Abstract
In road transport, varying fuel flow rates make it hard to maintain a consistent water ratio in non-surfactant emulsion fuels using the Real-Time Non-Surfactant Emulsion Fuel Supply System (RTES). Thus, it becomes more reasonable to establish an appropriate range of water content tailored to a road condition. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate fuel consumption and exhaust emissions of non-surfactant emulsion fuel in light-duty trucks equipped with RTES, focusing specifically on urban conditions. On-road testing and 300-s idling tests were used as the urban conditions to compare diesel with non-surfactant Water-in-Diesel Emulsion (WiDE) fuel with water percentages from low to high concentrations of water, namely WiDE low%, WiDE med%, and WiDE high%. During idling tests, all emulsion variants reduce fuel consumption. WiDE high% exhibits the most substantial NOx reduction of 9.2%. On-road testing reveals comparable WiDE and diesel fuel consumption, despite the RTES increased electrical load. WiDE high% shows an increment for NOx and CO emissions by 11.71% and 202.19%. In conclusion, a 7.4% to 21.1% water content range was suggested for non-surfactant emulsion fuel in urban road conditions.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper. Should any raw data files be needed, they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- WiDE:
-
Water-in-diesel emulsion
- NOx:
-
Nitrogen oxides
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxides
- GHGs:
-
Greenhouse gases
- EL:
-
Electrical load
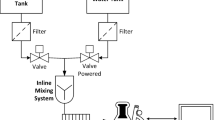
- RTES:
-
Real-time non-surfactant emulsion fuel supply system
References
Abdollahi, M., et al. (2020). Impact of water – biodiesel – diesel nano-emulsion fuel on performance parameters and diesel engine emission. Fuel, 280, 118576.
Ahmad, M. A., et al. (2018). Combustion performance and exhaust emissions fuelled with non-surfactant water-in-diesel emulsion fuel made from different water sources. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 1–15.
Akimoto, H., & Tanimoto, H. (2022). Rethinking of the adverse effects of NOx-control on the reduction of methane and tropospheric ozone – Challenges toward a denitrified society. Atmospheric Environment, 277, 119033.
Alahmer, A., et al. (2010). Engine performance using emulsified diesel fuel. Energy Convers Manag, 51(8), 1708–1713.
Arrhenius, S. (1896). On the influence of carbonic acid in the air upon the temperature of the ground. Philosophical Magazine Series 5, 41(251), 237–276.
Attia, A. M. A., & Kulchitskiy, A. R. (2014). Influence of the structure of water-in-fuel emulsion on diesel engine performance. Fuel, 116, 703–708.
Bradfield, M. (2008). https://www.delcoremy.com/documents/highefficiency-white-paper.aspx
Canselier, J. P., et al. (2002). Ultrasound emulsification—An overview. J Dispers Sci Technol, 23(1–3), 333–349.
European Environment Agency (2023). https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/dashboards/air-pollutant-emissions-data-viewer-5
Fahd, M. E. A., et al. (2013). Experimental investigation of the performance and emission characteristics of direct injection diesel engine by water emulsion diesel under varying engine load condition. Applied Energy, 102, 1042–1049.
Farzad, R., Pirker, S. and Schneiderbauer, S. (2017) A eulerian-eulerian-lagrangian hybrid model for the simulation of the droplet size distribution of liquid-liquid emulsions in stirred tank reactors, North American Mixing Forum 2017 - Core Programming Area at the 2017 AIChE Annual Meeting, 41–43.
Ismael, M. A., et al. (2018). The effect of fuel injection equipment on the dispersed phase of water-in-diesel emulsions. Applied Energy, 222, 762–771.
Ithnin, A. M., et al. (2018). Emulsifier-free Water-in-Diesel emulsion fuel: Its stability behaviour, engine performance and exhaust emission. Fuel, 215, 454–462.
Jafari, S. M., et al. (2008). Re-coalescence of emulsion droplets during high-energy emulsification. Food Hydrocoll, 22(7), 1191–1202.
Jeong, I. C., & Lee, K. H. (2008). Auto-ignition and micro-explosion behaviors of droplet arrays of water-in-fuel emulsion. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 9(6), 735–740.
Lin, C. Y., & Chen, L. W. (2008). Comparison of fuel properties and emission characteristics of two- and three-phase emulsions prepared by ultrasonically vibrating and mechanically homogenizing emulsification methods. Fuel, 87(10–11), 2154–2161.
Mahdi, W. N. I. W., et al. (2023). The effect of different in-line mixers producing emulsifier-free bio-diesel emulsion on the diesel engine combustion performance and exhaust emission. Fuel, 337, 126886.
Maiboom, A., & Tauzia, X. (2011). NOx and PM emissions reduction on an automotive HSDI Diesel engine with water-in-diesel emulsion and EGR: An experimental study. Fuel, 90(11), 3179–3192.
Mazlan, N. A., et al. (2018). Effects of different water percentages in non-surfactant emulsion fuel on performance and exhaust emissions of a light-duty truck. Journal of Cleaner Production, 179, 559–566.
Mohd Tamam, M. Q., et al. (2023). Performance and emission studies of a common rail turbocharged diesel electric generator fueled with emulsifier free water/diesel emulsion. Energy, 268, 126704.
Nguyen, D. H., et al. (2022). Tropospheric ozone and NOx: A review of worldwide variation and meteorological influences. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 28, 102809.
Oberthur, S. and Hermann, E.O. (1999) The Kyoto Protocol International Climate Policy for the 21st Century. 1st edn. Edited by A. Carius and R.A. Kraemer. New York: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Perreault, D. J., & Caliskan, V. (2004). Automotive Power Generation and Control. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 19(3), 618–630.
Rajamani, L. (2016). Ambition and differentiation in the 2015 paris agreement: Interpretative possibilities and underlying politics. International and Comparative Law Quarterly, 65(02), 493–514.
Ramlan, N. A., et al. (2016). Performance and emissions of light-duty diesel vehicle fuelled with non-surfactant low grade diesel emulsion compared with a high grade diesel in Malaysia. Energy Convers Manag, 130, 192–199.
Tsukahara, M. and Yoshimoto, Y. (1989) Influence of Emulsified Fuel Properties on the Reduction of BSFC in a Diesel Engine, SAE paper, 891841.
Yahya, W. J., et al. (2016). Performance of diesel engine equipped with real-time non-surfactant emulsion fuel supply system (RTES). Journal of Advanced Vehicle System ISSN, 1(1), 1–7.
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Advance Vehicle System (AVS), Malaysia-Japan International Institute of Technology (MJIIT), and Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) for their invaluable support in terms of equipment and finances. Special recognition is reserved for Universiti Teknologi Malaysia for providing financial support through a research grant (Q. K130000.3843.22H38 ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul Rashid, M.A., Ithnin, A.M., Yahya, W.J. et al. Performance and Emission of Non-surfactant Water-in-Diesel Emulsion Fuel Using Light-Duty Trucks on Urban Road Conditions. Int.J Automot. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-024-00041-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-024-00041-7