Abstract
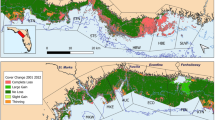
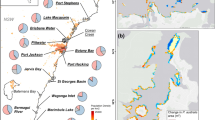
In 1994, 1995, and 1996, seagrasses in 46 of the 89 coastal embayments and portions of seven open-water near-shore areas in Massachusetts were mapped with a combination of aerial photography, digital imagery, and ground truth verification. In the open-water areas, 9,477.31 ha of seagrass were identified, slightly more than twice the 4,846.2 ha detected in the 46 coastal embayments. A subset of the 46 embayments, including all regions of the state were remapped in 2000, 2001, and 2002 and again in 2006 and 2007. We detected a wide range of changes from increases as high as 29% y−1 in Boston Harbor to declines as large as −33% y−1 in Salem Harbor. One embayment, Waquoit Bay, lost all of its seagrass during the mapping period. For the 12-year change analysis representing all geographic regions of the state, only three embayments exhibited increases in seagrass coverage while 30 of the original 46 embayments showed some indication of decline. For the decadal period, rates of decline in the individual embayments ranged from −0.06% y−1 to as high as −14.81% y−1. The median rate of decline by region ranged from −2.21% y−1 to −3.51% y−1 and was slightly less than the recently reported global rate of decline for seagrasses (−3.7% y−1). Accounting for the gains in three of the embayments, 755.16 ha (20.6%) of seagrass area originally detected was lost during the mapping interval. The results affirm that previously reported losses in a few embayments were symptomatic of more widespread seagrass declines in Massachusetts. State and Federal programs designed to improve environmental quality for conservation and restoration of seagrasses in Massachusetts should continue to be a priority for coastal managers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addy, C.E., and D.A. Aylward. 1944. Status of eelgrass in Massachusetts during 1943. Journal of Wildlife Management 8: 269–275.
Bell, S.S., M.S. Fonseca, and N.B. Stafford. 2006. Seagrass ecology: new contributions from a landscape perspective. In Seagrasses, biology, ecology and conservation, ed. W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte, 625–645. The Netherlands: Springer.
Biber, P.D., H.W. Paerl, C.L. Gallegos, and W.J. Kenworthy. 2004. Evaluating indicators of seagrass stress to light. In Estuarine indicators, ed. S.A. Bortone, 193–209. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Cambridge, M.L., and A.J. McComb. 1984. The loss of seagrasses in Cockburn Sound, Western Australia. I. The time course and magnitude of seagrass decline in relation to industrial development. Aquatic Botany 20: 229–243.
Carpenter, S.R. 2003. Regime shifts in lake ecosystems: pattern and variation. Volume 15 in the excellence in ecology series. Oldendorf/Luhe: Ecology Institute.
Costa, J.E. 1988. Eelgrass in Buzzards Bay: Distribution, production, and historical changes in abundance. EPA 503/4/88-002. pp 204.
Costa, J.E., B.L. Howes, A.E. Giblin, and I. Valiela. 1992. Monitoring nitrogen and indicators of nitrogen loading to support management action in Buzzards Bay. In Ecological indicators vol. 1, ed. D.H. McKenzie, D.E. Hyatt, and V.J. McDonald, 499–531. Research Triangle Park: Elsevier Applied Science.
Cottam, C. 1934. Eelgrass disappearance has serious effects on waterfowl and industry. US Department of Agriculture Yearbook, Separate 1430.
Cottam, C. 1933. Eelgrass, valuable sea plant, dying of mysterious disease. Science News Letter 24: 73.
Cottam, C., and D.A. Munro. 1954. Eelgrass status and environmental relations. Journal of Wildlife Management 18: 449–460.
Dennison, W.C., R.J. Orth, K.A. Moore, J.C. Stevenson, V. Carter, S. Kollar, P. Bergstrom, and R. Batiuk. 1993. Assessing water quality with submersed aquatic vegetation. Bioscience 43: 86–94.
Dexter, R.W. 1953. Recession of eelgrass at Cape Ann, Massachusetts. Ecology 34: 229–231.
De Jonge, V.N., and D.J. De Jong. 1992. Role of tide, light and fisheries in the decline of Zostera marina L. in the Dutch Wadden Sea. Netherlands Institute for Sea Research, Publication Series No. 20, pp 161–176.
Dobson, J.E., E.A. Bright, R.L. Ferguson, D.W. Field, L.L. Wood, K.D. Haddad, H. Iredale, III, J.R. Jensen, V.V. Klemas, R.J. Orth, and J.P. Thomas. 1995. NOAA Coastal Change Analysis Program (C-CAP): guidance for regional implementation. NOAA Technical Report NMFS 123.
Duarte, C.M., J.W. Fourqurean, D. Krause-Jensen, and B. Olesen. 2006. Dynamics of seagrass stability and change. In Seagrasses, biology, ecology and conservation, ed. W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte, 271–294. The Netherlands: Springer.
Duarte, C.M., N. Marba, D. Krause-Jensen, and M. Sanchez-Camacho. 2007. Testing the predictive power of seagrass depth limit models. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 652–656.
Erftemeijer, P.L.A., J.K.L. van Beek, C.A. Ochieng, Z. Jager, and H.J. Los. 2008. Eelgrass seed dispersal via floating generative shoots in the Dutch Wadden Sea: a model approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 358: 115–124.
Finkbeiner, M., B. Stevenson, and R. Seaman. 2001. Guidance for benthic habitat mapping: an aerial photographic approach. NOAA/CSC/20117-PUB.
Fonseca, M.S., and S.S. Bell. 1998. Influence of physical setting on seagrass landscapes near Beaufort, North Carolina, USA. Marine Ecology Progress Series 171: 109–121.
Fourqurean, J.W., and M.B. Roblee. 1999. Florida Bay: a recent history of ecological changes. Estuaries 22: 345–357.
Frederiksen, M.F., D. Krause-Jensen, M. Holmer, and J.S. Laursen. 2004. Long-term changes in area distribution of eelgrass (Zostera marina) in Danish coastal waters. Aquatic Botany 78: 167–181.
Fox, S.E., E. Stieve, I. Valiela, J. Hauxwell, and J. McClelland. 2008. Macrophyte abundance in Waquoit Bay: effects of land-derived nitrogen loads on seasonal abundance and multi-year biomass patterns. Estuaries and Coasts 31: 532–541.
Green, E.P., and F.T. Short. 2003. World Atlas of seagrasses. Berkeley: University of Calif. Press.
Hauxwell, J., J. Cebrian, C. Furlong, and I. Valiela. 2001. Macroalgal canopies contribute to eelgrass (Zostera marina) decline in temperate estuarine ecosystems. Ecology 82: 1007–1022.
Hauxwell, J., J. Cebrian, and I. Valiela. 2003. Eelgrass Zostera marina loss in temperate estuaries: relationship to land-derived nitrogen loads and effect of light limitation imposed by algae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 247: 59–73.
Holmer, M., and L. Laursen. 2002. Effect of shading of Zostera marina (eelgrass) on sulfur cycling in sediments with contrasting organic matter and sulfide pools. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 270: 25–37.
Kemp, W.M., R. Batiuk, R. Bartlesoni, P. Bergstrom, V. Carter, C.L. Gallegos, W. Hunley, L. Karrh, E. Koch, J.M. Landwehr, K.A. Moore, L. Murray, M. Naylor, N.B. Rybicki, J.C. Stevenson, and D.J. Wilcox. 2004. Habitat requirements for submerged aquatic vegetation in the Chesapeake Bay: water quality, light regime, and physical–chemical factors. Estuaries 27: 363–377.
Krause-Jensen, D., S. Sagert, H. Schubert, and C. Bostrom. 2008. Empirical relationships linking distribution and abundance of marine vegetation to eutrophication. Ecological Indicators 8: 515–529.
Leschen, A.S., K.H. Ford, and N. Tay Evans. 2010. Successful eelgrass (Zostera marina) restoration in a formerly eutrophic estuary (Boston Harbor) supports the use of a multifaceceted watershed approach to mitigating eelgrass loss. Estuaries and Coasts. doi:10.1007/s12237-010-9272-7.
Lewis, H.F., and C. Cottam. 1936. Eelgrass and other waterfowl foods—present status and future prospects. Proceedings of the North American Wildlife Conference 1: 498–501.
McGlathery, K.J. 2001. Macroalgal blooms contribute to the decline of seagrass in nutrient-enriched coastal waters. Journal of Phycology 37: 453–456.
Moore, K.A., and F.T. Short. 2006. Biology of zostera. In Seagrasses, biology, ecology and conservation, ed. W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte, 361–386. The Netherlands: Springer.
Odale, R.N. 1992. Cape Cod and the Islands: the geology of Cape Cod. East Orleans: Parnassus Imprints.
Olsen, J.L., S.T. Wytze, J.A. Coyer, T.H. Reusch, M. Billingham, C. Bostrom, E. Calvert, H. Christie, S. Granger, R. La Lumiere, N. Milchakova, M.P. Oudot-Le Secq, G. Procaccini, B. Sanjabi, E. Serrao, J. Veldsink, S. Widdicombe, and S. Wyllie-Echeverria. 2004. North Atlantic phylogeography and large-scale population differentiation of the seagrass Zostera marina L. Molecular Ecology 13: 1923–1941.
Orth, R.J., and K. Moore. 1983. Chesapeake Bay: an unprecedented decline in submerged aquatic vegetation. Science 222: 51–52.
Orth, R.J., M.L. Luckenback, S.R. Marion, K.A. Moore, and D.J. Wilcox. 2006a. Seagrass recovery in the Delmarva Coastal Bays, USA. Aquatic Botany 84: 26–36.
Orth, R.J., M.C. Harwell, and G.J. Inglis. 2006b. Ecology of seagrass seeds and dispersal strategies. In Seagrasses, biology, ecology and conservation, ed. W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte, 111–133. The Netherlands: Springer.
Orth, R.J., T.J.B. Carruthers, W.C. Dennison, C.M. Duarte, J.W. Fourqurean, K.L. Heck Jr., A.R. Hughes, G.A. Hendrick, W.J. Kenworthy, S. Olyarnik, F.T. Short, M. Waycott, and S.L. Williams. 2006c. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56: 987–996.
Orth, R.J., M.R. Williams, S.R. Marion, D.J. Wilcox, T.J.B. Carruthers, K.A. Moore, W.M. Kemp, W.C. Dennison, N. Rybicki, P. Bergstrom, and R.A. Batiuk. 2010. Long-term trends in submersed aquatic vegetation (SAV) in Chesapeake Bay, USA, related to water quality. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 1144–1163.
Rasmussen, E. 1977. The wasting disease of eelgrass (Zostera marina) and its effects on environmental factors and fauna. In Seagrass ecosystems, ed. C.P. McRoy and C. Helfferich, 1–51. New York: Marcel Dekker.
Scheffer, M., and S.R. Carpenter. 2003. Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: linking theory to observation. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 12: 648–656.
Short, F.R., and S. Wyllie Echeverria. 1996. Natural and human induced disturbance of seagrasses. Environmental Conservation 23: 17–27.
Short, F.T., B.W. Ibelings, and C. den Hartog. 1988. Comparison of a current eelgrass disease to the wasting disease in the 1930s. Aquatic Botany 30: 295–304.
Short, F.T., and D.M. Burdick. 1996. Quantifying eelgrass habitat loss in relation to housing development and nitrogen loading in Waquoit Bay, MA. Estuaries 19: 730–739.
Steward, J.S., and W.C. Green. 2007. Setting load limits for nutrients and suspended solids based upon seagrass depth-limit targets. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 657–670.
Thayer, Gordon W., W. Judson Kenworthy, and Mark S. Fonseca. 1984. The ecology of eelgrass meadows of the Atlantic coast: a community profile. US Fish and Wildlife Service. FWS/OBS-84/02. pp 147.
Tomasko, D.A., D.L. Bristol, and J.A. Ott. 2001. Assessment of present and future nitrogen loads, water quality, and seagrass (Thalassia testudinum) depth distribution in Lemon Bay Florida. Estuaries 24: 926–938.
Valiela, I., and J.E. Costa. 1988. Eutrophication of Buttermilk Bay: a Cape Cod coastal embayment: concentrations of nutrients and watershed nutrient budgets. Environmental Management 12: 539–553.
Valiela, I., K. Foreman, M. LaMontague, D. Hersh, J. Costa, P. Peckol, B. DeMeo-Anderson, C. D’Avanzo, M. Babione, C.H. Sham, J. Brawley, and K. Lajth. 1992. Coupling of watersheds and coastal waters: sources and consequences of nutrient enrichment in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts. Estuaries 15: 443–457.
Vaudrey, J.M.P., J.N. Kremer, B.F. Branco, and F.T. Short. 2010. Eelgrass recovery after nutrient enrichment reversal. Aquatic Botany. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2010.08.005.
Walker, D.I., G.A. Kendrick, and A.J. McComb. 2006. Decline and recovery of seagrass ecosystems—the dynamics of change. In Seagrasses, biology, ecology and conservation, ed. W.D. Larkum, R.J. Orth, and C.M. Duarte, 551–565. The Netherlands: Springer.
Waycott, M., C.M. Duarte, T.J.B. Carruthers, R.G. Orth, W.C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J.W. Fourqurean, K.A. Heck Jr., A.R. Hughes, G.A. Kendrick, W.J. Kenworthy, F.T. Short, and S.L. Williams. 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 12377–12381.
Wyllie-Echeverria, S., P. Arzel, and P.A. Cox. 2000. Seagrass conservation: lessons from ethnobotany. Pacific Conservation Biolgy 5: 329–335.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection. We thank Kathy Cronin, Jim Brown, Michael McHugh, Don Field, and Brooke Landry for laboratory and field assistance. Salary and equipment funding for W. Judson Kenworthy were provided by the Center for Coastal Fisheries and Habitat Research, NCCOS, NOS, NOAA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementry Table 1
Data for hectares of seagrass mapped in 47 Massachusetts embayments in four regions (North Shore, South Shore, Buzzards Bay, Islands) and seven open-water areas (DOC 79 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costello, C.T., Kenworthy, W.J. Twelve-Year Mapping and Change Analysis of Eelgrass (Zostera marina) Areal Abundance in Massachusetts (USA) Identifies Statewide Declines. Estuaries and Coasts 34, 232–242 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-010-9371-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-010-9371-5