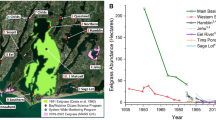
Abstract
Rapidly growing human populations have caused heavy modifications to the watersheds of many Mediterranean climate estuaries, subjecting them to excessive nutrient enrichment and harmful macroalgal blooms. Despite these impacts, comprehensive studies in these systems are rare and comparisons between systems are lacking. We surveyed five southern California estuaries that ranged in size from 93 to 1,000 ha and incorporated differing land usages and watershed sizes. We sampled environmental variables (sediment redox potential, organic content, total nitrogen and total phosphorus, water column nitrate, ammonium, and salinity) and macroalgal cover and biomass quarterly at three locations within each estuary over 15 months to compare spatial and wet vs. dry season patterns. Maximum mean water column nitrate concentration across all estuaries ranged from 47 to 1,700 μM, showing that all estuaries were highly enriched with nitrogen, at least at some times. Mean macroalgal biomass ranged from 0 to 1,500 g wet wt m−2. However, neither nutrient concentrations nor algal biomass showed consistent seasonal patterns as maximum values occurred in different seasons in different estuaries. Three-dimensional principal components analysis followed by regression analyses confirmed that macroalgal abundance was not directly related to water or sediment N concentrations. Rather each of these southern California estuaries showed individual patterns in all measured variables, which were most likely induced by a suite of physical modifications unique to each system and its watershed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrose, R.F., and A.R. Orme. 2000. Lower Malibu Creek and Lagoon resource enhancement and management: final report to the California State Coastal Conservancy. Los Angeles: University of California.
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environmental Federation. 1998. Flow injection analysis for orthophosphate. In: Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., Eaton, A.D. (Eds.), Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edition. American Public Health Association, Washington, pp. 4–149 to 144–150.
Armitage, A.R., and P. Fong. 2004. Upward cascading effects of nutrients: shifts in a benthic microalgal community and a negative herbivore response. Occologia 139: 560–567.
Armitage, A.R., T.A. Frankovich, and J.W. Fourqurean. 2006. Variable responses within epiphytic and benthic microalgal communities to nutrient enrichment. Hydrobiologia 569: 423–435.
Astill, H., and P. Lavery. 2001. The dynamics of unattached benthic macroalgal accumulations in the Swan-Canning Estuary. Hydrological Processes 15: 2387–2399.
Bintz, J.C., S.W. Nixon, B.A. Buckley, and S.L. Granger. 2003. Impacts of temperature and nutrients on coastal lagoon plant communities. Estuaries 26(3): 765–776.
Boyle, K.A., K. Kamer, and P. Fong. 2004. Spatial and temporal patterns in sediment and water column nutrients in a eutrophic southern California estuary. Estuaries 27(3): 378–388.
Bricker, S.B., B. Longstaff, W. Dennison, A. Jones, K. Boicourt, C. Wicks, and J. Woerner. 2008. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation's estuaries: a decade of change. Harmful Algae 8: 21–32.
Caffrey, J.M., N. Harrington, and B. Ward. 2002. Biogeochemical processes in a small California estuary. 1. Benthic fluxes and pore water constituents reflect high nutrient freshwater inputs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 233: 39–53.
Carlier, A., P. Riera, J.-M. Amouroux, J.-Y. Bodiou, M. Desmalades, and A. Grémare. 2008. Food web structure of two Mediterranean lagoons under varying degree of eutrophication. Journal of Sea Research 60: 264–275.
Carlson, R.M. 1978. Automated separation and conductimetric determination of ammonia and dissolved carbon dioxide. Analytical Chemistry 50: 1528–1531.
Castro, P., I. Valiela, and H. Freitas. 2007. Eutrophication in Portuguese estuaries evidenced by δ15N of macrophytes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 351: 43–51.
Chen, M.S., W. Stanislas, L.M. Lavkulich, W. Baeyens, L. Goeyens, and N. Brion. 2007. Organic matter and dissolved inorganic nitrogen distributions in estuarine muddy deposits. Aquatic Ecosystem Health and Management 10(1): 69–85. doi:10.1080/14634980701211896.
Clarke, K.R., and R.N. Gorley. 2001. PRIMER (Plymouth Routines In multivariate Ecological Research) v5: user manual/tutorial PRIMER-E Ltd, Plymouth.
Clarke, K.R., and R.H. Green. 1988. Statistical design and analysis for a ‘biological effects’ study. Marine Ecology Progress Series 46: 213–226.
Clarke, K.R., and R.M. Warwick. 1994. Similarity-based testing for community pattern: the two-way layout with no replication. Marine Biology 118: 167–176.
Cloern, J.E. 2001. Our evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210: 223–253.
CMWD (Calleguas Municipal Water District). 2006. Watershed coalition of Ventura County, integrated regional water management plan. 52–54.
Cohen, T., S.S. Que Hee, and R.F. Ambrose. 2001. Trace metals in fish and invertebrates of three California coastal wetlands. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42(3): 224–232.
Conley, D.J., H. Kaas, F. Mohlenberg, B. Rasmussen, and J. Windolf. 2000. Characteristics of Danish estuaries. Estuaries 23(6): 820–837.
Conley, D.J., J. Carstensen, G. Ærtebjerg, P.B. Christensen, T. Dalsgaard, J.L.S. Hansen, and A. Josefson. 2007. Long-term changes and impacts of hypoxia in Danish coastal waters. Ecological Applications 17: S165–S184. doi:10.1890/05-0766.1.
Domingues, R.B., T.P. Anselmo, A.B.. Barbosa, U. Sommer, and H.M. Galvão. 2011. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in the freshwater tidal zone of a turbid, Mediterranean estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 91(2): 282–297.
Dong, L.F., D.C.O. Thornton, D.B. Nedwell, and G.J.C. Underwood. 2000. Denitrification in sediments of the River Colne estuary, England. Marine Ecology Progress Series 203: 109–122.
Edwards, D.M., R.H. Reed, J.A. Chudek, R. Foster, and W.D.P. Stewart. 1987. Organic solute accumulation in osmotically-stressed Enteromorpha intestinalis. Marine Biology 95: 583–592.
Engelsen, A., S. Hulth, L. Pihl, and K. Sundback. 2008. Benthic trophic status and nutrient fluxes in shallow-water sediments. Estuaries and Coastal Shelf Sciences 78: 783–795.
Eyre, B.D., and A.J.P. Ferguson. 2002. Comparison of carbon production and decomposition, benthic nutrient fluxes and denitrification in seagrass, phytoplankton, benthic microalgae and macroalgae-dominated warm-temperate Australian lagoons. Marine Ecology Progress Series 229: 43–59.
Ferguson, A.J.P., B.D. Eyre, and J.M. Gay. 2004. Benthic nutrient fluxes in euphotic sediments along shallow sub-tropical estuaries, northern New South Wales, Australia. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 37: 219–235.
Flindt, M.R., L. Kamp-Nielsen, J.C. Marques, M.A. Pardal, M. Bocci, G. Bendoricchio, J. Salomonsen, S.N. Nielsen, and S.E. Jorgensen. 1997. Description of the three shallow estuaries: Mondego River (Portugal), Roskilde Fjord (Denmark), and the lagoon of Venice (Italy). Ecological Modeling 102: 17–31.
Fong, P. 1986. Monitoring and manipulation of phytoplankton dynamics in a Southern California estuary. Master's thesis, San Diego State University, San Diego, California.
Fong, P., and R.L. Kennison. 2010. Phase shifts, alternative stable states, and the status of southern California lagoons. In Coastal Lagoons: Critical Habitats of Environmental Change, ed. M.J. Kennish and J.W. Paerl, 227–251. Boca Raton: CRC.
Fong, P., R.M. Donohoe, and J.B. Zedler. 1993a. Competition with macroalgae and benthic cyanobacterial mats limits phytoplankton abundance in experimental microcosms. Marine Ecology Progress Series 100: 97–102.
Fong, P., J.B. Zedler, and R.M. Donohoe. 1993b. Nitrogen vs. phosphorus limitation of algal biomass in shallow coastal lagoons. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 906–923.
Fong, P., and J.B. Zedler. 1993. Temperature and light effects on the seasonal succession of algal communities in shallow coastal lagoons. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 171: 259–72.
Fong, P., and J.B. Zedler. 2000. Sources, sinks, and fluxes of nutrients (N+P) in a small highly modified urban estuary in southern California. Urban Ecosystems 4: 125–144.
Fong, P., J.J. Fong, and C.R. Fong. 2004. Growth, nutrient storage, and release of dissolved organic nitrogen by Enteromorpha intestinalis in response to pulses of nitrogen and phosphorus. Aquatic Botany 78: 83–95.
Fox, S.E., E. Stieve, I. Valiela, J. Hauxwell, and J. McClelland. 2008. Macrophyte abundance in Waquoit Bay: effects of land-derived nitrogen loads on seasonal and multi-year biomass patterns. Estuaries and Coasts 31: 532–541.
Fry, B., A. Gace, and J. McClelland. 2003. Chemical indicators of antropogenic nitrogen loading in four Pacific estuaries. Pacific Science 57: 77–101.
Fujita, R.M. 1985. The role of nitrogen status in regulating transient ammonium uptake and nitrogen storage by macroalgae. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 92: 283–301.
Giordano, J.C.P., M.J. Brush, and I.C. Anderson. 2011. Quantifying annual nitrogen loads to Virginia's coastal lagoons: sources and water quality response. Estuaries and Coasts 34: 297–309.
Grenz, C., J.E. Cloern, S.W. Hager, and B.E. Cole. 2000. Dynamics of nutrient cycling and related benthic nutrient and oxygen fluxes during a spring phytoplankton bloom in South San Francisco Bay (USA). Marine Ecology Progress Series 197: 67–80.
Hauxwell, J., J. McClelland, P. Behr, and I. Valiela. 1998. Relative importance of grazing and nutrient controls of macroalgal biomass in three temperate shallow estuaries. Estuaries 21: 347–360.
Hernandez, I., G. Peralta, J.L. Perez-Llorens, J.J. Vergara, and F.X. Niell. 1997. Biomass and dynamics of growth Ulva species in Palmones River estuary. Journal of Phycology 33: 764–772.
Hopkinson, C.S., A.E. Giblin, J. Tucker, and R.H. Garritt. 1999. Benthic metabolism and nutrient cycling along an estuarine salinity gradient. Estuaries 22: 863–881.
Howarth, R.W., and R. Marino. 2006. Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: evolving views over three decades. Limnology and Oceanography 51(1, part 2): 364–376.
Hunchak-Kariouk, K., and R.S. Nicholson. 2001. Watershed contributions of nutrients and other nonpoint source contaminants to the Barnegat Bay-Little Egg harbor estuary. Journal of Coastal Research 32: 28–81.
Kamer, K., and P. Fong. 2000. A fluctuating salinity regime mitigates the negative effect of reduced salinity on the estuarine macroalga, Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) link. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 254: 53–69.
Kamer, K., K.A. Boyle, and P. Fong. 2001. Macroalgal bloom dynamics in a highly eutrophic southern California estuary. Estuaries 24: 623–635.
Kamer, K., P. Fong, R.L. Kennison, and K. Schiff. 2004. The relative importance of sediment and water column supplies of nutrients to the growth and tissue content of the green macroalga Enteromorpha intestinalis across and estuarine resource gradient. Aquatic Ecology 38: 45–56.
Kemp, W.M., W.R. Boynton, J.E. Adolf, D.F. Boesch, W.C. Boicourt, G. Brush, J.C. Cornwell, T.R. Fisher, P.M. Gilbert, J.D. Hagy, L.W. Harding, E.D. Houde, D.G. Kimmel, W.D. Miller, R.I.E. Newell, M.R. Roman, E.M. Smith, and J.C. Stevenson. 2005. Eutrophication of Chesapeake Bay: historical trends and ecological interactions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 303: 1–29.
Kennish, M.J. 2002. Environmental threats and environmental future of estuaries. Environmental Conservation 29: 78–107. doi:10.1017/S0376892902000061.
Kennish, M.J., S.B. Bricker, W.C. Dennison, P.M. Gilbert, R.J. Livingston, K.A. Moore, R.T. Noble, H.W. Paerl, J.M. Ramstack, S. Seitzinger, D.A. Tomasko, and I. Valiela. 2007. Barnegat Bay-Little Egg Harbor Estuary: case study of a highly eutrophic coastal bay system. Ecological Applications 17(5): S3–S16.
Kennison, R.L. 2008. Evaluating ecosystem function of nutrient retention and recycling in excessively eutrophic estuaries. Ph.D. dissertation. University of California, Los Angeles, California
Kennison, R.L., K. Kamer, and P. Fong. 2011. Rapid nitrate uptake rates and large short term storage capacities may explain why opportunistic green macroalgae dominate shallow eutrophic estuaries. Journal of Phycology 47(3): 483–494.
Kinney, E.L., and I. Valiela. 2011. Nitrogen loading to Great South Bay: land use, sources, retention, and transport from land to bay. Journal of Canadian Research 27(4): 672–686.
Koch, M.S., E. Maltby, G.A. Oliver, and S.A. Bakkar. 1992. Factors controlling denitrification rates of tidal mudflats and fringing salt marshes in South-West England. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 34: 471–485.
Lartigue, J., and T.D. Sherman. 2005. Response of Enteromorpha sp. (Chlorophyceae) to a nitrate pulse: nitrate uptake, inorganic nitrogen storage and nitrate reductase activity. Marine Ecology Progress Series 292: 147–57.
Lavery, P.S., and A.J. McComb. 1991. Macroalgal–sediment nutrient interactions and their importance to macroalgal nutrition in a eutrophic estuary. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 32: 281–296.
Larry Walker Associates. 2008. Calleguas Creek Watershed Management Plan. Prepared for Los Angeles Regional Water Quality Control Board. California: Santa Monica.
Latimer, J.S., and S.A. Rego. 2010. Empirical relationship between eelgrass extent and predicted watershed-derived nitrogen loading for shallow New England estuaries. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 90: 213–240.
Lee, V., and S. Olsen. 1985. Eutrophication and management initiatives for the control of nutrient inputs to Rhode Island coastal lagoons. Estuaries 8(2B): 191–202.
Lillebø, A.I., J.M. Neto, I. Martins, T. Verdelhos, S. Leston, P.G. Cardoso, S.M. Ferreira, J.C. Marques, and M.A. Pardal. 2005. Management of a shallow temperate estuary to control eutrophication: the effect of hydrodynamics on the system's nutrient loading. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 65: 697–707.
Lotze, H.K., and W. Schramm. 2000. Ecophysiological traits explain species dominance patterns in macroalgal blooms. Journal of Phycology 36: 287–95.
Lyons, J., J. Ahern, J. McClelland, and I. Valiela. 1995. Macrophyte abundances in Waquoit Bay estuaries subject to different nutrient loads and the potential role of fringing salt marsh in groundwater nitrogen interception. The Biological Bulletin 189: 255–256.
McComb, A.J., R.P. Atkins, P.B. Birch, D.M. Gordon, and R.J. Lukatelich. 1981. Eutrophication in the Peel-Harvey estuarine system, western Australia. In Estuaries and nutrients, ed. B. Nielson and E. Cronin, 323–342. New Jersey: Humana.
Marcomini, A., A. Sfriso, B. Pavioni, and H.H. Orio. 1995. Eutrophication of the Lagoon of Venice: nutrient loads and exchanges. In Eutrophic Shallow Estuaries and Lagoons, ed. A.J. McComb, 59–80. Boca Raton: CRC.
Marques, J.C., S.N. Nielsen, M.A. Pardal, and S.E. Jørgensen. 2003. Impact of eutrophication and river management within a framework of ecosystem theories. Ecological Modeling 166: 147–168. doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(03)00134-0.
Martins, I., M.A. Pardal, A.I. Lillebo, M.R. Flindt, and J.C. Marques. 2001. Hydrodynamics as a major factor controlling the occurrence of green macroalgal blooms in a eutrophic estuary: a case study on the influence of precipitation and river management. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 52: 165–177.
McGlathery, K.J., D. Krause-Jensen, S. Rysgaard, and P.B. Christensen. 1997. Patterns of ammonium uptake within dense mats of the filamentous macroalga Chaetomorpha Linum. Aquatic Botany 59: 99–115.
Menendez, M., and F.A. Comin. 2000. Spring and summer proliferation of floating macroalgae in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (Tancada Lagoon, Ebro Delta, NE Spain). Estuaries, Coast and Shelf Sciences 51: 215–226.
Mitsch, W.J., and J.G. Gosselink. 1993. Wetlands. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Morand, P., and M. Merceron. 2005. Macroalgal population and sustainability. Journal of Coastal Research 21(5): 1009–1020.
Naldi, M., and P. Viaroli. 2002. Nitrate uptake and storage in the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh in relation to nitrate availability and thallus nitrate content in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Po River Delta, Italy). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 269: 65–83.
Nelson, T.A., A.V. Nelson, and M. Tjoelker. 2003. Seasonal and spatial patterns of “green tides” (ulvoid algal blooms) and related water quality parameters in the coastal waters of Washington State, USA. Botanica Marina 46: 263–275.
Nezlin, N.P., K. Kamer, J. Hyde, and E.D. Stein. 2009. Dissolved oxygen dynamics in a eutrophic estuary, Upper Newport Bay, California. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 82:139–151.
Nixon, S.W. 1995. Coastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes, and future concerns. Ophelia 41: 199–219.
Olsen, S.R., and L.E. Sommers. 1982. Phosphorus. In Methods of soil analysis: part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, ed. A.L. Page, 403–430. Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Page, H.M., R.L. Petty, and D.E. Meade. 1995. Influence of watershed runoff on nutrient dynamics in a southern California salt marsh. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 41(2): 163–180.
Paerl, H.W. 1997. Coastal eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: importance of atmospheric deposition and groundwater as “new” nitrogen and other nutrient sources. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 1154–1165.
Paerl, H.W., J. Dyble, L. Twomey, J.L. Pinckney, J. Nelson, and L. Kerkhof. 2002. Characterizing man-made and natural modifications of microbial diversity and activity in coastal ecosystems. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 81: 487–507. doi:10.1023/A:1020561422706.
Paerl, H.W. 2006. Assessing and managing nutrient-enhanced eutrophication in estuarine and coastal waters: interactive effects of human and climatic perturbations. Ecological Engineering 26: 40–54.
Patrício, J., H. Teixeira, J.M. Neto, and J.C. Marques. 2007. Opportunistic macroalgae metrics for transitional waters. Testing tools to assess ecological quality status in Portugal. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54: 1887–1896. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.08.003.
Peckol, P., and J.S. Rivers. 1995. Physiological responses of the opportunistic macroalgae Cladophora vagabunda (L.) van den Hoek and Gracelaria tikvahiae (McLachlan) to environmental disturbances associated with eutrophication. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 190: 1–16.
Pedersen, M.F. 1994. Transient ammonium uptake in the macroalga Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta): nature, regulation, and the consequences for choice of measuring technique. Journal of Phycology 30: 980–86.
Pednekar, A.M., S.B. Grant, Y. Jeong, Y. Poon, and C. Oancea. 2005. Influence of climate change, tidal mixing, and watershed urbanization on historical water quality in Newport Bay, a saltwater wetland and tidal embayment in southern California. Environmental Science and Technology 39: 9071–9082.
Pihl, L., G. Magnusson, I. Isaksson, and I. Wallentinus. 1996. Distribution and growth dynamics of ephemeral macroalgae in shallow bays on the Swedish west coast. Journal of Sea Research 35(1–3): 169–180.
Prokopy, W.R. 1995. Phosphorus in 0.5 M sodium bicarbonate soil extracts. QuikChem Method 12-115-01-1-B. Milwaukee: Lachat Instruments.
Raffaelli, D., S. Hull, and H. Milne. 1989. Long-term changes in nutrients, weed mats and shorebirds in an estuarine system. Cahiers de Biologie Marine 30: 259–270.
Robinson, T.H., A.L. Leydecker, A.A. Keller, and J.M. Melack. 2005. Steps towards modeling nutrient export in coastal Californian streams with a Mediterranean climate. Agricultural Water Management 77: 144–158. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2004.09.024.
Rose, K.L. 2006. Total maximum daily loads for organochlorine compounds. Santa Ana Regional Water Quality Control Board.
Rozen, T.F., M. Taillefert, R.E. Trouwborst, B.T. Glazer, S. Ma, J. Herszage, L.M. Valdes, K.S. Price, and G.W. Luther III. 2002. Iron–sulfur–phosphorus cycling in the sediments of a shallow coastal bay: implications for sediment nutrient release and benthic macroalgal blooms. Limnology and Oceanography 47(5): 1346–1354.
Rudnicki, R.M. 1986. Dynamics of macroalgae in Tijuana Estuary: response to simulated wastewater addition. Master's thesis. San Diego State University.
Schramm, W. 1999. Factors influencing seaweed responses to eutrophication: some results from EU-project EUMAC. Journal of Applied Phycology 11: 69–78.
Sfriso, A., A. Marcomini, and B. Pavoni. 1987. Relationships between macroalgal biomass and nutrient concentrations in a hypertrophic area of the Venice Lagoon Italy. Marine Environmental Research 22: 297–312.
Sfriso, A., B. Pavoni, A. Marcomini, and A.A. Orio. 1992. Macroalgae, nutrient cycles, and pollutants in the lagoon of Venice. Estuaries 15: 517–528.
Sfriso, A., C. Facca, and P.F. Ghetti. 2003. Temporal and spatial changes of macroalgae and phytoplankton in a Mediterranean coastal area: the Venice lagoon as a case study. Marine Environmental Research 56: 617–636.
Sfriso, A., C. Facca, S. Ceoldo, and A. Marcomini. 2005. Recording the occurrence of trophic level changes in the lagoon of Venice over the 90's. Environment International 31: 993–1001.
Sundbäck, K., A. Miles, S. Hulth, L. Pihl, P. Engström, E. Selander, and A. Svenson. 2003. Importance of benthic nutrient regeneration during initiation of macroalgal blooms in shallow bays. Marine Ecology Progress Series 246: 115–126.
Sundback, K., and K.J. McGlathery. 2005. Interaction between benthic macro- and microalgae in the marine environment. In Interactions between macro- and microorganisms in marine sediments, ed: E.J. Kristensen, E. Kostka, and R.H. Haese, 7–29. Washington: American Geophysical Union.
Svensson, J.M., G.M. Carrer, and M. Bocci. 2000. Nitrogen cycling in sediments of the Lagoon of Venice, Italy. Marine Ecology Progress Series 199: 1–11.
Taylor, D.I., S.W. Nixon, S.L. Granger, and B.A. Buckley. 1995. Nutrient limitation and the eutrophication of coastal lagoons. Marine Ecology Progress Series 127: 235–44.
Tett, P., R. Gowen, D. Mills, T. Fernandes, L. Gilpin, M. Huxham, K. Kennington, P. Read, M. Service, M. Wilkinson, and S. Malcolm. 2007. Defining and detecting undesirable disturbance in the context of eutrophication. Marine Pollution Bulletin 53: 282–297.
Thybo-Christensen, M., M.B. Rasmussen, and T.H. Blackburn. 1993. Nutrient fluxes and growth of Cladophora sericea in a shallow Danish bay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 100: 273–281.
Trimmer, M., D.B. Nedwell, D.B. Sivyer, and S.J. Malcolm. 2000. Seasonal organic mineralisation and denitrification in intertidal sediments and their relationship to the abundance of Enteromorpha sp. and Ulva sp. Marine Ecology Progress Series 203: 67–80.
Tyler, A.C., K.J. McGlathery, and I.C. Anderson. 2001. Macroalgae mediation of dissolved organic nitrogen fluxes in a temperate coastal lagoon. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 53: 155–168.
U.S. Army Corp of engineers. 1993. Reconnaissance Report Upper Newport Bay Orange County, California. Numerical modeling of hydrodynamics and transport, February 1993. Los Angeles District, California.
Valiela, I., K. Foreman, M. LaMontagne, D. Hersh, J. Costa, P. Peckol, B. DeMeo-Andreson, C. D'Avanzo, M. Babione, C.H. Sham, J. Brawley, and K. Lajtha. 1992. Couplings of watersheds and coastal waters sources and consequences of nutrient enrichment in Waquoit Bay Massachusetts. Estuaries 15: 443–457.
Valiela, I., G. Collins, J. Kremer, K. Lajtha, M. Geist, B. Seely, J. Brawley, and C.H. Sham. 1997. Nitrogen loading from coastal watersheds to receiving estuaries: new method and application. Ecological Applications 7(2): 358–380.
Valiela, I., M. Geist, J. McClelland, and G. Tomasky. 2000. Nitrogen loading from watersheds to estuaries: verification of the Waquoit Bay Nitrogen Loading Model. Biogeochemistry 49: 277–293.
Viaroli, P., C. Bondavalli, M. Naldi, and S. Bencivelli. 1996. Growth of the seaweed Ulva rigida C. Agardh in relation to biomass densities, internal nutrient pools and external nutrient supply in the Sacca di Goro lagoon (Northern Italy). Hydrobiologia 329: 93–103.
Viaroli, P., M. Bartoli, R. Azzoni, G. Giordani, C. Mucchino, M. Naldi, D. Nizzoli, and L. Taje. 2005. Nutrient and iron limitation to Ulva blooms in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy). Hydrobiologia 550: 57–71.
Villares, R., and A. Carballeira. 2003. Seasonal variation in the concentrations of nutrients in two green macroalgae and nutrient levels in sediments in the Rı́as Baixas (NW Spain). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Sciences 58: 887–900. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2003.07.004.
Young, A.J., J.C. Collins, and G. Russell. 1987. Ectypic variation in the osmotic responses of Enteromorpha intestinalis (L.) Link. Journal of Experimental Botany 38(193): 1309–1324.
Zedler, J.B. 1982. The ecology of southern California coastal salt marshes: a community profile (FWS/OBS-81/54). United States Fish and Wildlife. Washington: Service.
Zedler, J.B. 1996. Tidal wetland restoration: a scientific perspective and southern California focus. La Jolla, CA: California Sea Grant College System, University of California.
Zedler, J. B., C. S. Nordby, and B. E. Kus. 1992. The ecology of Tijuana Estuary: a National Estuarine Research Reserve. NOAA Office of Coastal Resource Management, Sanctuaries and Reserves Division, Washington, D.C., USA.
Zedler, J.B., J.C. Callaway, and G. Sullivan. 2001. Declining biodiversity: why species matter and how their functions might be restored in Californian tidal marshes. BioScience 51(12): 1005–1017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Wayne S. Gardner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennison, R.L., Fong, P. Extreme Eutrophication in Shallow Estuaries and Lagoons of California Is Driven by a Unique Combination of Local Watershed Modifications That Trump Variability Associated with Wet and Dry Seasons. Estuaries and Coasts 37 (Suppl 1), 164–179 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-013-9687-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-013-9687-z