Abstract
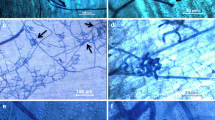
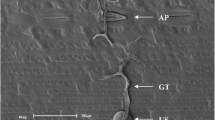
In histological and cytological investigations, the infection process of Phytophthora infestans, the late blight pathogen, was comparatively studied in several potato cultivars and somatic hybrid genotypes and their parents using fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy methods. The results showed that germination of zoospores of P. infestans and frequency of invading by infection hyphae did not differ among the cultivar-pathogen interactions, but, extension of hyphae in host cells markedly differed among these genotypes. In the susceptible genotypes the pathogen grew rapidly inter- and intracellularly, 12 h after inoculation (hai), and some digital like haustoria were formed and the cytoplasm of the host cells became disorganized. In the resistance genotypes, the pathogen was restricted to the site of initial penetration, although some hyphae could penetrate the epidermal cell, however, the host cells produced resistance responses, such as formed wall appositions when in contact with hyphae, and no haustoria like structures were found. In the somatic hybride genotypes, the host response was different according to their parents as shown by transmission electron microscopy. In the hybrid genotype 1508/2, like in the wild species S. bulbocastanum, no hyphae were found in host cells. In the other genotypes, hyphae of P. infestans spread intercellularly and formed haustoria, but the cytoplasm of hyphae and haustoria was disorganized and host cell resistant responses often appeared, such as, host cells were disorganized and necrotic and cell wall apposition were observed.
Resumen
En investigaciones histológicas y citológicas, el proceso de infección de Phytophthora infestans, el patógeno del tizón tardío, se estudió comparativamente en algunas variedades de papa y genotipos somáticos híbridos y sus progenitores usando microscopía de fluorescencia y métodos de microscopía electrónica. Los resultados mostraron que la germinación de zoosporas de P. infestans y la frecuencia de la invasión por infección de hifas no se diferenció entre las interacciones variedad-patógeno, pero la extensión de las hifas en células del hospedante se diferenció marcadamente entre estos genotipos. En los genotipos susceptibles el patógeno creció rápidamente inter e intra-celularmente 12 h después de la inoculación (hai), y se formaron algunos haustorios como dedos, desorganizándose el citoplasma de las células hospedantes. En los genotipos resistentes, el patógeno se restringió al sitio inicial de penetración, aunque algunas hifas pudieron penetrar las células epidermales, no obstante, las células hospederas produjeron respuestas de resistencia, tales como deposiciones de pared cuando se pusieron en contacto con las hifas y no se encontraron estructuras tipo haustorios. En los genotipos somáticos híbridos, la respuesta del hospedante fue diferente de acuerdo con sus progenitores como se muestra por microscopio electrónico de transmisión. En el genotipo híbrido 1580/2, como en la especie silvestre S. bulbocastanum, no se encontraron hifas en las células hospederas. En los otros genotipos, la hifa de P. infestans se dispersó intercelularmente y formó haustorios, pero el citoplasma de la hifa y de los haustorios estaba desorganizado y con frecuencia aparecieron respuestas de resistencia de las células, tales como la observación de la desorganización y necrosis de las células del hospedante y deposición de pared celular.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, F.H.E., and J. Friend. 1983. Resistance of potato tubers to infection by Phytophthora infestans: a structural study of haustorial encasement. Physiological Plant Pathology 22: 285–292.
Blackwell, E.M. 1953. Haustoria of Phytophthora infestans and some other species. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 36: 138–158.
Borgato, L., C. Conicella, F. Pisani, and A. Furini. 2007. Production and characterization of arboreous and fertile Solanum melongena, Solanum marginatum somatic hybrid plants. Planta 226: 961–969.
Budin, K.Z. 2002. Genetic foci of Solanum species, Petota Dumort, resistant to Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) De Bary. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 49: 229–235.
Carrasco, A., J.I. Ruiz de Galarreta, A. Rico, and E. Ritter. 2000. Transfer of PLRV resistance from Solanum verrucosum Schlechdt to potato (S. tuberosum L.) by protoplast electrofusion. Potato Research 43: 31–42.
Chen, Q., M. Kawchuk, D.R. Lynch, M.S. Goettel, and D.K. Fujimoto. 2003. Identification of late blight, Colorado potato beetle, and blackleg resistance in three Mexican and two South American wild 2x (1EBN) Solanum species. American Journal of Potato Research 80: 9–19.
Coffey, M.D., and U.E. Wilson. 1983. Histology and cytology of infection and disease caused by phytophthora. In Phytophthora. Its biology taxonomy, ecology and pathology, ed. D.C. Erwin, S. Bartnicki-Carcia, and P.H. Tsao, 289–301. St Paul: The American Phytopathological Society.
Colon, L.T., R. Eijlander, D.J. Budding, M.T. Van Ijzendoorn, M.M.J. Pieters, and J. Hoogendoorn. 1993. Resistant to late blight (Phytophthora infestans. (mont.) de bary) in Solanum nigrum, S. villosum, and their sexual hybrids with S. tuberosum and S. demissum. Euphytica 66: 55–64.
Cuypers, B., and K. Hahlbrock. 1988. Immunohistochemical studies of compatible and incompatible interactions of potato leaves with Phytophthora infestans and of the nonhost response to Phytophthora megasperma. Canadian Journal of Botany 66: 700–705.
Ferris, V. 1955. Histological study of pathogen-suscept relationships between Phytophthora infestans and derivatives of Solanum demissum. Phytopathology 45: 546–552.
Freytag, S., N. Arabatzis, K. Hahlbrock, and E. Schmelzer. 1994. Reversible cytoplasmic rearrangements precede wall apposition, hypersensitive cell death and defense-related gene activation in potato/Phytophthora infestans interactions. Planta 194: 123–135.
Gees, R., and H.R. Hohl. 1988. Cytological comparison of specific (R3) and general resistance to late blight in potato leaf tissue. Phytopathology 78: 350–357.
Greplová, M., H. Polzerová, and H. Vlastníková. 2008. Electrofusion of protoplasts from Solanum tuberosum, S. bulbocastanum and S. pinnatisectum. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 30: 787–796.
Helgeson, J.P., J.D. Pohlman, S. Austin, G.T. Haberlach, S.M. Wielgus, D. Ronis, L. Zambolim, P. Tooley, J.M. McGrath, R.V. James, and W.R. Stevenson. 1998. Somatic hybrids between Solanum bulbocastanum and potato: a new source of resistance to late blight. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 96: 738–742.
Hohl, H.R., and E. Suter. 1976. Host-parasite interfaces in a resistant and a susceptible cultivar of Solanum tuberosum inoculated with Phytophthora infestans: leaf tissue. Canadian Journal of Botany 54: 1956–1970.
Hood, M.E., and H.D. Shew. 1996. Applications of KOH-aniline blue fluorescence in the study of plant–fungal interactions. Phytopathology 86: 704–708.
Kang, Z.S., L. Huang, U. Krieg, A. Mauler-Machnik, and H. Buchenauer. 2001. Effects of tebuconazole on morphology, structure, cell wall components and trichothecene production of Fusarium culmorum in vitro. Pest Management Science 57: 491–500.
Lokossou, A. 2010. Dissection of the major late blight resistance cluster on potato linkage group IV. Wageningen, Holand, Wageningen University, PhD thesis.
Lokossou, A.A., H. Rietman, M. Wang, P. Krenek, H. van der Schoot, B. Henken, R. Hoekstra, V.G. Vleeshouwers, E.A. van der Vossen, R.G. Visser, E. Jacobsen, and B. Vosman. 2010. Diversity, distribution, and evolution of Solanum bulbocastanum late blight resistance genes. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 23: 1206–1216.
Naess, S.K., J.M. Bradeen, S.M. Wielgus, G.T. Haberlach, J.M. McGrath, and J.P. Helgeson. 2001. Analysis of the introgression of Solanum bulbocastanum DNA into potato breeding lines. Molecular Genetics and Genomics 265: 694–704.
Oberwalder, B., L. Schilde-Rentschler, B. Löffelhardt-Ruoss, and H. Ninnemann. 2000. Differences between hybrids of Solanum tuberosum L. and Solanum circaeifolium Bitt. obtained from symmetric and asymmetric fusion experiments. Potato Research 43: 71–82.
Polzerová, H., J. Patzak, and M. Greplova. 2011. Early characterization of somatic hybrids from symmetric protoplast electrofusion of Solanum pinnatisectum Dun. and Solanum tuberosum L. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 104: 163–170.
Ross, H. 1986. Potato breeding—Problems and perspectives. Hamburg: Paul Parey Verlag. 132.
Ruizde Galarreta, J.I., A. Carrasco, A. Salazar, I. Barrena, E. Iturritxa, R. Marquinez, F.J. Legorburu, and E. Ritter. 1998. Wild Solanum species as resistance sources against different pathogens of potato. Potato Research 41: 57–68.
Shimony, C., and J. Friend. 1975. Ultrastructure of the interaction between Phytophthora infestans and leaves of two cultivars of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Orion and Majestic. New Phytologist 74: 59–65.
Song, J., J.M. Bradeen, S.K. Naess, J.A. Raasch, S.M. Wielgus, G.T. Haberlach, J. Liu, H. Kuang, S. Austin-Phillips, C.R. Buell, J.P. Helgeson, and J. Jiang. 2003. Gene RB cloned from Solanum bulbocastanum confers broad spectrum resistance to potato late blight. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 100: 9128–9133.
Szczerbakowa, A., D. Boltowicz, R. Lebecka, P. Radomski, and B. Wielgat. 2005. Characteristics of the interspecific somatic hybrids Solanum pinnatisectum (+) S. tuberosum H-8105. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 27: 265–273.
Thieme, R., U. Darsow, T. Gavrilenko, D. Dorokhov, and H. Tiemann. 1997. Production of somatic hybrids between S. tuberosum L. and late blight resistant Mexican wild potato species. Euphytica 97: 189–200.
Thieme, R., E. Rakosy-Tican, T. Gavrilenko, O. Antonova, J. Schubert, M. Nachtigall, U. Heimbach, and T. Thieme. 2008. Novel somatic hybrids (Solanum tuberosum L. + Solanum tarnii) and their fertile BC1 progenies express extreme resistance to potato virus Y and late blight. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 116: 691–700.
Tomiyama, K. 1983. Research on the hypersensitive response. Annual Review of Phytopathology 21: 1–12.
Zlesak, D.C., and C.A. Thill. 2004. Foliar resistance to Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary (US-8) in 13 Mexican and South American Solanum sp. having EBNs of 1, 2, and 4 and implications for breeding. American Journal of Potato Research 81: 421–429.
Acknowledgments
This study has been financially supported by the German-Chinese co-operation project of agricultural science and technology and the 111 Project from Ministry of Education of China (project number B07049). We also thank Dr. Heinrich Buchenauer for valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Q., Thieme, R., Gao, X. et al. Investigation of Host Responses of Different Potato Genotypes at Tissue, Cellular and Subcellular Levels After Infection with Phytophthora infestans . Am. J. Potato Res. 90, 524–532 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-013-9324-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12230-013-9324-1