Abstract
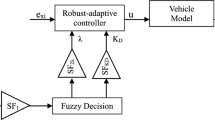
A fuzzy adaptive sliding mode controller for an air spring active suspension system is developed. Due to nonlinearity, preload-dependent spring force and parameter uncertainty in the air spring, it is difficult to control the suspension system. To achieve the desired performance, a fuzzy adaptive sliding mode controller (FASMC) is designed to improve the passenger comfort and the manipulability of the vehicle. The fuzzy adaptive system handles the nonlinearity and uncertainty of the air suspension. A normal linear suspension model with an optimal state feedback control is designed as the reference model. The simulation results show that this control scheme more effectively and robustly isolates vibrations of the vehicle body than the conventional sliding mode controller (CSMC).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, H., Liu, Z. Y. and Sun, P. Y. (2005). Application of constrained H ∞ control to active suspension systems on half-car models. ASME, J. Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, 127, 345–354.
Choi, S. B., Choi, Y. T. and Park, D. W. (2000). A sliding mode control of a full-car electrorheological suspension system via hardware in-the-loop simulation. ASME, J. Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 122, 144–121.
D’Amato, F. J. and Vissolo, D. E. (2000). Fuzzy control for active suspensions. Mechatronics, 10, 897–920.
Eickhoff, B. M. and Minnis, A. J. (1995). A review of modeling methods for railway vehicle suspension components. Vehicle System Dynamics, 24, 469–496.
Ge, S. S., Lee, T. H. and Harris, C. J. (1998). Adaptive Neural Network Control of Robotic Manipulators. World Scientific Publishing Co. Singapore.
Guaglia, G. and Sorli, M. (2001). Air suspension dimensionless analysis and design procedure. Vehicle System Dynamics 35,6, 443–475.
He, Y. and McPhee, J. (2005). Multidisciplinary design optimization of mechatronic vehicles with active suspensions. J. Sound and Vibration, 283, 217–241.
Hirose, M., Matsushige, S., Buma, S. and Kamiya, K. (1988). Toyota electronic modulated air suspension system for the 1986 Soarer. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electronics 35,2, 193–200.
Hrovat, D. (1997). Survey of advanced suspension developments and related optimal control application. Automatica 33,10, 1781–1817.
Huang, S. J. and Chao, H. C. (2000). Fuzzy logic controller for a vehicle active suspension system. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs., Part D: J. Automobile Eng., 214, 1–12.
Huang, S. J. and Lin, W. C. (2003). Adaptive fuzzy controller with sliding surface for vehicle suspension control. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Systems 11,4, 550–559.
Kim, C. and Ro, P. I. (1998). A sliding mode controller for vehicle active suspension systems with non-linearities. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs., Part D: J. Automobile Eng., 212, 79–92.
Kung, C. C. and Chen, T. H. (2005). Observer-based indirect adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control with state variable filters for unknown nonlinear dynamical systems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 155, 292–308.
Lu, J. (2004). A frequency-adaptive multi-objective suspension control strategy. ASME, J. Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 126, 700–707.
Ogawa, K., Satoh, K. and Enomoto, T. (2003). Development of damping control system for air suspension. JSAE Review, 17, 319–324.
Ramsbottom, M., Crolla, D. A. and Plummer, A. R. (1999). Robust adaptive control of an active vehicle suspension system. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs., Part D: J. Automobile Eng., 213, 1–17.
Rao, M. V. C. and Prahlad, V. (1997). A tunable fuzzy logic controller for vehicle-active suspension systems. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 85, 11–21.
Rattasiri, W. and Halgamuge, S. K. (2003). Computationally advantageous and stable hierarchical fuzzy systems for active suspension. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electronics 50,1, 48–61.
Slotine, J. J. and Li, W. (1991). Applied Nonlinear Control. Prentice Hall. New Jersey.
Suda, Y. and Kumaki, S. (1998). Study on curving characteristic of vehicles with nonlinear air suspension. JSME Int. J., Series C 41,3, 668–673.
Sunwoo, M., Cheok, K. C. and Huang, N. J. (1991). Model reference adaptive control for vehicle active suspension systems. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electronics 38,3, 217–222.
Ting, C. S., Li, T. H. and Kung, F. C. (1995). Design of fuzzy controller for active suspension system. Mechatronics 4,5, 365–383.
Toyofuku, K., Yamada, C., Kagawa, T. and Fujita, T. (1999). Study on dynamic characteristic analysis of air spring with auxiliary chamber. JSAE Review, 20, 349–355.
Utkin, V. I. (1977). Variable structure systems with sliding modes. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr, 22, 212–222.
Wang, J., Rad, A. B. and Chan, P. T. (2001). Indirect adaptive fuzzy sliding mode control: Part I: Fuzzy switching. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 122, 21–30.
Xiao, J. and Kulakowski, B. T. (2003). Sliding mode control of active suspension for transit buses based on a novel air-spring model. Proc. American Control Conf., Denver, Colorado, 3768–3773.
Yoshimura, T., Kume, A., Kurimoto, M. and Hino, J. (2001). Construction of an active suspension system of a quarter car model using the concept of sliding mode control. J. Sound and Vibration 239,2, 187–199.
Zhang, Y. Q., Zhao, Y. S., Yang, J. and Chen, L. P. (2007). A dynamic sliding-mode controller with fuzzy adaptive tuning for an active suspension system. Proc. Instn. Mech. Engrs., Part D: J. Automobile Eng., 221, 417–428.
Zuo, L., Slotine, J. J. and Nayfeh, S. A. (2005). Model reaching adaptive control for vibration isolation. IEEE Trans. Control Systems Technology 13,4, 611–617.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, W.N., Chen, L.P., Zhang, Y.Q. et al. Fuzzy adaptive sliding mode controller for an air spring active suspension. Int.J Automot. Technol. 13, 1057–1065 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-012-0108-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-012-0108-2