Abstract
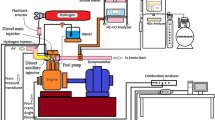
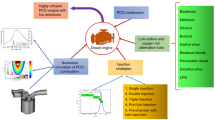
Currently, due to the severity of world-wide air pollution by substances emitted from vehicles, emission control is being enforced more strictly, and it is expected that the regulation requirements for emission will become even more severe. A new concept combustion technology that can reduce the Nitrogen oxides (NOx) and PM in relation to combustion is urgently required. As a core combustion technology among new combustion technologies for the next generation engine, the homogenous charge compression ignition (HCCI) is expanding its application range by adopting a multiple combustion mode, a catalyst, direct fuel injection and partially premixed charge compression ignition combustion using the split injection method. This paper used a split injection method in order to apply the partially premixed charge compression ignition combustion method without significantly altering engine specifications of the multiple combustion mode and practicality by referring to the results of studies on the HCCI engine. Furthermore, the effects of the ratio of the fuel injection amount on split injection are investigated. From the test results, the adequate combination of the ratio of the fuel injection amount for the split injection method has some benefit on exhaust and fuel economy performance in a naturally aspirated single cylinder diesel engine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dronniou, N., Lejeune, M., Balloul, I. and Higelin, P. (2005). Combination of high EGR rates and multiple injection strategies to reduce pollutant emissions. SAE Paper No. 2005-01-3726.
Hasegawa, R. and Yanagihara, H. (2003). HCCI combustion in DI diesel engine. SAE Paper No. 2003-01-0745.
Hashizume, T., Miyamoto, T., Akagawa, H. and Tsujimura, K. (1995). Combustion and emission characteristics of multiple stage diesel combustion. SAE Paper No. 980505.
Park, S. W., Suh, H. K. and Lee, C. S. (2005). Effects of a split injection on spray characteristics for a common-rail type diesel injection system. Int. J. Automotive Technology 6, 4, 315–322.
Yokota, H., Nakajima, H., Kakegawa, T. and Suzuki, T. (1997). A new concept for low emission diesel combustion. SAE Paper No. 970891.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, J.W., Kang, J.H., Kim, N.H. et al. Effects of the fuel injection ratio on the emission and combustion performances of the partially premixed charge compression ignition combustion engine applied with the split injection method. Int.J Automot. Technol. 9, 1–8 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-008-0001-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12239-008-0001-1