Abstract
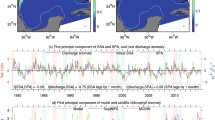
This study investigated the different responses of phytoplankton to El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) events in two major upwelling systems (Yuedong (YD) and Vietnam coastal (VC)) in the South China Sea (SCS). Results showed that in the YD system, chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) concentration was basically unaffected by the ENSO. Pearl River runoff and coastal current velocity (Cv) were the main controlling factors for Chl-a variations, and offshore Ekman transport (ETu) also played an important role. In the VC system, El Niño and La Niña reduced and enhanced the Chl-a, respectively. Specifically, the decreases in offshore current velocity (Cu), ETu, and Ekman pumping velocity (EPV) and Mekong River plume after El Niño events resulted in the weakening of the upwelling and reductions in the Chl-a. In contrast, enhanced Cu and Mekong River runoff increased Chl-a after La Niña events. However, due to the effects of the Madden–Julian Oscillation (MJO), the Chl-a may not always be negative after El Niño years in the VC system, as the MJO may reduce the weakening effect of the ENSO on upwelling strength. Overall, our results showed markedly different phytoplankton responses to ENSO events in different upwelling systems within the same marginal sea.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alheit, J., and A. Bakun. 2010. Population synchronies within and between ocean basins: Apparent teleconnections and implications as to physical–biological linkage mechanisms. Journal of Marine Systems 79 (3–4): 267–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.11.029
Atlas, R., J. Ardizzone, and R.N. Hoffman. 2008. Application of satellite surface wind data to ocean wind analysis. Proceedings of SPIE - the International Society for Optical Engineering 85 (1): 92–103. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.795371
Bai, Y., T.H. Huang, X.Q. He, S.L. Wang, Y.-C. Hsin, C.R. Wu, W.D. Zhai, H.K. Lui, and C.T.A. Chen. 2015. Intrusion of the Pearl River plume into the main channel of the Taiwan Strait in summer. Journal of Sea Research 95: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2014.10.003
Bakun, A. 1990. Global climate change and intensification of coastal ocean upwelling. Science 247 (4939): 198–201. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.247.4939.198
Bakun, A., B.A. Black, S.J. Bograd, M. Garcia-Reyes, A.J. Miller, R.R. Rykaczewski, and W.J. Sydeman. 2015. Anticipated effects of climate change on coastal upwelling ecosystems. Current Climate Change Reports 1 (2): 85–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40641-015-0008-4
Boyce, D.G., M.R. Lewis, and B. Worm. 2010. Global phytoplankton decline over the past century. Nature 466 (7306): 591–596. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09268
Chen, C.T.A., S. Jan, T.H. Huang, and Y.H. Tseng. 2010. Spring of no Kuroshio intrusion in the southern Taiwan Strait. Journal of Geophysical Research 115 (C8): C08011. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jc005804
Chen, X.Y., D.L. Pan, Y. Bai, X.Q. He, C.T.A. Chen, and Z.Z. Hao. 2013. Episodic phytoplankton bloom events in the Bay of Bengal triggered by multiple forcings. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 73: 17–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2012.11.011
Chen, Z.Y., W.P. Gong, H.Y. Cai, Y.Z. Chen, and H. Zhang. 2017. Dispersal of the Pearl River plume over continental shelf in summer. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 194: 252–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.06.025
Chu, P.C., Q.Y. Liu, Y.L. Jia, and C.W. Fan. 2002. Evidence of a barrier layer in the Sulu and Celebes Seas. Journal of Physical Oceanography 32 (11): 3299–3309. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(2002)032%3c3299:eoabli%3e2.0.co;2
Chu, X.Q., C.M. Dong, and Y.Q. Qi. 2017. The influence of ENSO on an oceanic eddy pair in the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 122 (3): 1643–1652. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016jc012642
Cropper, T.E., E. Hanna, and G.R. Bigg. 2014. Spatial and temporal seasonal trends in coastal upwelling off Northwest Africa, 1981–2012. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 86: 94–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsr.2014.01.007
Dang, X.Y., X.Y. Chen, Y. Bai, X.Q. He, C.-T.A. Chen, T. Li, D.L. Pan, and Z.K. Zhang. 2020. Impact of ENSO events on phytoplankton over the Sulu Ridge. Marine Environmental Research 157: 104934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2020.104934
Davenport, J., K.H. Mann, and J.R.N. Lazier. 1992. Dynamics of marine ecosystems: Biological–physical interactions in the oceans. Journal of Ecology 80 (3): 580. https://doi.org/10.2307/2260704
Dong, L.X., J.L. Su, L.A. Wong, Z.Y. Cao, and J.C. Chen. 2004. Seasonal variation and dynamics of the Pearl River plume. Continental Shelf Research 24 (16): 1761–1777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.006
Finney, B.P., J. Alheit, K.C. Emeis, D.B. Field, D. Gutiérrez, and U. Struck. 2010. Paleoecological studies on variability in marine fish populations: A long-term perspective on the impacts of climatic change on marine ecosystems. Journal of Marine Systems 79 (3–4): 316–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2008.12.010
Gan, J.P., A. Cheung, X.G. Guo, and L. Li. 2009. Intensified upwelling over a widened shelf in the northeastern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans 114: C09019. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JC004660
Grosse, J., D. Bombar, H.N. Doan, L.N. Nguyen, and M. Voss. 2010. The Mekong River plume fuels nitrogen fixation and determines phytoplankton species distribution in the South China Sea during low- and high-discharge season. Limnology and Oceanography 55 (4): 1668–1680. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.4.1668
Halpern, D. 2002. Offshore Ekman transport and Ekman pumping off Peru during the 1997–1998 El Niño. Geophysical Research Letters 29 (5): 19–1–19–4, https://doi.org/10.1029/2001gl014097
He, X.Q., Y. Bai, C.T.A. Chen, Y.C. Hsin, C.R. Wu, W.D. Zhai, Z.L. Liu, and F. Gong. 2014. Satellite views of the episodic terrestrial material transport to the southern Okinawa Trough driven by typhoon. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 119 (7): 4490–4504. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014jc009872
He, X.Q., D.F. Xu, Y. Bai, D.L. Pan, C.T.A. Chen, X.Y. Chen, and F. Gong. 2016a. Eddy-entrained Pearl River plume into the oligotrophic basin of the South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research 124: 117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2016.06.003
He, X.Q., D.L. Pan, Y. Bai, T.Y. Wang, C.T.A. Chen, Q.K. Zhu, Z.Z. Hao, and F. Gong. 2016b. Recent changes of global ocean transparency observed by SeaWiFS. Continental Shelf Research 143: 159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2016.09.011
Hein, H., B. Hein, T. Pohlmann, and B.H. Long. 2013. Inter-annual variability of upwelling off the South-Vietnamese coast and its relation to nutrient dynamics. Global and Planetary Change 110: 170–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.09.009
Hong, H.S., C.Y. Zhang, S.L. Shang, B.Q. Huang, Y.H. Li, X.D. Li, and S.M. Zhang. 2009. Interannual variability of summer coastal upwelling in the Taiwan Strait. Continental Shelf Research 29 (2): 479–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2008.11.007
Hong, H.S., C.T.A. Chen, Y.W. Jiang, J.Y. Lou, Z.Z. Chen, and J. Zhu. 2011. Source water of two-pronged northward flow in the southern Taiwan Strait in summer. Journal of Oceanography 67: 385–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-011-0036-1
Hu, J.Y., and X.H. Wang. 2016. Progress on upwelling studies in the China seas. Reviews of Geophysics 54 (3): 653–673. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015rg000505
Huang, T.H., C.T.A. Chen, W.Z. Zhang, and X.F. Zhuang. 2015. Varying intensity of Kuroshio intrusion into Southeast Taiwan Strait during ENSO events. Continental Shelf Research 103: 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2015.04.021
Huang, T.H., Z.X. Lun, C.R. Wu, and C.T.A. Chen. 2018. Interannual carbon and nutrient fluxes in southeastern Taiwan Strait. Sustainability 10 (2): 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10020372
Isoguchi, O., and Kawamura, H. 2006. MJO-related summer cooling and phytoplankton blooms in the South China Sea in recent years. Geophysical Research Letters 33 (16). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006gl027046
Jing, Z.Y., Y.Q. Qi, Z.L. Hua, and H. Zhang. 2009. Numerical study on the summer upwelling system in the northern continental shelf of the South China Sea. Continental Shelf Research 29 (2): 467–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2008.11.008
Jing, Z.Y., Qi, Y.Q., and Du, Y. 2011. Upwelling in the continental shelf of northern South China Sea associated with 1997–1998 El Niño. Journal of Geophysical Research 116 (C2). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jc006598
Kuo, N.J., Q.N. Zheng, and C.R. Ho. 2004. Response of Vietnam coastal upwelling to the 1997–1998 ENSO event observed by multisensor data. Remote Sensing of Environment 89 (1): 106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.10.009
Kuo, N.J., Q.N. Zheng, and C.R. Ho. 2000. Satellite observation of upwelling along the western coast of the South China Sea. Remote Sensing of Environment 74 (3): 463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(00)00138-3
Lindstrom, E., R. Lukas, R. Fine, E. Firing, S. Godfrey, G. Meyers, and M. Tsuchiya. 1987. The western equatorial Pacific Ocean circulation study. Nature 330 (6148): 533–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/330533a0
Liu, L., J. Li, W. Tan, Y. Wu, Y.L. Liu, and H.W. Wang. 2018. Extreme Sea Level Rise off the Northwest Coast of the South China Sea in 2012. Journal of Ocean University of China 17 (5): 991–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-018-3681-9
Liu, X., J. Wang, X.H. Cheng, and Y. Du. 2012. Abnormal upwelling and chlorophyll-a concentration off South Vietnam in summer 2007. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 117: C07021. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012jc008052
Loick-Wilde, N., D. Bombar, H.N. Doan, L.N. Nguyen, A.M. Nguyen-Thi, M. Voss, and J.W. Dippner. 2017. Microplankton biomass and diversity in the Vietnamese upwelling area during SW monsoon under normal conditions and after an ENSO event. Progress in Oceanography 153: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2017.04.007
McCreary, B.D., J.P. Rossiter, and D.M. Robertson. 1996. Recessive (true) microcephaly: A case report with neuropathological observations. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research 40 (1): 66–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2788.1996.tb00604.x
McPhaden, M.J., S.E. Zebiak, and M.H. Glantz. 2006. ENSO as an integrating concept in Earth science. Science 314 (5806): 1740–1745. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1132588
Nair, R.R., V. Ittekkot, S.J. Manganini, V. Ramaswamy, B. Haake, E.T. Degens, B.N. Desai, and S. Honjo. 1989. Increased particle-flux to the deep ocean related to monsoons. Nature 338 (6218): 749–751. https://doi.org/10.1038/338749a0
Pan, A.J., X.F. Wan, J.D. Xu, X.G. Guo, and L. Li. 2006. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the barrier layer in the northeast of South China Sea. Chinese Science Bulletin 51 (8): 951–957. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.08.013
Philander, S.G., and A. Fedorov. 2003. Is El Niño sporadic or cyclic? Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 31 (1): 579–594. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.31.100901.141255
Rasanen, T.A., and M. Kummu. 2013. Spatiotemporal influences of ENSO on precipitation and flood pulse in the Mekong River Basin. Journal of Hydrology 476: 154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.10.028
Rayner, N.A., D.E. Parker, E.B. Horton, C.K. Folland, L.V. Alexander, D.P. Rowell, E.C. Kent, and A. Kaplan. 2003. Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. Journal of Geophysical Research 108 (D14): 4407. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jd002670
Richardson, A.J. 2008. In hot water: Zooplankton and climate change. ICES Journal of Marine Science 65 (3): 279–295. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsn028
Richardson, A.J., and D.S. Schoeman. 2004. Climate impact on plankton ecosystems in the Northeast Atlantic. Science 305 (5690): 1609–1612. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1100958
Sala, E., and N. Knowlton. 2006. Global marine biodiversity trends. Annual Review of Environment and Resources 31 (1): 93–122. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.energy.31.020105.100235
Shaw, P.T., and S.Y. Chao. 1994. Surface circulation in the South China Sea. Deep Sea Research Part I 41 (11–12): 1663–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/0967-0637(94)90067-1
Shen, Y.F., Z.Y. Jing, K.Y. Tan, and L.L. Xie. 2019. Comparison of the responses of the Qingdong upwelling and the Vietnam coastal upwelling to super El Niño events. Advances in Marine Science 37 (3): 374–386. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-6647.2019.03.002
Sun, D.Y., Y. Huan, S.Q. Wang, Z.F. Qiu, Z.B. Ling, Z.H. Mao, and Y.J. He. 2019. Remote sensing of spatial and temporal patterns of phytoplankton assemblages in the Bohai Sea. Yellow Sea, and East China Sea, Water Research 157: 119–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.081
Sydeman, W.J., M. Garcia-Reyes, D.S. Schoeman, R.R. Rykaczewski, S.A. Thompson, B.A. Black, and S.J. Bograd. 2014. Climate change and wind intensification in coastal upwelling ecosystems. Science 345 (6192): 77–80. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251635
Vialard, J., and P. Delecluse. 1998a. An OGCM study for the TOGA decade Part I: Role of Salinity in the Physics of the Western Pacific Fresh Pool. Journal of Physical Oceanography 28 (6): 1071–1088. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1998)028%3c1071:aosftt%3e2.0.co;2
Vialard, J., and P. Delecluse. 1998b. An OGCM Study for the TOGA Decade Part II: Barrier-Layer Formation and Variability. Journal of Physical Oceanography 28 (6): 1089–1106. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1998)028%3c1089:aosftt%3e2.0.co;2
Wang, D.K., H. Wang, M. Li, G.M. Liu, and X.Y. Wu. 2013. Role of Ekman transport versus Ekman pumping in driving summer upwelling in the South China Sea. Journal of Ocean University of China 12 (3): 355–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11802-013-1904-7
Wang, D.W., T.C. Gouhier, B.A. Menge, and A.R. Ganguly. 2015. Intensification and spatial homogenization of coastal upwelling under climate change. Nature 518 (7539): 390–394. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14235
Wang, D.X., Y.Q. Shu, H.J. Xue, J.Y. Hu, J. Chen, W. Zhuang, T.T. Zu, and J.D. Xu. 2014. Relative contributions of local wind and topography to the coastal upwelling intensity in the northern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 119 (4): 2550–2567. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013jc009172
Wang, D.X., Z. Wei, S.P. Xie, J.Y. Hu, Y.Q. Shu, and R.S. Wu. 2012. Coastal upwelling in summer 2000 in the northeastern South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 117: C04009. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011jc007465
Wang, Y.Q., D.Y. Liu, and D.L. Tang. 2016. Application of a generalized additive model (GAM) for estimating chlorophyll-a concentration from MODIS data in the Bohai and Yellow Seas China. International Journal of Remote Sensing 38 (3): 639–661. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1268733
Wang, Z.H., Chen, X.Y., Bai, Y., He, X.Q., and Zhang, X.P. 2018. Abnormal upwelling off the southeast of Vietnam in summer 2016, Proc. SPIE 10784, Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions 2018 107840Q (10 October 2018).https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2324042
Wheeler, M.C., and H.H. Hendon. 2004. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: Development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Monthly Weather Review 132 (8): 1917–1932. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0493(2004)132%3c1917:aarmmi%3e2.0.co;2
Xie, S.P., Xie, Q., Wang, D.X., and Liu, W.T. 2003. Summer upwelling in the South China Sea and its role in regional climate variations. Journal of Geophysical Research 108 (C8): 3261. 17–1–17–13. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003jc001867
Yankovsky, A.E., and R.W. Garvine. 1998. Subinertial dynamics on the Inner New Jersey Shelf during the upwelling season. Journal of Physical Oceanography 28 (12): 2444–2458. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0485(1998)0282.0.CO;2
Zhao, H., and D.L. Tang. 2007. Effect of 1998 El Niño on the distribution of phytoplankton in the South China Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 112: C02017. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JC003536
Zhao, H., J. Zhao, X.L. Sun, F.J. Chen, and G.Q. Han. 2018. A strong summer phytoplankton bloom southeast of Vietnam in 2007, a transitional year from El Niño to La Niña. PLoS One 13 (1): e0189926. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189926
Zu, Y.C., S.G. Sun, W. Zhao, P.L. Li, B.C. Liu, Y. Fang, and A.A. Samah. 2019. Seasonal characteristics and formation mechanism of the thermohaline structure of mesoscale eddy in the South China Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 38 (4): 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1222-4
Acknowledgements
We thank NASA for providing the SeaWiFS and Aqua/MODIS monthly composite chlorophyll data; the Copernicus for providing the monthly water temperature, salinity, and current data; the RSS for providing CCMP data; and the Ministry of Water Resources of the Peoples Republic of China for offering the Pearl River discharge data. We thank SOED/SIO/MNR satellite ground station, satellite data processing & sharing center, and marine satellite data online analysis platform (SatCO2) for their help with data collection and processing. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments to improve the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant #2017YFA0603004), the Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou) (GML2019ZD0602), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants #41825014 and #41706207), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2017R52001), and the Zhejiang Talent Program (LR18D060001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Hongbin Liu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, X., Bai, Y., Gong, F. et al. Different Responses of Phytoplankton to the ENSO in Two Upwelling Systems of the South China Sea. Estuaries and Coasts 45, 485–500 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-021-00987-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-021-00987-2