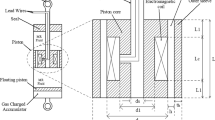
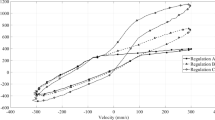
Abstract
In this study, a large bus is tested to measure its dynamic response by the single-lane change test and the rapid stop test. A full car model is established by ADAMS/Car for computer simulation. For multibody modeling of a large bus, user-defined templates are used in the simulation. Simulation results of the single-lane change test and the rapid braking test are compared to the results of the physical experiments, in which several sensors are installed to measure the vehicle’s responses. The results obtained from the simulation show good agreement with the tests’ results. A dynamic model for the MR(magnetic-rheological) damper is also developed by employing the Magic Formula model, which is widely used in the nonlinear modeling of a tire. Bump simulation of a full car with the MR damper is carried out to verify the performance of the MR damper. The comparison of the simulation results obtained with the MR damper model to the results obtained with the traditional passive damper model showed improved response of the vehicle with the MR damper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, K. W. and Hwang, W. G. (1994). A study on the handling characteristics of a medium bus during a single lane change manoeuvre. Proc. KSAE Fall Conf., Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 77–82.
Ang, W. L., Li, W. H. and H. Du (2004). Experimental and modeling approaches of a MR damper performance under harmonic loading. J. Institution of Engineers 44,4, Singapore.
Gillespie, T. D. (1992). Fundumentals of Vehicle Dynamics, Second Printing. Society of Automotive Engineers. USA.
Kamath, G. M. and Wereley, N. M. (1997). Nonlinear viscoelastic-plastic mechanism-based model of an electrorheological damper. J. Guidance, Control, and Dynamics 20,6, 1125–1132.
Karnopp, D., Crobsy, M. J. and Harwood, R. A. (1974). Vibration control using semi-active force generators. J. Engineering for Industry. Trans. ASME, 619–626.
Kim, C. W., Oh, T. S. and Kim, H. Y. (2003). Research of the dynamic behavior of express bus using the running mode test. Proc. KSAE Fall Conf., Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 492–496.
Lee, D.-Y. and Wereley, N. M. (2000). Analysis of electroand magneto-rheological flow mode dampers using Herschel-Buckley model. Proc. SPIE, 3989, 244–255.
Pacejka, H. B. (2002). Tire And Vehicle Dynamic. SAE. USA.
Park, B. W., Kim, W. Y., Ann, K. W. and Hwang, W. G. (1996). A study on an evaluation of handling performance of large bus. Proc. KSAE Spring Conf., Korean Society of Automotive Engineers, 160–165.
Sakai, C., Ohmori, H. and Sano, A. (2003). Modeling of MR damper with hysteresis for adaptive vibration control. Proc. 42nd IEEE Conf. Decision and Control, Maui, Hawaii, USA.
Suh, K. H., Kuk, J. Y. and Chyun, I. B. (2001). A study on the handling performances of a large-sized bus with the change of rear suspension geometry. Trans. Korean Society of Automotive Engineers 9,4, 176–183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Choi, S., Lee, J. et al. Damper modeling for dynamic simulation of a large bus with MR damper. Int.J Automot. Technol. 12, 521–527 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-011-0061-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-011-0061-5