Abstract
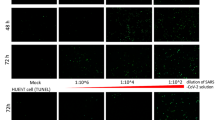
Human adenovirus type 55 (HAdV-B55) is a re-emergent acute respiratory disease pathogen that causes adult community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). Previous studies have shown that the receptor of HAdV-B14, which genome is highly similar with HAdV-B55, is human Desmoglein 2 (DSG2). However, whether the receptor of HAdV-B55 is DSG2 is undetermined because there are three amino acid mutations in the fiber gene between HAdV-B14 and HAdV-B55. Here, firstly we found the 3T3 cells, a mouse embryo fibroblast rodent cell line which does not express human DSG2, were able to be infected by HAdV-B55 after transfected with pcDNA3.1-DSG2, while normal 3T3 cells were still unsusceptible to HAdV-B55 infection. Next, A549 cells with hDSG2 knock-down by siRNA were hard to be infected by HAdV-B3/-B14/-B55, while the control siRNA group was still able to be infected by all these types of HAdVs. Finally, immunofluorescence confocal microscopy indicated visually that Cy3-conjugated HAdV-B55 viruses entered A549 cells by binding to DSG2 protein. Therefore, DSG2 is a major receptor of HAdV-B55 causing adult CAP. Our finding is important for better understanding of interactions between adenoviruses and host cells and may shed light on the development of new drugs that can interfere with these processes as well as for the development of potent prophylactic vaccines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alba R, Bradshaw AC, Parker AL, Bhella D, Waddington SN, Nicklin SA, van Rooijen N, Custers J, Goudsmit J, Barouch DH, McVey JH, Baker AH (2009) Identification of coagulation factor (F)X binding sites on the adenovirus serotype 5 hexon: effect of mutagenesis on FX interactions and gene transfer. Blood 114:965–971
Andrews PW, Knowles BB, Parkar M, Pym B, Stanley K, Goodfellow PN (1985) A human cell-surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody and controlled by a gene on human chromosome 1. Ann Hum Genet 49:31–39
Annasara L, Liaci AM, Liu Y, Frängsmyr L, Frank M, Blaum BS, Chai W, Podgorskie II, Harrach B, Benko M, Feizi T, Stehle T, Arnberga N (2017) Polysialic acid is a cellular receptor for human adenovirus 52. Proc Nati Acad Scie U S A 115:E4264–E4273
Bai M, Harfe B, Freimuth P (1993) Mutations that alter an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) sequence in the adenovirus type 2 penton base protein abolish its cell-rounding activity and delay virus reproduction in flat cells. J Virol 67:5198–5205
Baker AT, Mundy RM, Davies JA, Rizkallah PJ, Parker AL (2019) Human adenovirus type 26 uses sialic acid-bearing glycans as a primary cell entry receptor. Sci Adv 5:3567–3567
Cao B, Huang GH, Pu ZH, Qu JX, Yu XM, Zhu Z, Dong JP, Gao Y, Zhang YX, Li XH, Liu JH, Wang H, Xu Q, Li H, Xu W, Wang C (2014) Emergence of community-acquired adenovirus type 55 as a cause of community-onset pneumonia. Chest 145:79–86
Chen Y, Liu F, Wang C, Zhao M, Deng L, Zhong J, Zhang Y, Ye J, Jing S, Cheng Z, Guan Y, Ma Y, Sun Y, Zhu B, Zhang Q (2016) Molecular identification and epidemiological features of human adenoviruses associated with acute respiratory infections in hospitalized children in southern China, 2012–2013. PloS one 11:0155412
Cheng Z, Yan Y, Jing S, Li W-G, Chen W-W, Zhang J, Li M, Zhao S, Cao N, Ou J, Zhao S, Wu X, Cao B, Zhang Q (2018) Comparative genomic analysis of re-emergent human adenovirus type 55 pathogens associated with adult severe community-acquired pneumonia reveals conserved genomes and capsid proteins. Front Microbiol 9:1180
Chitaev NA, Troyanovsky SM (1997) Direct Ca2+-dependent heterophilic interaction between desmosomal cadherins, desmoglein and desmocollin, contributes to cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 138:193–201
Chmielewicz B, Benzler J, Pauli G, Krause G, Bergmann F, Schweiger B (2005) Respiratory disease caused by a species B2 adenovirus in a military camp in Turkey. J Med Virol 77:232–237
Cowin P (1994) Unraveling the cytoplasmic interactions of the cadherin superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:10759–10761
Cui X, Wen L, Wu Z, Liu N, Yang C, Liu W, Ba Z, Wang J, Yi S, Li H, Liang B, Li P, Jia L, Hao R, Wang L, Hua Y, Wang Y, Qiu S, Song H (2015) Human adenovirus type 7 infection associated with severe and fatal acute lower respiratory illness and nosocomial transmission. J Clin Microbiol 53:746–749
Cupelli K, Muller S, Persson BD, Jost M, Arnberg N, Stehle T (2010) Structure of adenovirus type 21 knob in complex with CD46 reveals key differences in receptor contacts among species B adenoviruses. J Virol 84:3189–3200
Di Paolo NC, Kalyuzhniy O, Shayakhmetov DM (2007) Fiber shaft-chimeric adenovirus vectors lacking the KKTK motif efficiently infect liver cells in vivo. J Virol 81:12249–12259
Feng Y, Yi C, Liu X, Qu L, Su W, Shu T, Zheng X, Ye X, Luo J, Hao M, Sun X, Li L, Liu X, Yang C, Guan S, Chen L, Feng L (2020) Human desmoglein-2 and human CD46 mediate human adenovirus type 55 infection, but human desmoglein-2 plays the major roles. J Virol 94:00747–720
Fleischli C, Sirena D, Lesage G, Havenga MJ, Cattaneo R, Greber UF, Hemmi S (2007) Species B adenovirus serotypes 3, 7, 11 and 35 share similar binding sites on the membrane cofactor protein CD46 receptor. J Gen Virol 88:2925–2934
Gaggar A, Shayakhmetov DM, Lieber A (2003) CD46 is a cellular receptor for group B adenoviruses. Nat Med 9:1408–1412
Gao HW, Wei MT, Fan HJ, Ding H, Wei W, Liu ZQ, Zhang YZ, Lv Q, Dong WL, Hou SK (2018) Dynamic changes in clinical characteristics during an outbreak of human adenovirus serotype 55 in china. Disaster Med Public Health Prep 12:464–469
Geng X, Zhang J, Yang G (2013a) Investigation of an adenovirus-induced respiratory disease outbreak. Adv Infect Dis 3:257
Geng X, Zhang J, Yang G (2013b) Investigation of an adenovirus-induced respiratory disease outbreak. Adv Infect Dis 03:257–262
Girouard G, Garceau R, Thibault L, Oussedik Y, Bastien N, Li Y (2013) Adenovirus serotype 14 infection, New Brunswick, Canada, 2011. Emerg Infect Dis 19:119–122
Gu L, Liu Z, Li X, Qu J, Guan W, Liu Y, Song S, Yu X, Cao B (2012) Severe community-acquired pneumonia caused by adenovirus type 11 in immunocompetent adults in Beijing. J Clin Virol 54:295–301
Gustafsson DJ, Segerman A, Lindman K, Mei YF, Wadell G (2006) The Arg279Gln [corrected] substitution in the adenovirus type 11p (Ad11p) fiber knob abolishes EDTA-resistant binding to A549 and CHO-CD46 cells, converting the phenotype to that of Ad7p. J Virol 80:1897–1905
Hage E, Huzly D, Ganzenmueller T, Beck R, Schulz TF, Heim A (2014) A human adenovirus species B subtype 21a associated with severe pneumonia. J Infect 69:490–499
Haralambieva IH, Ovsyannikova IG, Vierkant RA, Poland GA (2008) Development of a novel efficient fluorescence-based plaque reduction microneutralization assay for measles virus immunity. Clin Vaccine Immunol 15:1054–1059
Harmon RM, Green KJ (2013) Structural and functional diversity of desmosomes. Cell Commun Adhes 20:171–187
Henning P, Andersson KM, Frykholm K, Ali A, Magnusson MK, Nygren PA, Granio O, Hong SS, Boulanger P, Lindholm L (2005) Tumor cell targeted gene delivery by adenovirus 5 vectors carrying knobless fibers with antibody-binding domains. Gene Ther 12:211–224
Hierholzer JC, Pumarola A, Rodriguez-Torres A, Beltran M (1974) Occurrence of respiratory illness due to an atypical strain of adenovirus type 11 during a large outbreak in Spanish military recruits. Am J Epidemiol 99:434–442
Huang S, Reddy V, Dasgupta N, Nemerow GR (1999) A single amino acid in the adenovirus type 37 fiber confers binding to human conjunctival cells. J Virol 73:2798–2802
Jeffrey M Bergelson JAC, Gustavo D, Evelyn A Kurt-Jones, Anita K, Jeong S Hong, Marshall S Horwitz, Richard L Crowell, Robert W Finberg (1997) Isolation of a common receptor for coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 275:1320–1323
Ji T, Li L, Li W, Zheng X, Ye X, Chen H, Zhou Q, Jia H, Chen B, Lin Z, Chen H, Huang S, Seto D, Chen L, Feng L (2021) Emergence and characterization of a putative novel human adenovirus recombinant HAdV-C104 causing pneumonia in Southern China. Virus Evol 7:018
Jing S, Zhang J, Cao M, Liu M, Yan Y, Zhao S, Cao N, Ou J, Ma K, Cai X, Wu J, Mei Y-F, Zhang Q (2019) Household transmission of human adenovirus type 55 in case of fatal acute respiratory disease. Emerg Infect Dis 25:1756–1758
Jones MS 2nd, Harrach B, Ganac RD, Gozum MM, Dela Cruz WP, Riedel B, Pan C, Delwart EL, Schnurr DP (2007) New adenovirus species found in a patient presenting with gastroenteritis. J Virol 81:5978–5984
Kajon AE, Dickson LM, Metzgar D, Houng HS, Lee V, Tan BH (2010) Outbreak of febrile respiratory illness associated with adenovirus 11a infection in a Singapore military training cAMP. J Clin Microbiol 48:1438–1441
Kalyuzhniy O, Di Paolo NC, Silvestry M, Hofherr SE, Barry MA, Stewart PL, Shayakhmetov DM (2008) Adenovirus serotype 5 hexon is critical for virus infection of hepatocytes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5483–5488
Kritz AB, Nicol CG, Dishart KL, Nelson R, Holbeck S, Von Seggern DJ, Work LM, McVey JH, Nicklin SA, Baker AH (2007) Adenovirus 5 fibers mutated at the putative HSPG-binding site show restricted retargeting with targeting peptides in the HI loop. Mol Ther 15:741–749
Lafolie J, Mirand A, Salmona M, Lautrette A, Archimbaud C, Brebion A, Regagnon C, Chambon M, Mercier-Delarue S, Le Goff J, Henquell C (2016) Severe pneumonia associated with adenovirus type 55 infection, France, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis 22:2012–2014
Lenman A, Liaci AM, Liu Y, Frangsmyr L, Frank M, Blaum BS, Chai W, Podgorski II, Harrach B, Benko M, Feizi T, Stehle T, Arnberg N (2018) Polysialic acid is a cellular receptor for human adenovirus 52. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E4264–E4273
Leopold PL, Ferris B, Grinberg I, Worgall S, Hackett NR, Crystal RG (1998) Fluorescent virions: dynamic tracking of the pathway of adenoviral gene transfer vectors in living cells. Hum Gene Ther 9:367–378
Li X, Kong M, Su X, Zou M, Guo L, Dong X, Li L, Gu Q (2014) An outbreak of acute respiratory disease in China caused by human adenovirus type B55 in a physical training facility. Int J Infect Dis 28:117–122
Lion T (2014) Adenovirus infections in immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients. Clin Microbiol Rev 27:441–462
Liu J, Nian Q-G, Zhang Y, Xu L-J, Hu Y, Li J, Deng Y-Q, Zhu S-Y, Wu X-Y, Qin E-D, Jiang T, Qin C-F (2014) In vitro characterization of human adenovirus type 55 in comparison with its parental adenoviruses, types 11 and 14. PloS one 9:100665
Lu Q-B, Tong Y-G, Wo Y, Wang H-Y, Liu E-M, Gray GC, Liu W, Cao W-C (2014) Epidemiology of human adenovirus and molecular characterization of human adenovirus 55 in China, 2009–2012. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 8:302–308
Marttila M, Persson D, Gustafsson D, Liszewski MK, Atkinson JP, Wadell G, Arnberg N (2005) CD46 is a cellular receptor for all species B adenoviruses except types 3 and 7. J Virol 79:14429–14436
Miyazawa N, Leopold PL, Hackett NR, Ferris B, Worgall S, Falck-Pedersen E, Crystal RG (1999) Fiber swap between adenovirus subgroups B and C alters intracellular trafficking of adenovirus gene transfer vectors. J Virol 73:6056–6065
Pasarica M, Loiler S, Dhurandhar NV (2008) Acute effect of infection by adipogenic human adenovirus Ad36. Arch Virol 153:2097–2102
Persson BD, Schmitz NB, Santiago C, Zocher G, Larvie M, Scheu U, Casasnovas JM, Stehle T (2010) Structure of the extracellular portion of CD46 provides insights into its interactions with complement proteins and pathogens. PLoS Pathog 6:1001122
Philipson L, Lonberg-Holm K, Pettersson U (1968) Virus-receptor interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol 2:1064–1075
Roelvink PW, Lizonova A, Lee JG, Li Y, Bergelson JM, Finberg RW, Brough DE, Kovesdi I, Wickham TJ (1998) The coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor protein can function as a cellular attachment protein for adenovirus serotypes from subgroups A, C, D, E, and F. J Virol 72:7909–7915
Salama M, Amitai Z, Amir N, Gottesman-Yekutieli T, Sherbany H, Drori Y, Mendelson E, Carmeli Y, Mandelboim M (2016) Outbreak of adenovirus type 55 infection in Israel. J Clin Virol 78:31–35
Segerman A, Atkinson JP, Marttila M, Dennerquist V, Wadell G, Arnberg N (2003) Adenovirus type 11 uses CD46 as a cellular receptor. J Virol 77:9183–9191
Short JJ, Pereboev AV, Kawakami Y, Vasu C, Holterman MJ, Curiel DT (2004) Adenovirus serotype 3 utilizes CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2) as cellular attachment receptors. Virology 322:349–359
Short JJ, Vasu C, Holterman MJ, Curiel DT, Pereboev A (2006) Members of adenovirus species B utilize CD80 and CD86 as cellular attachment receptors. Virus Res 122:144−153
Signas C, Akusjarvi G, Pettersson U (1985) Adenovirus 3 fiber polypeptide gene: implications for the structure of the fiber protein. J Virol 53:672–678
Stichling N, Suomalainen M, Flatt JW, Schmid M, Pacesa M, Hemmi S, Jungraithmayr W, Maler MD, Freudenberg MA, Pluckthun A, May T, Koster M, Fejer G, Greber UF (2018) Lung macrophage scavenger receptor SR-A6 (MARCO) is an adenovirus type-specific virus entry receptor. PLoS Pathog 14:1006914
Sun B, He H, Wang Z, Qu J, Li X, Ban C, Wan J, Cao B, Tong Z, Wang C (2014) Emergent severe acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by adenovirus type 55 in immunocompetent adults in 2013: a prospective observational study. Crit Care 18:456
Tan D, Zhu H, Fu Y, Tong F, Yao D, Walline J, Xu J, Yu X (2016) Severe community-acquired pneumonia caused by human adenovirus in immunocompetent adults: a multicenter case series. PLoS One 11:0151199
Uhlen M, Zhang C, Lee S, Sjostedt E, Fagerberg L, Bidkhori G, Benfeitas R, Arif M, Liu Z, Edfors F, Sanli K, von Feilitzen K, Oksvold P, Lundberg E, Hober S, Nilsson P, Mattsson J, Schwenk JM, Brunnstrom H, Glimelius B et al. (2017) A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science 357:eaan2507
Vassal-Stermann E, Mottet M, Ducournau C, Iseni F, Vragniau C, Wang H, Zubieta C, Lieber A, Fender P (2018) Mapping of Adenovirus of serotype 3 fibre interaction to desmoglein 2 revealed a novel “non-classical” mechanism of viral receptor engagement. Sci Rep 8:8381
Waddington SN, McVey JH, Bhella D, Parker AL, Barker K, Atoda H, Pink R, Buckley SM, Greig JA, Denby L, Custers J, Morita T, Francischetti IM, Monteiro RQ, Barouch DH, van Rooijen N, Napoli C, Havenga MJ, Nicklin SA, Baker AH (2008) Adenovirus serotype 5 hexon mediates liver gene transfer. Cell 132:397–409
Walsh MP, Seto J, Jones MS, Chodosh J, Xu W, Seto D (2010) Computational analysis identifies human adenovirus type 55 as a re-emergent acute respiratory disease pathogen. J Clin Microbiol 48:991–993
Wang H, Liaw YC, Stone D, Kalyuzhniy O, Amiraslanov I, Tuve S, Verlinde CL, Shayakhmetov D, Stehle T, Roffler S, Lieber A (2007) Identification of CD46 binding sites within the adenovirus serotype 35 fiber knob. J Virol 81:12785–12792
Wang H, Tuve S, Erdman DD, Lieber A (2009) Receptor usage of a newly emergent adenovirus type 14. Virology 387:436–441
Wang H, Li ZY, Liu Y, Persson J, Beyer I, Moller T, Koyuncu D, Drescher MR, Strauss R, Zhang XB, Wahl JK 3rd, Urban N, Drescher C, Hemminki A, Fender P, Lieber A (2011) Desmoglein 2 is a receptor for adenovirus serotypes 3, 7, 11 and 14. Nat Med 17:96–104
Wang H, Ducournau C, Saydaminova K, Richter M, Yumul R, Ho M, Carter D, Zubieta C, Fender P, Lieber A (2015) Intracellular signaling and desmoglein 2 shedding triggered by human adenoviruses Ad3, Ad14, and Ad14P1. J Virol 89:10841–10859
Yang Z, Zhu Z, Tang L, Wang L, Tan X, Yu P, Zhang Y, Tian X, Wang J, Zhang Y, Li D, Xu W (2009) Genomic analyses of recombinant adenovirus type 11a in China. J Clin Microbiol 47:3082–3090
Yi L, Zou L, Lu J, Kang M, Song Y, Su J, Zhang X, Liang L, Ni H, Ke C, Wu J (2017) A cluster of adenovirus type B55 infection in a neurosurgical inpatient department of a general hospital in Guangdong, China. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 11:328–336
Yu Z, Zeng Z, Zhang J, Pan Y, Chen M, Guo Y, Yu N, Chodosh J, Fu N, Che X, Zhang Q (2016) Fatal community-acquired pneumonia in children caused by re-emergent human adenovirus 7d associated with higher severity of illness and fatality rate. Sci Rep 6:37216
Zhang Q, Su X, Gong S, Zeng Q, Zhu B, Wu Z, Peng T, Zhang C, Zhou R (2006) Comparative genomic analysis of two strains of human adenovirus type 3 isolated from children with acute respiratory infection in southern China. J Gen Virol 87:1531–1541
Zhang Q, Su X, Seto D, Zheng B-j, Tian X, Sheng H, Li H, Wang Y, Zhou R (2009) Construction and characterization of a replication-competent human adenovirus type 3-based vector as a live-vaccine candidate and a viral delivery vector. Vaccine 27:1145–1153
Zhang Q, Seto D, Cao B, Zhao S, Wan C (2012a) Genome sequence of human adenovirus type 55, a re-emergent acute respiratory disease pathogen in China. J Virol 86:12441–12442
Zhang Q, Seto D, Zhao S, Zhu L, Zhao W, Wan C (2012b) Genome sequence of the first human adenovirus type 14 isolated in China. J Virol 86:7019–7020
Zhang Q, Dehghan S, Seto D (2016a) Pitfalls of restriction enzyme analysis in identifying, characterizing, typing, and naming viral pathogens in the era of whole genome data, as illustrated by HAdV type 55. Virol Sin 31:448–453
Zhang SY, Luo YP, Huang DD, Fan H, Lu QB, Wo Y, Chen G, Zhang XA, Li Y, Tong YG, Cao WC, Liu W (2016b) Fatal pneumonia cases caused by human adenovirus 55 in immunocompetent adults. Infect Dis (lond) 48:40–47
Zhang Q, Jing S, Cheng Z, Yu Z, Dehghan S, Shamsaddini A, Yan Y, Li M, Seto D (2017) Comparative genomic analysis of two emergent human adenovirus type 14 respiratory pathogen isolates in China reveals similar yet divergent genomes. Emerg Microbes Infect 6:92
Zhang J, Kang J, Dehghan S, Sridhar S, Lau S, Ou J, Woo P, Zhang Q, Seto D (2019) A survey of recent adenoviral respiratory pathogens in Hong Kong reveals emergent and recombinant human adenovirus type 4 (HAdV-E4) circulating in civilian populations. Viruses 11:129
Zhao S, Wan C, Ke C, Seto J, Dehghan S, Zou L, Zhou J, Cheng Z, Jing S, Zeng Z, Zhang J, Wan X, Wu X, Zhao W, Zhu L, Seto D, Zhang Q (2014) Re-emergent human adenovirus genome type 7d caused an acute respiratory disease outbreak in Southern China after a twenty-one year absence. Sci Rep 4:7365
Zhou X, Robinson CM, Rajaiya J, Dehghan S, Seto D, Jones MS, Dyer DW, Chodosh J (2012) Analysis of human adenovirus type 19 associated with epidemic keratoconjunctivitis and its reclassification as adenovirus type 64. Invest Ophthalmol vis Sci 53:2804–2811
Zhu Z, Zhang Y, Xu S, Yu P, Tian X, Wang L, Liu Z, Tang L, Mao N, Ji Y, Li C, Yang Z, Wang S, Wang J, Li D, Xu W (2009) Outbreak of acute respiratory disease in China caused by B2 species of adenovirus type 11. J Clin Microbiol 47:697–703
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFE0204503) and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2021A1515010788 and 2018B030312010) as well as from the Guangzhou Healthcare Collaborative Innovation Major Project (201803040004 and 201803040007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QZ designed the experiments. JZ, KM, XW, YJ, SZ, JO, WL, WG, and XW carried out the experiments. JZ, HZ, BY, CW, WZ, JW, and QZ analyzed the data. JZ, JW, and QZ wrote the paper and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that they have no conflict of interests.
Animal and Human Rights Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary information
ESM2 (mp4 3938 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ma, K., Wang, X. et al. Desmoglein 2 (DSG2) Is A Receptor of Human Adenovirus Type 55 Causing Adult Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Virol. Sin. 36, 1400–1410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-021-00414-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-021-00414-7