Abstract
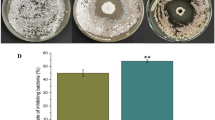
The occurrence of potato common scab (PCS) in Yunnan Province is progressively increasing. To screen for high-efficiency control agents against PCS, this experiment used 70% Ambam, 20% zinc thiazole, 60% Azoxystrobin, 90% Neophytamycin, 46.1% Copper hydroxide, 80% Ethylicin, and three Ambam-based compound formulations to conduct laboratory, greenhouse, and field control tests. In this study, 10 different species of Streptomyces (S. turgidiscasies, S. scabies, S. enissocaesillies, S. luridiscaliei, S. caviscabies, S. anulatus, S. aureofaciens, S. acidiscabies, S. europaeicabiei, and S. griseus) were used to screen the bactericides described above in the laboratory, and the results show that the anti-bacterial effects of different pesticides differ significantly. In Kirby-Bauer test, the inhibition zone diameter of Ambam is the biggest, and average diameter is 74.3 cm. The second largest diameter is three compounded formulations containing Ambam, while Kocide 3000 showed an average diameter is 38 mm. Kocide 3000, Ambam alone, and the three compounded.
Resumen
La aparición de roña común de la papa (PCS) en la provincia de Yunnan está aumentando progresivamente. Para probar agentes de control de alta eficiencia contra PCS, este experimento utilizó 70% de Ambam, 20% de tiazol de zinc, 60% de azoxistrobina, 90% de neofitamicina, 46.1% de hidróxido de cobre, 80% de etilicilina y tres formulaciones de compuestos a base de Ambam para realizar pruebas de laboratorio, invernadero y control de campo. En este estudio, se utilizaron 10 especies diferentes de Streptomyces (S. turgidiscasies, S. scabies, S. enissocaesillies, S. luridiscaliei, S. caviscabies, S. anulatus, S. aureofaciens, S. acidiscabies, S. europaeicabiei y S. griseus) para probar los bactericidas descritos anteriormente en el laboratorio, y los resultados muestran que los efectos antibacterianos de diferentes plaguicidas difieren significativamente. En la prueba de Kirby-Bauer, el diámetro de la zona de inhibición de Ambam es el más grande, y el diámetro promedio es de 74,3 cm. El segundo diámetro más grande son tres formulaciones compuestas que contienen Ambam, mientras que Kocide 3000 mostró un diámetro promedio de 38 mm. Kocide 3000, Ambam solo, y los tres compuestos.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bencheikh, M., and B. Setti. 2007. Characterization of Streptomyces scabies isolated from common scab lesions on potato tubers by morphological,biochemical and pathogenicity tests in Chlef region in western Algeria. Sciences & Technologie C Biotechnologies 26: 61–67.
Bouchek-Mechiche, K., L. Gardan, D. Andrivon, and P. Normand. 2006. Streptomyces turgidiscabies and streptomyces reticuliscabiei: one genomic species, two pathogenic groups. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 56 (12): 2771–2776.
Cao, Z., G. Khodakaramian, and K. Arakawa. 2012. Isolation of borrelidin as a phytotoxic compound from a potato pathogenic Streptomyces strain. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry 76 (2): 353–357.
Chen, W., W. Fang, and W. Zheng. 2013. Crop cultivation substrate disinfection technology and its application prospects. Fujian Agricultural Machinery 03: 42–45.
Dees, M.W., A. Sletten, and A. Hermansen. 2013. Isolation and characterization of Streptomyces species from potato common scab lesions in Norway. Plant Pathology 62 (1): 217–225.
Fang, L., X. Feng, H. Jiang, T. Cao, and Y. Chen. 2009. Flow injection chemiluminescence analysis of environmental hormone pesticide dasenium. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry 37 (5): 781–781.
Flores-Gonzalez, R., I. Velasco, and F. Montes. 2008. Detection and characterization of Streptomyces causing potato common scab in Western Europe. Plant Pathology 57 (1): 162–169.
Gao, Y., J. Xu, N. Liu, Q. Zhou, X. Ding, J. Zhan, X. Cheng, J. Huang, Y. Lu, and Y. Yang. 2019. Current status and management strategies for potato insect pests and diseases in China. Plant Protection 45 (05): 106–111.
Gong, C., H. Zhang, Y. Xu, M. Yang, S. Jiang, S. Song, and D. Yu. 2017. Effects of winter potato cultivation on disease escape and yield increase in Yunnan. Chinese Potato Journal 31(06): 346–352.
Guo, D., S. Hong, M. Zhang, and K. Zhou. 2022. Effects of different seed soaking agents on germination and emergence of rapeseed under straw returning conditions. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin 38 (14): 11–17.
Jiang, W., Z. Huang, B. Gao, K. Hui, and L. Sun. 2017. Control effects of different pesticides on wheat seed aphid and sheath blight. Modern Agricultural Sciences And Technology 2017 (01): 96–97.
Kang, R., and S.R. Wang. 2013. Preliminary identification of the pathogen of potato scab in Gansu. Plant Protection 39 (3): 78–82.
Karahan, A. 2006. Determination of Streptomyces species harmful on potatoes in central Anatolia region and reactions of major potato cultivars against common species. Ph.D.thesis. Graduate School of Naturel and Applied Sciences, Ankara University.
Kersj, A., K.D. Cameron, and M.V. Joshi. 2005. A large, mobile pathogenicity island confers plant pathogenicity on Streptomyces species. Molecular Microbiology 55 (4): 1025 1033.
Lambert, D.H., and R. Loria. 1989. Streptomyces scabies sp.nov.,nom.rev. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 39 (4): 387–392.
Lehtonen, M.J., H. Ranatala, and J.F. Kreuze. 2004. Occurrence and survival of potato scab pathogens(Streptomyces species)on tuber lesions:quick diagnosis based on a PCR-based assay. Plant Pathology 53 (3): 280–287.
Leiminger, J., M. Frank, and C. Wenk. 2013. Distribution and characterization of Streptomyces species causing potato common scab in Germany. Plant Pathology 62 (3): 611–623.
Lerat, S., A. Simao-Beaulieu, and C. Beaulieu. 2009. Genetic and physiological determinants of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity. Molecular Plant Pathology 10: 579–585.
Li, Q., and J. Li. 2006. Field efficacy trials of several fungicides against cucumber powdery mildew. GanSu Agricultural Science And Technological 2006 (06): 25–26.
Liang, H., H. Lv, Y. Gao, Y. Wu, M. Wang, K. Zhao, and W. Zhang. 2021. The control effect of 98% mianlong on scab in potato production. Agrochemicals 60 (02): 150–153.
Liu, D., Neil Anderson, and Linda L. Kinkel. 2000. Field Evaluation of Antagonistic Streptonmyces Strains on Biocontrol of Potato Scab. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica 30 (3): 237–244.
Menkissoglu, O., and S.E. Lindow. 1991. Chemical forms of copper on leaves in relation to the bactericidal activity of cupric hydroxide deposits. on plants Phytopathology 81: 1263–1270.
Miyajima, K., F. Tanaka, and T. TakeuchiI. 1998. Streptomyces turgidiscabies sp.nov. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 48 (2): 495–502.
Mohamed Hosny, Kamal, A. M., Mahmoud R. Abo-Elyousr, Asran, and A. Farag, and Saead. 2014. Chemical control of potato common scab disease under field conditions. Archives of Phytopathology and Plant Protection (18).
Natsume, M., M. Komiya, F. Koyanagi, N. Tashiro, H. Kawaide, and H. Abe. 2005. Phytotoxin produced by streptomyces, sp. causing potato russet scab in japan. Journal of General Plant Pathology 71 (5): 364–369.
Nolte, P., G.A. Secor, and N.C. Gudmestad. 1987. Wound healing, decay and chemical treatment of cut potato tuber tissue. American Journal of Potato Research 64 (1): 1–9.
Park, D.H. 2007. Characterization of Streptomycetes Causing Potato Common Scab in Korea. Plant Disease 87 (11): 1290–1296.
Park, D.H., Y.M. Yu, and J.S. Kim. 2003. Characterization of streptomycetes causing potato common scab in Korea. Plant Disease 87 (11): 1290–1296.
Powelson, M., and R. Rowe. 2008. Managing diseases caused by seedborne and soilborne fungi and fungus-like pathogens. In Potato health management, 2nd ed., ed. D. Johnson, 183–195. St. Paul, MN: APS Press.
Shannei, Y. H., and Y. Zheng. 1985. The control of common scab and powdery scab on potato. Horticulture & Seed 1985(2):23–25.
Shen, Y., J. Feng, X. Yuan, and X. Chen. 2017. The General Situation of the Application and Research on Protective Fungicide Mancozeb. Modern Agrochemicals 16 (06): 1–5.
St-Onge, R., C. Goyer, and R. Cofin. 2008. Genetic diversity of Streptomyces spp.causing common scab of potato in eastern Canada. Systematic and Applied Microbiology 31 (6–8): 474–484.
Sun, G., Z. Li, K. Yan, L. Chen, and N. Si. 2020. Study on the improved method of screening fungicides for potato scab. Agrochemicals 59(04):303–305.
Sun, J., G. Jin, and X. Liu. 2015. Control effects of different fungicides and application methods on potato common scab disease. Chinese Potato Journal 29(02):107–111.
Tagawa, M., H. Tamaki, and A. Manome. 2010. Isolation and characterization of antagonistic fungi against potato scab pathogens from potato field soils. Fems Microbiology Letters 305 (2): 136–142.
Thwaites, R., S.J. Wale, and D. Nelson. 2010. Streptomyces turgidiscabies and S.acidiscabies:two new causal agents of common scab of potato(Solanum tuberosum)in the UK. Plant Pathology 59 (4): 804–804.
Wang, X., Z. Du, S. Guo, and X. Zhang. 2002. The control effect of 0.1%HgCl2 against common scab on virus free potato micro tubers. Chinese Potato Journal 16 (4): 248–248.
Wanner, L.A. 2007. A new strain of Streptomyces causing common scab in potato. Plant Disease 91 (4): 352–359.
Xia, S., and W. Sheng. 2022. Research progress on potato scab and its control in China. Plant Protection 48 (01): 7–16 + 28.
Xu, X., G. Mang, Z. Jiang, X. Wei, Z. Ren, Z. Ji, and Y. Gai. 2017. Investigation on impact factors of potato scab and integrating control techniques. Horticulture & Seed 6:47–50.
Xu, S., M. Liu, M. Li, J. Guo, Y. Qi, Z. Hu, and X. Li. 2022. Field efficacy evaluation of different fungicides on root rot of highland barley. GanSu Agricultural Science And Technological 53 (04): 78–83.
Yang, M., R. Wang, W. Du, C. Gong, D. Yu, W. Zhao, S. Song, and H. Zhang. 2018. The pathogenic Streptom yces species causing potato scab in Yunnan Province. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica 48 (04): 445–454.
Yu, Q., J. Jia, Y. Geng, H. Yan, and G. Qiu. 2004. Prevention and treatment of scab disease in the production of virus-free potato minitubers. Chinese Potato Journal 18 (6): 345–347.
Zhang, J., Y. Yin, R. Yan, S. Ha, T. Lin, Y. Cheng, and B. Hu. 2013. Occurrence and control approach of potato Common Scab (Streptomyces spp.) in Inner Mongolia. Chinese Potato Journal 27(1):56–59.
Zhang, L., L. Cheng, X. Bian, and G. Xie. 2019. Study on pathogen of potato scab in China and its prevention and control. Zhejiang Agricultural Science 60 (10): 1778–1781.
Zhang, M., W. Zhao, X. Yu, W. Yang, T. Zhang, and D. Liu. 2009. Genetic Diversity of Potato Scab Pathogens in China Based on 16S rDNA sequence. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 42 (2): 499–504.
Zhang, Y., Y. Wei, and L. Gao. 2011. The technology on Potato common scab prevention and control. Northwest Horticulture 04: 42–43.
Zhang, Y. 2018. Thiocarbamate: a reliable resistance management tool and future prospects. World Pesticides 40 (04): 15-17 + 26.
Zhao, W., W. Yang, and Y. Li. 2006. Characterization and identification on the pathogen of potato scab in China. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 39 (2): 313–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, J., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H. et al. Efficacy of Bactericides Against Potato Common Scab Caused by Streptomyces in Yunnan, China. Am. J. Potato Res. 99, 326–335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-022-09883-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-022-09883-2