Abstract
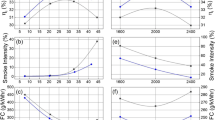
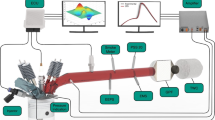
The soot morphological study and NOx emissions of soybean oil methyl ester (SME) in a passenger diesel vehicle were investigated experimentally. The soot morphological characteristics were conducted at various injection pressures, engine speeds and engine loads. Soot sampling and image processing analysis with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) were used to investigate the influence on particulate morphologies. The dimensions of average primary particles and the size of the radius of gyration were gradually decreased as injection pressures increased at all operating engine conditions. The average radius of gyration was increased with increasing engine load, while the average primary particle size decreased. NOx emissions were gradually increased with the increasing injection pressure at all operating engine conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buyukkaya, E. (2010). Effects of biodiesel on a DI diesel engine performance, emission and combustion characteristics. Fuel, 89, 3099–3105.
Chen, H., Shi-Jin, S. and Jian-Xin, W. (2007). Study on combustion characteristics and PM emission of diesel engines using ester-ethanol-diesel blended fuels. Proc. Combust. Inst., 31, 2981–2989.
Cheng, C. H., Cheung, C. S., Chan, T. L., Lee, S. C., Yao, C. D. and Tsang, K. S. (2008). Comparison of emissions of a direct injection diesel engine operating on biodiesel with emulsified and fumigated methanol. Fuel, 87, 1870–1879.
Di, Y., Cheung, C. S. and Huang, Z. (2009) Experimental investigation on regulated and unregulated emissions of a diesel engine fueled with ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel blended with biodiesel from waste cooking oil. Sci. Total Environ., 407, 835–846.
Fang, T., Coverdill, R. E., Lee, C. F. and White, R. A. (2008). Effects of injection angles on combustion processes using multiple injection strategies in an HSDI diesel engine. Fuel, 87, 2323–3239.
Hountalas, D. T., Mavropoulos, G. C. and Binder, K. B. (2008). Effect of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) temperature for various EGR rates on heavy duty DI diesel engine performance and emissions. Energy, 33, 272–283.
Hu, B., Yang, B. and Koylu, U. O. (2003). Soot measurements at the axis of an ethylene/air non-premixed turbulent jet flame. Combust. Flame, 134, 93–106.
Kim, M. Y., Yoon, S. H. and Lee, C. S. (2008). Characteristics of particulate emissions of compression ignition engine fueled with biodiesel derived from soybean. J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, 130, 052805.
Lee, K. O., Cole, R., Sekar, R., Choi, M. Y., Kang, J. S., Bae, C. S. and Shin, H. D. (2002). Morphological investigation of the microstructure, dimensions, and fractal geometry of diesel particulates. Proc. Combust. Inst., 29, 647–653.
Lee, K. O. and Zhu, J. (2005). Effects of exhaust system components on particulate morphology in a light-duty diesel engine. SAE Paper No. 2005-01-0184.
Mathis, U., Mohr, M., Kaegi, R., Bertola, A. and Boulouchos, K. (2005). Influence of diesel engine combustion parameters on primary soot particle diameter. Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, 1887–1892.
Murayama, T., Zheng, M., Chikahisa, T., Oh, Y., Fujiwara, Y., Tosaka, S., Yamashita, M. and Yoshitake, H. (1995). Simultaneous reductions of smoke and NOx from a DI diesel engine with EGR and dimethyl carbonate. SAE Paper No. 952518.
Nabi, M. N., Akhter, M. S. and Shahada, N. M. Z. (2006). Improvement of engine emissions with conventional diesel fuel and diesel-biodiesel blends. Bioresour. Technol., 97, 372–378.
Pischinger, F., Lepperhoff, G. and Houben, M. (1994). Soot Formation in Combustion. Springer-Verlag. Berlin.
Qi, D., Leick, M., Liu, Y. and Lee, C. F. (2011). Effect of EGR and injection timing on combustion and emission characteristics of split injection strategy DI-diesel engine fueled with biodiesel. Fuel, 90, 1884–1891.
Samuel, L. M. and Choi, M. Y. (2002). Morphology of soot collected in microgravity droplet flames. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 45, 1109–1116.
Zhang, J., He, K., Shi, X. and Zhao, Y. (2009). Effect of SME biodiesel blends on PM2.5 emission from a heavy-duty engine. Atmos. Environ., 43, 2442–2448.
Zhu, J., Lee, K. O., Yozgatligil, A. and Choi, M. Y. (2005). Effects of engine operating conditions on morphology, microstructure, and fractal geometry of light-duty diesel engine particulates. Proc. Combust. Inst., 30, 2781–2789.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D., Choi, S.C. & Lee, C.S. Impact of SME blended fuel combustion on soot morphological characteristics in a diesel engine. Int.J Automot. Technol. 14, 757–762 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-013-0083-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-013-0083-2