targets. Drug Discov Today 7:1013–1019
Zeng Q, Hong W, Tan YH (1998) Mouse PRL-2 and PRL-3, two potentially prenylated protein tyrosine phosphatases homologous to PRL-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 244:421–427
Mohn KL, Laz TM, Hsu JC, Melby AE, Bravo R, Taub R (1991) The immediate-early growth response in regenerating liver and insulin-stimulated H-35 cells: comparison with serum-stimulated 3T3 cells and identification of 41 novel immediate-early genes. Mol Cell Biol 11:381–390
Diamond RH, Cressman DE, Laz TM, Abrams CS, Taub R (1994) PRL-1, a unique nuclear protein tyrosine phosphatase, affects cell growth. Mol Cel Biol 14:3752–3762
Werner SR, Lee PA, DeCamp MW, Crowell DN, Randall SK, Crowell PL (2003) Enhanced cell cycle progression and down regulation of p21Cip1/Waf1 by PRL tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett 202:201–211
Matter WF, Estridge T, Zhang C, Belagaje R, Stancato L, Dixon J, Johnson B et al (2001) Role of PRL-3, a human muscle-specific tyrosine phosphatase, in angiotensin-II signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 283:1061–1068
Zeng Q, Dong JM, Guo K, Li J, Tan HX, Koh V, Pallen CJ et al (2003) PRL-3 and PRL-1 promote cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Res 63:2716–2722
Saha S, Bardelli A, Buckhaults P, Velculescu VE, Rago C, St Croix B, Romans KE et al (2001) A phosphatase associated with metastasis of colorectal cancer. Science 294:1343–1346
Wu X, Zeng H, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Sha H, Ge X, Zhang M et al (2004) Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 promotes motility and metastasis of mouse melanoma cells. Am J Pathol 164:2039–2054
Kato H, Semba S, Miskad UA, Seo Y, Kasuga M, Yokozaki H (2004) High expression of PRL-3 promotes cancer cell motility and liver metastasis in human colorectal cancer: a predictive molecular marker of metachronous liver and lung metastases. Clin Cancer Res 10:7318–7328
Qian F, Li YP, Sheng X, Zhang ZC, Song R, Dong W, Cao SX et al (2007) PRL-3 siRNA inhibits the metastasis of B16-BL6 mouse melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med 13:151–159
Bardelli A, Saha S, Sager JA, Romans KE, Xin B, Markowitz SD, Lengauer C (2003) PRL-3 expression in metastatic cancers. Clin Cancer Res 9:5607–5615
Miskad UA, Semba S, Kato H, Yokozaki H (2004) Expression of PRL-3 phosphatase in human gastric carcinomas: close correlation with invasion and metastasis. Pathobiology 71:176–184
Miskad UA, Semba S, Kato H, Matsukawa Y, Kodama Y, Mizuuchi E, Maeda N et al (2007) High PRL-3 expression in human gastric cancer is a marker of metastasis and grades of malignancies: an in situ hybridization study. Virchows Arch 450:303–310
Wang L, Peng L, Dong B, Kong L, Yan L, Xie Y, Shou C (2006) Overexpression of phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 in breast cancer: association with a poor clinical outcome. Ann Oncol 17:1517–1522
Polato F, Codegoni A, Fruscio R, Perego P, Mangioni C, Saha S, Bardelli A et al (2005) PRL-3 phosphatase is implicated in ovarian cancer growth. Clin Cancer Res 11:6835–6839
Ren T, Jiang B, Xing X, Dong B, Peng L, Meng L, Xu H et al (2009) Prognostic Significance of Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-3 Expression in Ovarian Cancer. Pathol Oncol Res (Epub ahead of print)
Nakanuma Y, Sripa B, Vatanasapt V, Leong ASY, Ponchon T, Ishak KG (2000) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. In: Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA (eds) World Health Organization classification of tumours: pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 173–180
Junking M, Wongkham C, Sripa B, Sawanyawisuth K, Araki N, Wongkham S (2008) Decreased expression of galectin-3 is associated with metastatic potential of liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Eur J Cancer 44:619–626
Peng L, Ning J, Meng L, Shou C (2004) The association of the expression level of protein tyrosine phosphatase PRL-3 protein with liver metastasis and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130:521–526
Nichols JC, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF, Wiesner RH, Nagorney DM, Ritts RE Jr (1993) Diagnostic role of serum CA19–9 for cholangiocarcinoma in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Mayo Clin Proc 68:874–879
Patel AH, Harnois DM, Klee GG, LaRusso NF, Gores GJ (2000) The utility of CA19–9 in the diagnoses of cholangiocarcinoma in patients without primary sclerosing cholangitis. Am J Gastroenterol 95:204–207
Paik KY, Jung JC, Heo JS, Choi SH, Choi DW, Kim YI (2008) What prognostic factors are important for resected intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma? J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23:766–770
Acknowledgement
The authors thank Dr. Chengyong Qin for his valuable proposals. The technical assistance of the Scientific Center of Shandong Provincial Hospital is also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Zhu, M., Zhang, S. et al. Expression and Prognostic Value of PRL-3 in Human Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 16, 169–175 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9200-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9200-y