Abstract
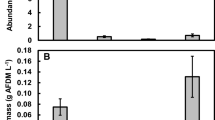
We examined the effect of whole-ecosystem nutrient enrichment on herbivory in saltmarsh creek-wall habitats in the Plum Island Estuary (Massachusetts, USA). Located between the macrophyte-dominated high marsh and adjoining mudflats, creek walls are steep vertical habitats vegetated with productive filamentous algae and associated epiphytes. Annual nitrate and phosphate loading rates were increased approximately ×10–15 in creeks mimicking short-term (2-month) and chronic (6-year) eutrophication. We assessed the diets of epifaunal invertebrates (three gastropods and one amphipod species) that potentially graze on benthic algae using natural isotope abundance data and per capita grazing rate measurements derived from 13C prelabeled algae. Substantial dietary contributions from benthic algae were observed in all consumers even though previous research has indicated most rely on Spartina detritus as the principal food resource. The amphipod Orchestia grillus and the snail Melampus bidentatus grazed benthic algae in excess of 500 μg algal C g C−1 h−1, whereas the snail Nassarius obsoletus and hydrobiid snails grazed at lower rates. Few dietary changes were detected with short-term enrichment. Algal grazing rates of N. obsoletus and M. bidentatus increased with chronic enrichment probably as a functional response to increased algal productivity. O. grillus grazed at a high rate and parasitic infection did not affect its consumption of benthic algae. The abundance and frequency of occurrence of O. grillus on creek-wall habitats increased with chronic nutrient enrichment suggesting amphipods contribute to top–down control on benthic algae and slow algal growth as nutrient enrichment occurs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1992) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th ed. American Waterworks Association and Water Pollution Control Federation, Washington.
Armitage, A.R., and J.W. Fourqurean. 2009. Stable isotope reveal complex changes in trophic relationships following nutrient addition in a coastal marine ecosystem. Estuar Coast 32: 1152–1164.
Bertness, M.D., P.J. Ewanchug, and B.R. Silliman. 2002. Anthropogenic modification of New England salt marsh landscapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 1395–1398.
Bousfield, E.L., and R.W. Heard. 1986. Systematics distributional ecology and some host–parasite relationships of Uhlorchestia uhleri (Shoemaker) and U spartinophila new species (Crustacea: Amphipoda) endemic to salt marshes of the Atlantic Coast of North America. J Crustacean Biol 6: 264–274.
Canfield, D.E., A.N. Glazer, and P.G. Falkowski. 2010. The evolution of Earth’s nitrogen cycle. Science 330: 192–196.
Carpenter, S.R. 1989. Replication and treatment strenght in whole-lake experiments. Ecology 70: 453–463.
Carpenter, S.R., S.W. Chrisholm, C.J. Krebs, D.W. Schlinder, and R.F. Wright. 1995. Ecosystem experiments. Science 269: 324–327.
Costanza, R., R. d’Arge, R. de Groot, S. Farber, M. Grasso, B. Hannon, K. Limburg, S. Naeem, R.V. O’Neil, J. Paruelo, R.G. Raskin, P. Sutton, and M. van den Belt. 1997. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387: 253–260.
Crompton, D.W.T. (1970) An ecological approach to acanthocephalan physiology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Curtis, L.A., and L.E. Hurd. 1979. On the broad nutritional requirements of the mudsnail, Ilyanassa (Nassarius) obsoleta (Say) and its polytrophic role in the food web. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 41: 289–297.
Darby, F.A., and R.E. Turner. 2008. Consequences of eutrophication to salt marsh roots, rhizomes, and soils. Marine Ecology Progress Series 363: 63–70.
Deegan, L.A., J.L. Bowen, D. Drake, J.W. Fleeger, C.T. Fiedrichs, K.A. Galván, J.E. Hobbie, C.S. Hopkinson, D.S. Johnson, J.M. Johnson, L.E. LeMay, E. Miller, B.J. Peterson, C. Picard, S. Sheldom, M. Sutherland, J. Vallino, and R.S. Warren. 2007. Susceptiblity of salt-marshes to nutrient enrichment and predator removal. Ecological Applications 17: S42–S63.
Deegan, L.A., D.S. Johnson, R.S. Warren, B. Peterson, J.W. Fleeger, S. Fagherazzi, and W.M. Wollheim. 2012. Coastal eutrophication as a driver of saltmarsh loss. Nature 490: 388–392.
DeNiro, M.J., and S. Epstein. 1981. Influence of the diet on the distribution of nitrogen isotopes in animals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 45: 341–351.
Diaz, R.J., and R. Rosenberg. 2008. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 321: 926–929.
Drake, D.C., B.J. Peterson, K.A. Galván, L.A. Deegan, C.S. Hopkinson, J.M. Johnson, K. Koop-Jakobsen, L.E. LeMay, and C. Picard. 2009. Salt marsh ecosystem biogeochemical responses to nutrient enrichment: a paired 15N tracer study. Ecology 90: 2535–2546.
Duffy, E.J., and M.E. Hay. 2000. Strong impacts of grazing amphipods on the organization of a benthic community. Ecological Monographs 70: 237–263.
E.P.A. (2002) In, Book 2002 EPA/620/R-02/003. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, National Health and Research Laboratory, Atlantic Ecology Divisioni, Narangasett.
Ferreira, J.G., J.H. Andersen, A. Borja, S.B. Bricker, J. Camp, M.C. de Silva, E. Garces, A.S. Heiskanen, C. Humborg, L. Ignatiades, C. Lancelot, A. Menesguen, P. Tett, N. Hoepffner, and U. Claussen. 2011. Overview of eutrophication indicators to assess environmental status within the European Marine Framework Strategy Framework Directive. Est Coast Shelf Sci 93: 117–131.
Fielding, N.J., C. MacNeil, J.T.A. Dick, R.W. Elwood, G.E. Riddell, and A.M. Dunn. 2003. Effects of the acanthocephlan parasite Echinorhynchus truttae on the feeding ecology of Gammarus pulex (Crustacea: Amphipoda). J Zool Lond 261: 321–325.
Fleeger, J.W., D.S. Johnson, K.A. Galván, and L.A. Deegan. 2008. Top–down and bottom–up control of infauna varies across the saltmarsh landscape. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 357: 20–34.
Fox, S.E., M. Teichberg, Y. Olsen, L. Heffner, and I. Valiela. 2009. Restructuring of benthic communities in eutrophic estuaries: lower abundance of preys leads to trophic shifts from omnivory to grazing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 380: 43–57.
Fry B (2006) Stable isotope ecology. Springer, New York.
Galloway, J.N., A.R. Townsend, J.W. Erisman, M. Bekunda, Z. Cai, J. Freney, L.A. Martinelli, S.P. Seitzinger, and M.A. Sutton. 2008. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions and potential solutions. Science 320: 889–892.
Galván, K. 2008. The diet of saltmarsh consumers. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University.
Galván, K., J.W. Fleeger, and B. Fry. 2008. Stable isotope addition reveals dietary importance of phytoplankton and microphytobenthos to saltmarsh infauna. Marine Ecology Progress Series 359: 37–49.
Galván, K.A., J.W. Fleeger, B. Peterson, D. Drake, L.A. Deegan, and D.S. Johnson. 2011. Natural abundance stable isotopes and dual isotope tracer additions help to resolve resources supporting saltmarsh food web. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 410: 1–11.
Giordani, G., J.M. Zaldivar, and P. Viaroli. 2009. Simple tools for assessing water quality and trophic status in transitional water ecosystems. Ecological Indicators 9: 982–991.
Gruber, N., and J.N. Galloway. 2008. An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451: 293–296.
Hillebrand, H., B. Worm, and H.K. Lotze. 2000. Marine microbenthic community structure regulated by nitrogen loading and grazing pressure. Marine Ecology Progress Series 204: 27–38.
Hillebrand, H., M. Kahlert, A.L. Haglund, U.G. Berninger, S. Nagel, and S. Wickham. 2002. Control of microbenthic communities by grazing and nutrient supply. Ecology 83: 2205–2219.
Hurd, L.E. 1985. On the importance of carrion to reproduction in an omnivorous estuarine neogasteropode, Ilyanassa obsoleta (Say). Oecologia 65: 513–515.
Jaschinski, S., and C. Sommer. 2010. Positive effects of mesograzers on epiphytes in an eelgrass system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 401: 77–85.
Johnson, D.S. 2011. High-marsh invertebrates are susceptible to eutrophication. Marine Ecology Progress Series 438: 143–152.
Johnson, D.S., and J.W. Fleeger. 2009. Weak response of saltmarsh infauna to ecosystem-wide nutrient enrichment and fish predator reduction: a four-year study. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 373: 35–44.
Johnson, D.S., and M. Short. 2013. Chronic nutrient enrichment increase the density and biomass of the mudsnail, Nassarius obsoletus. Estuar Coast 36: 28–35.
Johnson, D.S., J.W. Fleeger, K.A. Galván, and E.B. Moser. 2007. Worm holes and their space-time continuum: spatial and temporal variability of macroinfaunal annelids in a northern New England salt marsh. Estuar Coast 30: 226–237.
Johnson, D.S., J.W. Fleeger, and L.A. Deegan. 2009. Large-scale manipulation reveal top–down and bottom–up controls interact to alter habitat utilization by saltmarsh fauna. Marine Ecology Progress Series 377: 33–41.
Jonge, V.N.D. 1980. Fluctuations in the organic carbon to chlorophyll-a ratios in estuarine benthic diatom populations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 2: 345–353.
Juanes, J.A., X. Guinda, A. Puente, and J.A. Revilla. 2008. Macroalgae, a suitable indicator of the ecological status of coastal rocky communities in the NE Atlantic. Ecological Indicators 8: 351–359.
Keats, R.A., L.J. Osher, and H.A. Neckles. 2004. The effect of nitrogen loading on a brackish estuarine faunal community: a stable isotope approach. Estuaries 27: 460–471.
Lee, S.C., and B.R. Silliman. 2006. Competitive displacement of a detritivorous salt marsh snail. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 339: 75–85.
Lockfield, K. 2011. Chronic nutrient enrichment effects on mummichog, Fundulus heteroclitus in a northeastern Massachusetts salt marsh. Masters, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge.
Lopez, G.R., J.S. Levinton, and L.B. Slobodkin. 1977. The effect of grazing by the detritivore Orchestia grillus on Spartina litter and its associated microbial community. Oecologia 30: 111–127.
McCahon, C.P., A.F. Brown, and D. Pascoe. 1988. The effect of acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis (Muller 1776) on the acute toxicity of cadmium to its intermediate host, the amphipod Gammarus pulex (L.). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 17: 239–243.
Middelburg, J.J., C. Barranguet, H.T.S. Boschker, P.M.J. Herman, T. Moens, and C.H.R. Heip. 2000. The fate of intertidal microphytobenthos carbon. An in situ 13C labelling study. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1224–1234.
Minagawa, M., and E. Wada. 1984. Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chain: further evidence and the δ15N and animal age. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 48: 1135–1140.
Mitwally, H.M., Fleeger, J.W. (2013) Long-term nutrient fertilization effects on salt marsh meiofauna. Hydrobiologia. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1496-7
Parnell, A.C., R. Inger, S. Bearhop, and A.L. Jackson. 2010. Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation. PloS One 5: e9672.
Pascal, P.Y., J.W. Fleeger, H.T.S. Boschker, H.M. Mitwally, and D.S. Johnson. 2013. Response of the benthic food web to short- and long-term nutrient enrichment in saltmarsh mudflats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 474: 27–41.
Pascoe, D., T.J. Kedwards, S.J. Blockwell, and E.J. Taylor. 1995. Gammarus pulex (L.) feeding bioassay—effects of parasitism. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 55: 629–632.
Peterson, B.J., L.A. Deegan, J. Helfrich, J.E. Hobbie, M. Hullar, B. Moller, T.E. Ford, A. Hershey, A. Hiltner, G. Kipphut, M.A. Lock, D.M. Fiebig, V. McKinley, M.C. Miller, J.R. Vestal, R. Ventullo, and G. Volk. 1993. Biological response of a tundra river to fertilization. Ecology 74: 653–672.
Posey, M., C. Powell, L. Cahoon, and D. Lindquist. 1995. Top down vs. bottom up control of benthic community composition on an intertdal tideflat. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 185: 19–31.
Rosemond, A.D., C.M. Pringle, and A. Ramirez. 2001. A test of top–down and bottom–up control in a detritus-based food web. Ecology 82: 2279–2293.
Sardá, R., I. Valiela, and K. Foreman. 1996. Decadal shifts in a salt marsh macroinfaunal community in response to sustained long-term experimental nutrient enrichment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 205: 63–81.
Taylor, A.C., S.W. Nixon, S.L. Granger, J.P. Buckley, J.P. McMahon, and H.J. Lin. 1995. Responses of coastal lagoon plant comminuties to different forms of nutrient enrichment—a mesocosm experiment. Aquatic Botany 52: 19–34.
Thompson, L.S. 1984. Comparison of the diets of the tidal marsh snail, Melampus bidentatus and the amphipod, Orchestia grillus. Nautilus 98: 44–53.
Valiela, I., and M.L. Cole. 2002. Comparative evidence that salt marshes and mangrove may protect seagrass meadows from land-derived nitrogen loads. Ecosystems 5: 92–102.
Vermeulen, S., S. Sturaro, S. Goberts, J.M. Bouquegneau, and G. Lepoint. 2011. Potential early indicators of anthropogenically derived nutrients: a mutiscale stable isotope analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 422: 9–22.
Wear, D.J., M.J. Sullivan, A.D. Moore, and D.F. Millie. 1999. Effects of water-column enrichment on the production dynamics of three seagrass species and their epiphytic algae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 179: 201–213.
Acknowledgments
Pierre-Yves Pascal conducted this research while being supported by a postdoctoral fellowship funded by Department of Energy Office of Biological and Environmental Research Award DE-FG02-05ER64070 and the Louisiana State University College of Science. We thank the Marshview field crew for maintaining nutrient enrichment experiment and for valuable help in field collecting invertebrates. We thank Marshall Otter for stable isotopic analyses. The National Science Foundation funded this work under grant numbers 9726921, 0213767, 0816963, 1058747, and 0423565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascal, PY., Fleeger, J.W. Diverse Dietary Responses by Saltmarsh Consumers to Chronic Nutrient Enrichment. Estuaries and Coasts 36, 1115–1124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-013-9624-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-013-9624-1