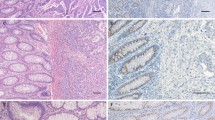
Abstract
In this study, gastric cancer progression was correlated with the over-expression of erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular (Eph)A2 receptor and down-expression of epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin). Immunohistochemistry of EphA2 and E-cadherin were performed on these tumor samples from 165 primary lesions of gastric cancer. The results showed that expression of EphA2 was obviously increased in gastric cancer tissues (P < 0.01), which was positively correlated with the depth of cancer invasion, tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, the expression of E-cadherin was significantly reduced (P < 0.01), which was negatively correlated with the depth of cancer invasion, grade of tumor differentiation, TNM stage and lymph node metastasis (P < 0.05). The correlation between EphA2 and E-cadherin expression was negative (r = −0.198, P = 0.011). In conclusion, either the over-expression of EphA2 or the down-expression of E-cadherin is correlated with cancer progression and lymphogenous metastasis in gastric cancer, suggesting that both of them may play an important role in tumor progression and metastasis.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Eph:
-
erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular
- E-cadherin:
-
epithelial cadherin
- RTK:
-
receptor tyrosine kinase
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered solution
- DAB:
-
diaminobenzidine tetrachloride
- TNM:
-
tumor-node-metastasis
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloprotease
References
Catalano V, Labianca R, Beretta GD et al (2005) Gastric cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 54:209–241
Dicken BJ, Bigam DL, Cass C et al (2005) Gastric adenocarcinoma: review and considerations for future directions. Ann Surg 241:27–39
Sulman EP, Tang XX, Allen C et al (1997) ECK, a human EPH-related gene, maps to 1p36.1, a common region of alteration in human cancers. Genomics 40:371–374
Walker-Daniels J, Hess AR, Hendrix MJC et al (2003) Differential regulation of EphA2 in normal and malignant cells. Am J Pathol 162:1037–1042
Miyazaki T, Kato H, Fukuchi M et al (2003) EphA2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 103:657–663
Zeng G, Hu Z, Kinch MS et al (2003) High-level expression of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Pathol 163:2271–2276
Kinch MS, Moore MB, Harpole DH et al (2003) Predictive value of the EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in lung cancer recurrence and survival. Clin Cancer Res 9:613–618
Han L, Dong Z, Qiao Y et al (2005) The clinical significance of EphA2 and Ephrin A-1 in epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Gynecol Oncol 99:278–286
Abraham S, Knapp DW, Cheng L et al (2006) Expression of EphA2 and Ephrin A-1 in carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Clin Cancer Res 12:353–360
Bussemakers MJ, van Bokhoven A, Mees SG et al (1993) Molecular cloning and characterization of the human E-cadherin cDNA. Mol Biol Rep 17:123–128
Takeichi M (1993) Cadherins in cancer: implications for invasion and metastasis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:806–811
Chen H, Paradies NE, Fedor-Chaiken M et al (1997) E-cadherin mediates adhesion and suppresses cell motility via distinct mechanisms. J Cell Sci 110:345–356
Hazan RB, Qiao R, Keren R et al (2004) Cadherin switch in tumor progression. Ann NY Acad Sci 1014:155–163
Zantek ND, Azimi M, Fedor-Chaiken M et al (1999) E-cadherin regulates the function of the EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell Growth Differ 10:629–638
Thaker PH, Deavers M, Celestino J et al (2004) EphA2 expression is associated with aggressive features in ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 10:5145–5150
Lin YG, Han LY, Kamat AA et al (2007) EphA2 overexpression is associated with angiogenesis in ovarian cancer. Cancer 109:332–340
Shiozaki H, Tahara H, Oka H et al (1991) Expression of immunoreactive E-cadherin adhesion molecule in human cancer. Am J Pathol 139:17–23
Jawhari A, Jordan S, Poole S et al (1997) Abnormal immunoreactivity of the E-cadherin-catenin complex in gastric carcinoma: relationship with patient survival. Gastroenterology 112:46–54
Zhou Y, Ran J, Tang C (2007) Effect of celecoxib on E-cadherin, VEGF, Microvessel density and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 6:269–275
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (eds) (1997) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors, 5th edn. Wiley, New York
Ogawa K, Pasqualini R, Lindberg RA et al (2000) The ephrin-A1 ligand and its receptor, EphA2, are expressed during tumor neovascularization. Oncogene 19:6043–6052
Zelinski DP, Zantek ND, Stewart JC et al (2001) EphA2 overexpression causes tumorigenesis of mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 61:2301–2306
Fang WB, Brantley-Sieders DM, Parker MA et al (2005) A kinase-dependent role for EphA2 receptor in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 24:7859–7868
Lu C, Shahzad MM, Wang H et al (2008) EphA2 overexpression promotes ovarian cancer growth. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1–6
Zantek ND, Walker-Daniels J, Stewart J et al (2001) MCF-10A-NeoST: a new cell system for studying cell-ECM and cell-cell interactions in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 7:3640–3648
Kinch MS, Carles-Kinch K (2003) Overexpression and functional alterations of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase in cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 20:59–68
Kikawa KD, Vidale DR, Van Etten RL et al (2002) Regulation of the EphA2 kinase by the low molecular weight tyrosine phosphatase induces transformation. J Biol Chem 277:39274–39279
Parri M, Buricchi F, Taddei ML et al (2005) EphrinA1 repulsive response is regulated by an EphA2 tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem 280:34008–34018
Chen HC, Chu RY, Hsu PN et al (2003) Loss of E-cadherin expression correlates with poor differentiation and invasion into adjacent organs in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer Lett 201:97–106
Lee KH, Shin SJ, Kim KO et al (2006) Relationship between E-cadherin, matrix metalloproteinase-7 gene expression and clinicopathological features in gastric carcinoma. Oncol Rep 16:823–830
Guilford PJ, Hopkins JB, Grady WM et al (1999) E-cadherin germline mutations define an inherited cancer syndrome dominated by diffuse gastric cancer. Hum Mutat 14:249–255
Tamura G, Yin J, Wang S et al (2000) E-Cadherin gene promoter hypermethylation in primary human gastric carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:569–573
Koizume S, Tachibana K, Sekiya T et al (2002) Heterogeneity in the modification and involvement of chromatin components of the CpG island of the silenced human CDH1 gene in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4770–4780
Catimel B, Layton M, Church N et al (2006) In situ phosphorylation of immobilized receptors on biosensor surfaces: application to E-cadherin/beta-catenin interactions. Anal Biochem 357:277–288
Noë V, Fingleton B, Jacobs K et al (2001) Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin and stromelysin-1. J Cell Sci 114:111–118
Rios-Doria J, Day KC, Kuefer R et al (2003) The role of calpain in the proteolytic cleavage of E-cadherin in prostate and mammary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:1372–1379
Saito T, Masuda N, Miyazaki T et al (2004) Expression of EphA2 and E-cadherin in colorectal cancer: correlation with cancer metastasis. Oncol Rep 11:605–611
Orsulic S, Kemler R (2000) Expression of Eph receptors and ephrins is differentially regulated by E-cadherin. J Cell Sci 113:1793–1802
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, W., Chen, Z., Wu, S. et al. Expression of EphA2 and E-cadherin in Gastric Cancer: Correlated with Tumor Progression and Lymphogenous Metastasis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 15, 473–478 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9132-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-008-9132-y