Abstract
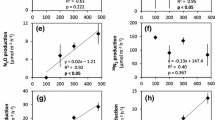
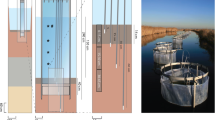
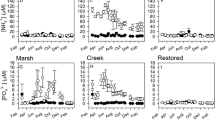
Since the 1970s, a shift from inorganic to organic nitrogen-based fertilizer has occurred worldwide, and now urea constitutes greater than 50 % of the global nitrogenous fertilizer usage. As a result, concentrations of urea will likely increase in waterways, facilitating transport to coastal wetland habitats where microbial-mediated transformations have the ability to alleviate excess nitrogen (N) pollution. To assess this biological potential for N removal in a brackish marsh ecosystem, we conducted a 5-day laboratory experiment where we monitored denitrification rate potentials (DNP) in microcosms with intact, vegetated sods, testing treatments of different urea solutions (37.5 and 166.5 mM urea) and a nitrate solution (98.9 mM KNO3). The addition of urea, regardless of concentration, did not stimulate DNP, while nitrate additions did. Ammonium (NH4 +) accumulated in the porewater in response to urea treatments, with approximately 80–90 % of urea being hydrolyzed during the experiment. Nitrate concentrations in the nitrate treatment were near zero by the end of the experiment, while measureable amounts of urea were still present in both urea treatments. An increase in DNP followed nitrate additions, but an accumulation of NH4 + after urea additions suggests that urea pollution may not be removed by coastal wetlands as efficiently as nitrate pollution, especially when nitrification is limited under anaerobic conditions. Further work exploring the most likely pathways for removal of excess NH4 + is necessary to describe the potential impact that increased urea concentrations could have on coastal ecosystems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrahami, S., W. Liesack, and R. Conrad. 2003. Effects of temperature and fertilizer on activity and community structure of soil ammonia oxidizers. Environmental Microbiology 5: 691–705.
Beman, J. Michael, Kevin R. Arrigo, and Pamela A. Matson. 2005. Agricultural runoff fuels large phytoplankton blooms in vulnerable areas of the ocean. Nature 7030: 211–214.
Berg, G.M., M. Balode, I. Purina, S. Bekere, C. Béchemin, and S. Maestrini. 2003. Plankton community composition in relation to availability and uptake of oxidized and reduced nitrogen. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 30: 263–274.
Berman, T. 1974. Urea in the waters of Lake Kinneret (Sea of Galilee. Limnology and Oceanography 19: 977–980.
Berman, T., and S. Chava. 1999. Algal growth on organic compounds as nitrogen sources. J Plankton Res 21: 977–980.
Berrada, H., G. Font, and J.C. Moltó. 2003. Determination of urea pesticide residues in vegetable, soil, and water samples. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry 33: 19–41.
Bo, S.Y., J.H. Shi, H.W. Gao, J.H. Qi, J.J. Qiao, and J. Zhang. 2009. Urea in aerosol and rainwater over the East China Sea in winter and spring. Huan jing ke xue Huanjing kexue/[bian ji, Zhongguo ke xue yuan huan jing ke xue wei yuan hui" Huan jing ke xue" bian ji wei yuan hui 30: 14–22.
Bogard, Matthew J., Derek B. Donald, Kerri Finlay, and Peter R. Leavitt. 2012. Distribution and regulation of urea in lakes of central North America. Freshwater Biology 6: 1277–1292.
Bollmann, Annette, and Hendrikus J. Laanbroek. 2001. Continuous culture enrichments of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria at low ammonium concentrations. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 3: 211–221.
Cornell, S.E., T.D. Jickells, and C.A. Thornton. 1998. Urea in rainwater and atmospheric aerosol. Atmospheric Environment 32: 1903–1910.
Cozzi, S., A. Mistaro, S. Sparnocchia, L. Colugnati, O. Bajt, and L. Toniatti. 2014. Anthropogenic loads and biogeochemical role of urea in the Gulf of Trieste. Sci Total Environ 493: 271–281.
Dalsgaard, T., B. Thamdrup, and D.E. Canfield. 2005. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in the marine environment. Research in Microbiology 156: 457–464.
De-Xi, L.I.N., F.A.N. Xiao-Hui, H.U. Feng, Z.H.A.O. Hong-Tao, and L.U.O. Jia-Fa. 2007. Ammonia volatilization and nitrogen utilization efficiency in response to urea application in rice fields of the Taihu Lake region, China. Pedosphere 17: 639–645.
Di, H.J., and K.C. Cameron. 2008. Sources of nitrous oxide from 15N-labelled animal urine and urea fertilizer with and without a nitrification inhibitor, dicyandiamide (DCD. Soil Research 1: 76–82.
Dollhopf, Sherry L., Jung-Ho Hyun, April C. Smith, Harold J. Adams, Sean O’Brien, and Joel E. Kostka. 2005. Quantification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and factors controlling nitrification in salt marsh sediments. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1: 240–246.
Dunbabin, J.S., and K.H. Bowmer. 1992. Potential use of constructed wetlands for treatment of industrial wastewaters containing metals. Science of the Total Environment 111: 151–168.
Faulkner, S. P., and Richardson, C. J. 1989. Physical and chemical characteristics of freshwater wetland soils. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment 41–72.
Flores, E., and A. Herreo. 2005. Nitrogen assimilation and nitrogen control in cyanobacteria. Biochemical Society Transactions 33: 164–167.
Galloway, James N., William H. Schlesinger, Hiram Levy, Anthony Michaels, and Jerald L. Schnoor. 1995. Nitrogen fixation: anthropogenic enhancement-environmental response. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 2: 235–252.
Galloway, James N., John D. Aber, Jan Willem Erisman, Sybil P. Seitzinger, Robert W. Howarth, Ellis B. Cowling, and B. Jack Cosby. 2003. The nitrogen cascade. Bioscience 4: 341–356.
Ginn, H.P., L.A. Pearson, and B.A. Neilan. 2009. Hepatotoxin biosynthesis and regulation in cyanobacteria—the putative involvement of nitrogen and iron homeostasis mechanisms. Mass spectrometry 1: 69.
Glibert, P.M., et al. 2001. Harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland, USA: comparison of 1997, 1998, and 1999 events. Estuaries 24: 875–883.
Glibert, P.M., Cynthia A. Heil, David J. Hollander, M. Revilla, A. Hoare, J. Alexander, and S. Murasko. 2004. Evidence for dissolved organic nitrogen and phosphorus uptake during a cyanobacterial bloom in Florida Bay. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 280: 73.
Glibert, Patricia M., T. Mark Trice, Bruce Michael, and Lois Lane. 2005. Urea in the tributaries of the Chesapeake and coastal bays of Maryland. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 1-4: 229–243.
Glibert, Patricia M., John Harrison, Cynthia Heil, and Sybil Seitzinger. 2006. Escalating worldwide use of urea—a global change contributing to coastal eutrophication. Biogeochemistry 3: 441–463.
Glibert, P.M., R. Maranger, D.J. Sobota, and L. Bouwman. 2014. The Haber Bosch–harmful algal bloom (HB–HAB) link. Environmental Research Letters 9: 105001.
Goeyens, Leo, N. Kindermans, M. Abu Yusuf, and M. Elskens. 1998. A room temperature procedure for the manual determination of urea in seawater. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 4: 415–418.
Gribsholt, Britta, Eric Struyf, Anton Tramper, Maria G.I. Andersson, Natacha Brion, Loreto De Brabandere, Stefan Van Damme, et al. 2006. Ammonium transformation in a nitrogen-rich tidal freshwater marsh. Biogeochemistry 3: 289–298.
Hamersley, M. R., and Howes, B. L. 2005. Coupled nitrification–denitrification measured in situ in a Spartina alterniflora marsh with a 15NH4+ tracer.
Hansell, D.A. 1993. Results and observations from the measurement of DOC and DON in seawater using a high-temperature catalytic oxidation technique. Marine Chemistry 41: 195–202.
Hartman, Wyatt H., Curtis J. Richardson, Rytas Vilgalys, and Gregory L. Bruland. 2008. Environmental and anthropogenic controls over bacterial communities in wetland soils. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 46: 17842–17847.
Hefting, M., et al. 2004. Water table elevation controls on soil nitrogen cycling in riparian wetlands along a European climatic gradient. Biogeochemistry 67: 113–134.
Heil, C.A., M. Revilla, P.M. Glibert, and S. Murasko. 2007. Nutrient quality drives differential phytoplankton community composition on the southwest Florida shelf. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 1067–1078.
Heisler, John, Patricia M. Glibert, JoAnn M. Burkholder, Donald M. Anderson, William Cochlan, William C. Dennison, Quay Dortch, et al. 2008. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: a scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 1: 3–13.
Howarth, Robert, Donald Anderson, James Cloern, Chris Elfring, Charles Hopkinson, Brian Lapointe, Tom Malone, et al. 2000. Nutrient pollution of coastal rivers, bays, and seas. Issues in Ecology 7: 1–15.
Humbert, Sylvia, Jakob Zopfi, and Sonia-Estelle Tarnawski. 2012. Abundance of anammox bacteria in different wetland soils. Environmental Microbiology Reports 5: 484–490.
Jetten, M.S., M. Strous, K.T. Van de Pas-Schoonen, J. Schalk, U.G. van Dongen, A.A. van de Graaf, and J.G. Kuenen. 1998. The anaerobic oxidation of ammonium. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 22: 421–437.
Jørgensen, Niels O.G. 2006. Uptake of urea by estuarine bacteria. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 3: 227–242.
Kirwan, M.L., and J.P. Megonigal. 2013. Tidal wetland stability in the face of human impacts and sea-level rise. Nature 504: 53–60.
Koop-Jakobsen, Ketil, and Anne E. Giblin. 2009. Anammox in tidal marsh sediments: the role of salinity, nitrogen loading, and marsh vegetation. Estuaries and Coasts 2: 238–245.
Koper, Teresa E., John M. Stark, Mussie Y. Habteselassie, and Jeanette M. Norton. 2010. Nitrification exhibits Haldane kinetics in an agricultural soil treated with ammonium sulfate or dairy-waste compost. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2: 316–322.
Lam, P., et al. 2007. Linking crenarchaeal and bacterial nitrification to anammox in the Black Sea. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104: 7104–7109.
Liang, X.Q., Y.X. Chen, H. Li, G.M. Tian, W.Z. Ni, M.M. He, and Z.J. Zhang. 2007. Modeling transport and fate of nitrogen from urea applied to a near-trench paddy field. Environmental Pollution 150: 313–320.
Mendelssohn, I.A., and K.L. McKee. 1988. Spartina alterniflora die-back in Louisiana: time-course investigation of soil waterlogging effects. Journal of Ecology 76: 509–521.
Mendelssohn, I.A., K.L. McKee, and W.H. Patrick. 1981. Oxygen deficiency in Spartina alterniflora roots: metabolic adaptation to anoxia. Science 214: 439–441.
Mobley, H.L., and R.P. Hausinger. 1989. Microbial ureases: significance, regulation, and molecular characterization. Microbiological Reviews 1: 85–108.
Mobley, H.L., M.D. Island, and R.P. Hausinger. 1995. Molecular biology of microbial ureases. Microbiological reviews 59: 451–480.
Morrissey, Ember M., and Rima B. Franklin. 2014. Resource effects on denitrification are mediated by community composition in tidal freshwater wetlands soils. Environmental microbiology 1520–1532.
Mulvaney, R.L., Khan, S. A., and Mulvaney, C.S. 1997. Nitrogen fertilizers promote denitrification. Biology and Fertility of Soils 24(2), 211--220.
Nicholls, J.C., and M. Trimmer. 2009. Widespread occurrence of the anammox reaction in estuarine sediments. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 55: 105–113.
Nicol, G.W., S. Leininger, C. Schleper, and J.I. Prosser. 2008. The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environmental Microbiology 10: 2966–2978.
Norton, Jeanette M., and John M. Stark. 2011. Regulation and measurement of nitrification in terrestrial systems. Methods in Enzymology 486: 343–368.
Nugroho, R.A., W.F.M. Röling, A.M. Laverman, H.R. Zoomer, and H.A. Verhoef. 2005. Presence of Nitrosospira cluster 2 bacteria corresponds to N transformation rates in nine acid Scots pine forest soils. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 53: 473–481.
Palta, M.M., J.G. Ehrenfeld, and P.M. Groffman. 2014. Hotspots” and “hot moments” of denitrification in urban brownfield wetlands. Ecosystems 17: 1121–1137.
Parsons, Timothy, Yoshiaki Maita, and Carol Lalli. 1984. A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. New York: Pergamon Press Ltd..
Pedersen, Morten Foldager, and Jens Borum. 1993. An annual nitrogen budget for a seagrass Zostera marina population. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 101: 169–169.
Pinckney, James L., Hans W. Paerl, Patricia Tester, and Tammi L. Richardson. 2001. The role of nutrient loading and eutrophication in estuarine ecology. Environmental Health Perspectives 5: 699.
Rabalais, Nancy N., R. Eugene Turner, and William J. Wiseman Jr. 2002. Gulf of Mexico hypoxia, AKA "the dead zone". Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics: 235–263.
Reddy, K.R., W.H. Patrick, and C.W. Lindau. 1989. Nitrification-denitrification at the plant root-sediment interface in wetlands. Limnology and Oceanography 6: 1004–1013.
Remsen, Charles C. 1971. The distribution of urea in coastal and oceanic waters. Limnology and Oceanography 5: 732–740.
Revilla, Marta, Jeffrey Alexander, and Patricia M. Glibert. 2005. Urea analysis in coastal waters: comparison of enzymatic and direct methods. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 7: 290–299.
Revsbech, N.P., J.P. Jacobsen, and L.P. Nielsen. 2005. Nitrogen transformations in microenvironments of river beds and riparian zones. Ecological Engineering 24(5): 447–455.
Rivera-Monroy, V.H., et al. 2010. Denitrification in coastal Louisiana: a spatial assessment and research needs. Journal of Sea Research 63: 157–172.
Saby, B.R. 1969. Influence of moisture tension on nitrate accumulation in soils. Soil Science Society American Proceeding 33: 263–266.
Saggar, S., et al. 2013. Quantification of reductions in ammonia emissions from fertiliser urea and animal urine in grazed pastures with urease inhibitors for agriculture inventory: New Zealand as a case study. Science of the Total Environment 465: 136–146.
Sahrawat, K.L. 1982. Nitrification in some tropical soils. Plant and Soil 65: 281–286.
Schjønning, Per, Ingrid K. Thomsen, Per Moldrup, and Bent T. Christensen. 2003. Linking soil microbial activity to water-and air-phase contents and diffusivities. Soil Science Society of America Journal 1: 156–165.
Seitzinger, S., John A. Harrison, J.K. Böhlke, A.F. Bouwman, R. Lowrance, B. Peterson, C. Tobias, and G. Van Drecht. 2006. Denitrification across landscapes and waterscapes: a synthesis. Ecological Applications 6: 2064–2090.
Shi, Wei, and Jeanette M. Norton. 2000. Microbial control of nitrate concentrations in an agricultural soil treated with dairy waste compost or ammonium fertilizer. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 10: 1453–1457.
Silva, R.G., K.C. Cameron, H.J. Di, and E.E. Jorgensen. 2005. A lysimeter study to investigate the effect of dairy effluent and urea on cattle urine N losses, plant uptake and soil retention. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 4: 57–78.
Singh, Rachhpal, and P.H. Nye. 1984. The effect of soil pH and high urea concentrations on urease activity in soil. Journal of Soil Science 4: 519–527.
Solomon, Caroline M., Jackie L. Collier, Gry Mine Berg, and Patricia M. Glibert. 2010. Role of urea in microbial metabolism in aquatic systems: a biochemical and molecular review. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 1: 67–88.
Sørensen, Jan. 1978. Denitrification rates in a marine sediment as measured by the acetylene inhibition technique. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 1: 139–143.
Souza, P.A., A.G. Ponette-González, W.Z. de Mello, K.C. Weathers, and I.A. Santos. 2015. Atmospheric organic and inorganic nitrogen inputs to coastal urban and montane Atlantic forest sites in southeastern Brazil. Atmospheric Research 160: 126–137.
Stark, J., T. Oyen, P. Meire, and S. Temmerman. 2015. Observations of tidal and storm surge attenuation in a large tidal marsh. Limnology and Oceanography 60: 1371–1381.
Strous, M., J.G. Kuenen, and M.S. Jetten. 1999. Key physiology of anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65: 3248–3250.
Swensen, Berit, and Bal Ram Singh. 1997. Transport and transformation of urea and its derivatives through a mineral subsoil. Journal of Environmental Quality 6: 1516–1523.
Switzer, T. 2008. Urea loading from a spring storm—Knysna estuary, South Africa. Harmful Algae 8: 66–69.
Timperley, M.H., R.J. Vigor-Brown, M. Kawashima, and M. Ishigami. 1985. Organic nitrogen compounds in atmospheric precipitation: their chemistry and availability to phytoplankton. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 42: 1171–1177.
Tourna, Maria, Thomas E. Freitag, and James I. Prosser. 2010. Stable isotope probing analysis of interactions between ammonia oxidizers. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 8: 2468–2477.
Violaki, K., and N. Mihalopoulos. 2011. Urea: an important piece of water soluble organic nitrogen (WSON) over the Eastern Mediterranean. Sci Total Environ 409: 4796–4801.
Wall, L.G., J.L. Tank, T.V. Royer, and M.J. Bernot. 2005. Spatial and temporal variability in sediment denitrification within an agriculturally influenced reservoir. Biogeochemistry 76: 85–111.
Wessén, E., K. Nyberg, J.K. Jansson, and S. Hallin. 2010. Responses of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidizers to soil organic and fertilizer amendments under long-term management. Applied Soil Ecology 45: 193–200.
Zhao, Zheng, et al. 2014. Quantifying nitrogen loading from a paddy field in Shanghai, China with modified DNDC model. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 197: 212–221.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to Dr. Behzad Mortazavi for his support and allowing us to complete our DNP analysis in his laboratory, and Joshua Jones for his guidance at Big Branch Marsh NWR. For their help in the field and with additional microcosm and sample preparation, we thank Jamie Galloway, Adam Constantin, and Mindy Russo. Also, we thank the anonymous reviewers for their comments and edits during the review process of this manuscript. Funding for this work was provided by the University of Alabama Howard Hughes Medical Institute undergraduate research program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Charles Simenstad
Electronic supplementary material
Online Resource 1
Greenhouse air temperature and microcosms soil temperature during experimental duration (DOC 71 kb)
Online Resource 2
Change in porewater soluble reactive phosphorus measured in treatments. Points are mean values measured from replicate microcosms (n = 5). Error bars (where visible) are standard deviation (DOC 44 kb)
Online Resource 3
Change in porewater dissolved organic carbon in treatments. Points are mean values measured from replicate microcosms (n = 5). Error bars (where visible) are standard deviation (DOC 102 kb)
Online Resource 4
Change in porewater nitrite in treatments. Points are mean values measured from replicate microcosms (n = 5). Error bars (where visible) are standard deviation (DOC 39 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, P.O., Cherry, J.A. & Edmonds, J.W. Organic Nitrogen Runoff in Coastal Marshes: Effects on Ecosystem Denitrification. Estuaries and Coasts 40, 437–446 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0161-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0161-6