Abstract
Marsh periwinkle snails (Littoraria irrorata) are common in salt marshes of the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coast and often occupy important ecological roles. Much of the published research examining the abundance and role of this species has been conducted in marshes dominated by smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora). We investigated the distribution and morphology of L. irrorata in marshes dominated by black needlerush (Juncus roemerianus) an important marsh species that commonly forms monotypic conditions in more mesohaline conditions. Eight marshes along the coastal border of Alabama and west Florida, USA, were sampled for L. irrorata and other environmental data (plant density and biomass) at four different proximities to the marsh-bay edge. We also examined L. irrorata abundance, shell size, and biomass across a salinity gradient (quantified using a salinity regime index). We found that (1) abundance of L. irrorata in J. roemerianus-dominated marshes (1.0 ± 1.0 to 25.3 ± 12.6 snails m−2) were within the lower range of snail densities reported for S. alterniflora-dominated marshes elsewhere, (2) most L. irrorata were detected along the 10-m waterward edge of the marsh, and (3) considering snails at the waterward edge, a positive relationship (r2 = 0.53, p = 0.04) was detected between marsh salinity and snail density along with a negative relationship (r2 = 0.86, p < 0.01) between marsh salinity and mean snail shell length. Mechanisms associated with L. irrorata abundance and morphology are unclear but likely relate to various aspects of salinity and tidal connectivity. These results suggest that mesohaline J. roemerianus marshes may be marginal in terms of L. irrorata habitat; however, further research is encouraged.

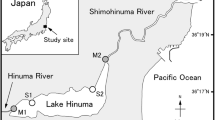
source: Map Data ©2021 Google, INGEI, USA)



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham, F.O. 1972. The influence of environmental stimuli on the direction of movement of the supralittoral gastropod Littorina irrorata. Bulletin of Marine Science 22 (2): 309–335.
Bulger, A.J., B.P. Hayden, M.E. Monaco, D.M. Nelson, and M.G. McCormick-Ray. 1993. Biologically-based salinity zones derived from a multivariate analysis. Estuaries 16: 311–322.
Butler, J.A., G.L. Heinrich, and M.L. Mitchell. 2012. Diet of the Carolina diamondback terrapin (Malaclemys terrapin centrata) in northeastern Florida. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 11 (1): 124–128.
Childdress, M.J. and K.J. Parmenter. 2012. Dying of thirst: impact of reduced freshwater inflow on South Carolina blue crabs. Proceedings of the 2012 South Carolina Water Resources Conference, held October 10–11, 2012 at the Columbia Metropolitan Convention Center.
Christensen, J.D., M.E. Monaco, and T.A. Lowery. 1997. An index to assess the sensitivity of Gulf of Mexico species to changes in estuarine salinity regimes. Gulf Research Reports 9 (4): 219–229.
Crist, R.W., and W.C. Banta. 1983. Distribution of the marsh periwinkle Littorina irrorata (Say) in a Virginia salt marsh. Gulf and Caribbean Research 7 (3): 225–235.
de la Cruz, A.A., and B.C. Gabriel. 1974. Caloric, elemental, and nutritive changes in decomposing Juncus roemerianus leaves. Ecology 55: 882–886.
Eleuterius, L.N. 1976. The distribution of Juncus roemerianus in the salt marshes of North America. Chesapeake Science 17: 289–292.
Failon, C.M., S.S. Wittyngham, and D.S. Johnson. 2020. Ecological associations of Littoraria irrorata with Spartina cynosuroides and Spartina alterniflora. Wetlands 40 (5): 1317–1325.
Graça, M.A., S.Y. Newell, and R.T. Kneib. 2000. Grazing rates of organic matter and living fungal biomass of decaying Spartina alterniflora by three species of saltmarsh invertebrates. Marine Biology 136: 281–289.
Hamilton, P.V. 1976. Predation on Littorina irrorata (mollusca: Gastropoda) by Callinectes sapidus (crustacea: Portunidae). Bulletin of Marine Science 26: 403–409.
Hamilton, P.V., and M.A. Winter. 1982. Behavioural responses to visual stimuli by the snail Littorina irrorata. Animal Behaviour 30: 752–760.
Hutchens, J.J., and K. Walters. 2006. Gastropod abundance and biomass relationships with salt marsh vegetation within ocean-dominated South Carolina, USA estuaries. Journal of Shellfish Research 25: 947–953.
Kemp, P.F., S.Y. Newell, and C.S. Hopkinson CS,. 1990. Importance of grazing on the salt-marsh grass Spartina alterniflora to nitrogen turnover in a macrofaunal consumer, Littorina irrorata, and to decomposition of standing-dead Spartina. Marine Biology 104: 311–319.
Kiehn, W.M., and J.T. Morris. 2009. Relationships between Spartina alterniflora and Littoraria irrorata in a South Carolina salt marsh. Wetlands 29 (3): 818–825.
Lewis, D.B., and L.A. Eby. 2002. Spatially heterogeneous refugia and predation risk in intertidal salt marshes. Oikos 96 (1): 119–129.
Nelson, D. 2015. Estuarine salinity zones in Gulf of Mexico Atlas. Stennis Space Center (MS): National Centers for Environmental Information: https://gulfatlas.noaa.gov/.
Orlando, S.P. Jr., L.P. Rozas, G.H. Ward, and C.J. Klein. 1993. Salinity characteristics of Gulf of Mexico estuaries. NOAA/NOS Office of Ocean Resources Conservation and Assessment, Silver Spring, MD. 209 pp.
Rietl, A.J., M.G. Sorrentino, and B.J. Roberts. 2018. Spatial distribution and morphological responses to predation in the salt marsh periwinkle. Ecosphere 9: e02316.
Schalles, J.F., C.M. Hladik, A.A. Lynes, and S.C. Pennings. 2013. Landscape estimates of habitat types, plant biomass, and invertebrate densities in a Georgia salt marsh. Oceanography 26: 88–97.
Silliman, B.R., and J.C. Zieman. 2001. Top-down control of Spartina alterniflora growth by periwinkle grazing in a Virginia salt marsh. Ecology 82: 2830–2845.
Silliman, B.R., and M.D. Bertness. 2002. A trophic cascade regulates salt marsh primary production. Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America 99: 10500–10505.
Silliman, B.R., J. Van De Koppel, M.D. Bertness, L.E. Stanton, and I.A. Mendelssohn. 2005. Drought, snails, and large-scale die-off of southern US salt marshes. Science 310 (5755): 1803–1806.
Stout, J.P. 1984. The ecology of irregularly flooded salt marshes of the northeastern Gulf of Mexico: a community profile. National Coastal Ecosystems Team, Division of Biological Services, Research and Development, Fish and Wildlife Service, US Department of the Interior.
Sullivan, M.J., and C.A. Moncreiff. 1990. Edaphic algae are an important component of salt marsh food-webs: Evidence from multiple stable isotope analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 62: 149–159.
Vermeij, G.J. 1972. Intraspecific shore-level size gradients in intertidal mollusks. Ecology 53 (4): 693–700.
Warren, J.H. 1985. Climbing as an avoidance behavior in the salt marsh periwinkle, Littorina irrorata (Say). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 89: 11–28.
West, D.L., and A.H. Williams. 1986. Predation by Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun) within Spartina alterniflora (Loisel) marshes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 100 (1–3): 75–95.
Zengel, S., C.L. Montague, S.C. Pennings, S.P. Powers, M. Steinhoff, G. Fricano, C. Schlemme, M. Zhang, J. Oehrig, Z. Nixon, and S. Rouhani. 2016. Impacts of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on salt marsh periwinkles (Littoraria irrorata). Environmental Science & Technology 50 (2): 643–652.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Alan Wilson for administering the supporting undergraduate research program and providing project support. The Weeks Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve provided dormitory access during fieldwork.
Funding
Funding for author Garcia and partial project support was provided by the National Science Foundation- Research Experiences for Undergraduates (NSF-REU) for Warm-Water Ecology at Auburn University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Charles T. Roman
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, C.J., Garcia, C. & Cash, J.S. Distribution and Morphology of Littoraria irrorata in Mesohaline Tidal Marshes Dominated by Juncus roemerianus. Estuaries and Coasts 45, 2650–2659 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-022-01093-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-022-01093-7