Abstract
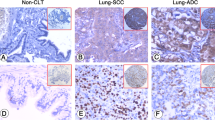
Chemotherapies are widely used in the treatment of lung cancer. However, little is known about their effect in the expression of different tissue markers. Seventeen lung cancer tissue blocks obtained by bronchoscopic biopsies together with their corresponding surgical biopsies after neoadjuvant chemotherapy were studied. They included 9 adenocarcinomas (ADC) and 8 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC). Immunohistochemistry was performed on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues to study the expression of Ki-67, p53, Bcl-2, Bax, Fas-ligand and ERCC1 (excision repair cross-complementation group 1). Out of 17 NSCLC 6 expressed proapoptotic markers and 4 expressed antiapoptotic markers, while in 7 cases the apoptotic markers did not show detectable changes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Six of 17 bronchoscopic NSCLC cases expressed increased level of Ki-67 after neoadjuvant treatment. Eight bronchoscopic NSCLC tissues (6 SCC, 2 ADC) expressed ERCC1. All but one ADC became ERCC1 negative after neoadjuvant therapy. There was no newly expressed ERCC1 positive case in the surgical biopsy group. Platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy had no effect on the apoptotic activity of 17 patients’ tumor specimen, however, 6 of 17 bronchoscopic NSCLC cases expressed increased level of Ki-67 after neoadjuvant treatment, in 3 cases the level of Ki-67 became decreased, while 8 cases had no detectable change of proliferation activity. The results of the present study suggest that platinum-based chemotherapy probably induces a selection of tumor cells with more aggressive phenotype, and also affects the expression of tissue marker (ERCC1) that could have predictive value.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- ADC:
-
adenocarcinoma
- SCC:
-
squamous cell carcinoma
- BAC:
-
bronchiolo-alveolar carcinoma
- ERCC1:
-
excision repair cross-complementation group 1
References
U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. United States Cancer Statistics: 2002–2004 Incidence and Mortality Web-based Report Version. Atlanta (GA): Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and National Cancer Institute; 2007
Noble J, Ellis PM, Mackay JA et al (2006) Second-line or subsequent systemic therapy for recurrent or progressive non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and practice guideline. J Thorac Oncol 9:1042–58
Junker K, Langner K, Klinke F et al (2001) Grading of tumor regression in non-small cell lung cancer: morphology and prognosis. Chest. 120(5):1584–91
Morero JL, Poleri C, Martin C et al (2007) Influence of apoptosis and cell cycle regulator proteins on chemotherapy response and survival in stage IIIA/IIIB NSCLC patients. J Thorac Oncol. 4:293–8
Ikuta K, Takemura K, Kihara M et al (2005) Defects in apoptotic signal transduction in cisplatin-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 13(6):1229–34
Filipits M, Pirker R, Dunant A et al (2007) Cell cycle regulators and outcome of adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer: the International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Biologic Program. J Clin Oncol. 25(19):2735–40
Olaussen KA, Dunant A, Fouret P et al (2006) DNA repair by ERCC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer and cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 355:983–91
Rigas JR, Kelly K (2007) Current treatment paradigms for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2(Suppl 2):S77–85
Gilligan D, Nicolson M, Smith I et al (2007) Preoperative chemotherapy in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer: results of the MRC LU22/NVALT 2/EORTC 08012 multicentre randomised trial and update of systematic review. Lancet. 369(9577):1929–37
de Marinis F, Tedesco B, Treggiari S et al (2007) Role of induction chemotherapy in resectable N2 non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 5(Suppl 5):S31–4
Abratt RP, Lee JS, Han JY et al (2006) Phase II trial of gemcitabine-carboplatin-paclitaxel as neoadjuvant chemotherapy for operable non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2:135–40
Stinchcombe TE, Socinski MA (2007) The role of induction therapy for resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Drugs. 67(3):321–32
De Pauw R, van Meerbeeck JP (2007) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 19(2):92–7
Meert AP, Martin B, Verdebout JM et al (2004) Correlation of different markers (p53, EGF-R, c-erbB-2, Ki-67) expression in the diagnostic biopsies and the corresponding resected tumors in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 44(3):295–301
Lang DS, Droemann D, Schultz H et al (2007) A novel human ex vivo model for the analysis of molecular events during lung cancer chemotherapy. Respir Res. 14;8:43
Fujii T, Toyooka S, Ichimura K et al (2008) ERCC1 protein expression predicts the response of cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 59(3):377–84
Acknowledgements
The authors thank László Kopper MD PhD DSc for his professional advice, Katalin Vajda MD for her diagnostic work and Anna Tamási for her excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pápay, J., Sápi, Z., Egri, G. et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Lung Cancer Affects the Expression of Certain Biomarkers Including ERCC1. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 15, 445–450 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9155-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-009-9155-z