Abstract
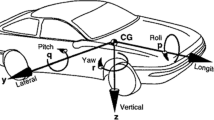
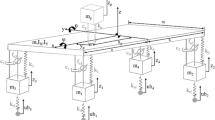
Tolerance design of vehicle suspension is an important factor that affects the ride and handling quality and cost of the vehicle. Also, applying geometric tolerance to an analysis model is found to be a difficult process. This paper presents a method for tolerance analysis of wheel alignment of vehicle suspension. Monte-Carlo simulation method is applied to multibody elasto-kinematic model to analyze the accumulated geometric tolerances. As an example, Macpherson Strut Type front half car model is used, and wheel alignment dispersion and contribution ratio to the dispersion by accumulated geometric tolerances is computed. This paper also presents an efficient modeling and analysis method for elasto-kinematic model of vehicle suspensions by computing the stiffness matrix analytically. The simulation results of a Macpherson Strut Type demonstrates the validity and accuracy of the proposed method.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ai :
-
rotation matrix of body fixed ref. frame of body i
- C:
-
compliance matrix
- F′:
-
force and moment vector
- fc :
-
cartesian force vector
- nc :
-
cartesian moment vector
- K:
-
system stiffness matrix
- \(\bar K\) :
-
global system stiffness matrix
- q:
-
generalized coordinate
- Q:
-
generalized force vector
- δπ i :
-
virtual angular displacement of body i
- δq :
-
virtual displacement of generalized coordinate
- δz :
-
virtual displacement of cartesian coordinate of body
- ω i :
-
angular velocity vector of body i
References
Katsumaru, S., Yagezawa, K., Yatabe, T., Fujii, K., Ohhashi, T. and Mori, K. (2005). Practical tolerance analysis simulation. JSAE Paper No. 20050503.
Kim, S. S. and Choi, K. S. (1997). Efficient vehicle dynamic analysis based on quasi-static analysis of suspension model. Spring Conf. Proc., Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 2, 249–256.
Kim, Y. S. and Jang, D. Y. (2009). Optimization of geometric dimension & tolerance parameters of front suspension system for vehicle pulls improvement. Trans. Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers A 33, 9, 903–912.
Lanzavecchia, M. and Radice, P. M. (2008). Road vehicle robust design: Chassis and suspension tolerances impact on the handling and stability behavior. SAE Paper No. 2008-01-0710.
Lee, J. Y. (2010). Quality Control with tolerance analysis. Korean Inst. Industrial Engineers 36, 4, 243–247.
Li, Z., Yue, J., Kokolaras, M., Camelio, J., Papalambros, P. Y. and Hu, S. J. (2004). Product tolerance allocation in compliant multistation assembly through variation propagation and analytical target cascading. ASME Int. Mechanical Engineering Cong. and Exposition, IMECE2004-60521.
Rotundo, R. and Amato, L. (2008). Robust design of an automotive suspension: A study on the reduction of tolerances. SAE Paper No. 2008-01-0712.
Tahk, J. K. (2005). Accumulated tolerance analysis for optimal tolerance design. Fall Conf. Proc., Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 3, 1743–1752.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.K., Kim, S.S., Cho, Y.G. et al. Accumulated tolerance analysis of suspension by geometric tolerances based on multibody elasto-kinematic analysis. Int.J Automot. Technol. 17, 255–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-016-0025-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-016-0025-x