Abstract
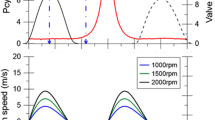
This paper is for the investigation on the turbulence kinetic energy distribution according to the design parameters of the intake system. The design parameter to be discussed is the intake valve angle. For this purpose, particle image velocimetry was introduced into the steady flow bench, in which four engine heads with 11, 16, 21 and 26 ° valve angles were evaluated changing valve lift. The experiment was conducted at 1.75 B evaluation position. The effect of valve angles and lift was analyzed by the planar flow characteristics of in-cylinder flow and the turbulence kinetic energy variation along the radial direction. 11, 16, and 21 ° have high turbulence kinetic energy near the cylinder wall with the highest flow velocity, and the turbulence kinetic energy around the swirl center is relatively low, indicating the same qualitative characteristics. 26 ° tends to be differentiated from other valve angles, and spatially very complex and fluctuating flow occurred. Complex turbulence kinetic energy distribution pattern appears at all valve angles, while the average turbulence kinetic energy shows a parabolic form as the valve lift increases because of the influence of the flow entry direction by the valve lift.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B:
-
cylinder bore
- CI:
-
compression ignition
- PIV:
-
particle image velocimetry
- RMS:
-
root mean square
- SI:
-
spark ignition
- TKE:
-
turbulence kinetic energy
References
Cho, S. and Ohm, I. (2017). Study on evaluation method of flow characteristics in steady flow bench (5) — Effect of evaluation position. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 25, 2, 179–189.
Heywood, J. B. (2018). Internal Combustion Engine Fundamentals. McGraw-Hill. New York, NY, USA.
Hyun, J. H. (2019). TKE Distributions according to Valve Angle in Steady Flow of an SI Engine. Ph.D. Dissertation, Seoul National University of Science and Technology. Seoul, Korea.
Lee, S., Ohm, I. Y. and Sung, J. Y. (2015). Comparison of swirl ratio measured by impulse swirl meter and particle image velocimetry in a steady flow bench of SI engine. J. Korean Society of Marine Engineering 39, 4, 437–442.
Noh, Y. K. (2003). A Theory of Turbulence. Sigma Press. Seoul, South Korea.
Ohm, I. Y. (2013) E ffects of intake valve angle on combustion characteristic in an SI engine. Int. J. Automotive Technology 14, 4, 529–537.
Ohm, I. Y. and Cho, Y. S. (2001a). In-cylinder fuel behavior according to fuel injection timing and port characteristics in an SI engine: Part I-without Swirl. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 9, 2, 19–27.
Ohm, I. Y. and Cho, Y. S. (2001b). In-cylinder fuel behavior according to fuel injection timing and port characteristics in an SI engine: Part II-With low/medium swirl. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 9, 3, 9–17.
Ohm, I. Y. and Cho, Y. S. (2001c). In-cylinder fuel behavior according to fuel injection timing and port characteristics in an SI engine: Part III-With high swirl. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 9, 3, 18–26.
Ohm, I. Y. and Myung, C. L. (2002). In-cylinder flow measurement using PIV. Spring Conf. Proc. KSAE, 1, 80–87.
Park, C. and Ohm, I. (2015a). Study on evaluation method of flow characteristics in steady flow bench (1) — Raising issue. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 23, 1, 88–96.
Park, C. and Ohm, I. (2015b). Study on evaluation method of flow characteristics in steady flow bench (2) — Comparison of ISM and PIV measurement. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 23, 1, 139–147.
Park, C., Sung, J. and Ohm, I. (2016a). Study on evaluation method of flow characteristics in steady flow bench (3) — Velocity profile (1). Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 24, 2, 169–182.
Park, C., Sung, J. and Ohm, I. (2016b). Study on evaluation method of flow characteristics in steady flow bench (4) — Velocity profile (2). Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 24, 2, 242–254.
Perry, A. E. and Chong, M. S. (1987). A description of eddying motions and flow patterns using critical-point concepts. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 19, 1, 125–155.
Yang, C. H. and Ohm, I. Y. (2018). Study on evaluation method of flow characteristics in steady flow bench (6) — Effect of axial velocity. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 26, 2, 174–186.
Wilcox, D. C. (1994). Turbulence Modeling for CFD. DCW Industries, Inc. La Cañada, CA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hyun, J.H., Ohm, I.Y. TKE Distribution According to the Intake Valve Angle in Steady Flow of the Pent-Roof SI Engine. Int.J Automot. Technol. 22, 1003–1010 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-021-0090-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-021-0090-7