Abstract
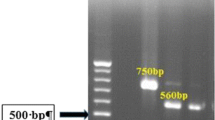
Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) is an important public health problem in Turkey. CL has been most frequently seen in Sanliurfa. There is an expectation of increase in the population of leishmaniasis cases with the influence of Syrian refugees arriving in Turkey. In this study we aimed to diagnosis of CL and identifying of parasite from Leishmania isolates by using ITS 1 PCR RFLP. Samples were collected from 135 CL patients in Sanliurfa. After the specimens were inoculated in medium NNN, the ones which were cultures positive were cultivated in RPMI 1640 followed by PCR-RFLP. Genomic DNA was extracted phenol-chloroform procedure. Samples were examined by using ITS 1 PCR followed by RFLP analysis. Our results indicated that two species, L. tropica (132 samples) and L. major (3 samples), are responsible for cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sanlıurfa. Our study is the first scientific study in which it is reported molecular analyses of cutaneous leishmaniasis cases caused by L. major in Sanliurfa in Southestern Anatolia Region. Because CL cases caused by L.major are detected in our study, it is considered that genotyping is important for diagnosis of Leishmania and following change of epidemiology.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
03 January 2018
In this article (Molecular Identification of Leishmania spp. Isolates Causes Cutaneous Leishmaniasis (CL) in Sanliurfa Province, Turkey, Where CL is Highly Endemic) Table 1 titled “The pH values of yogurts collected from villages in Turkey” doesn’t belong to this article.
References
Afad (2013) Syrian refugees in Turkey: 2013 field survey results. https://www.afad.gov.tr/Dokuman/TR/61-2013123015505-syrian-refugees-in-turkey-2013. Accessed 11 Aug 2014
Akçalı C, Culha G, Inaloz HS, Savaş N, Önlen Y, Savaş L, Kırtak N (2007) Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Hatay. J Turkish Acad Dermatol 1(1):1
Al-Nahhas SA, Kaldas RM (2013) Characterization of Leishmania species isolated from cutaneous human samples from central region of Syria by RFLP analysis. ISRN Parasitol 2013: article ID 308726, 5 pages. https://doi.org/10.5402/2013/308726
AlSamarai AM, AlObaidi HS (2009) Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iraq. J Infect Dev Ctries 3(2):123–129. https://doi.org/10.3855/jidc.59
Amro A, Gashout A, Al-Dwibe H, Alam MZ, Annajar B, Hamarsheh O, Shubar H, Schönian G (2012) First molecular epidemiological study of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Libya. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6(6):e1700. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0001700
Aslan G (1996) Şanlıurfa ilinde kutanöz leishmaniasis (cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sanliurfa city). Gaziantep Univ Fac Med 7:77–81
Azizi HR, Hejazi SH, Borjian Boroujeni A, Jafari M, Taghizadeh N (2013) Detection and identification of Leishmania isolates from patients with Cutaneous Leishmaniasis (CL) in Isfahan (central region of Iran) by PCR method. Arch Razi Inst 68(2):153–158
El-Beshbishy HA, Al-Ali KH (2013) Molecular characterization of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Al-Madinah Al- Munawarah province, western Saudi Arabia. Int J Infect Dis 17(5):e334–e338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2012.11.015.
Erbaydar T, Serpen A, Kurt AO (2012) Zoonozlar. HASUDER Türkiye Sağlık Raporu 2012.(HASUDER Turkey Health Report 2012). Bulaşıcı Hastalıklar Bölümü (Contagious Disease), 88–91. http://halksagligiokulu.org/anasayfa/components/com_booklibrary/ebooks/Turkiye_Saglik_Raporu_2012.pdf
Eslami G, Salehi R, Khosravi S, Doudi M (2012) Genetic analysis of clinical isolates of Leishmania major from Isfahan, Iran. J Vector Borne Dis 49:168–174
Faulde M, Schrader J, Heyl G, Amirih M (2008) Differences in transmission seasons as an epidemiological tool for characterization of anthroponotic and zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in northern Afghanistan. Acta Trop 105(2):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2007.10.011
Ghawar W, Toumi A, Snoussi MA, Chlif S, Zâatour A, Boukthir A, Hamida NB, J C, Diouani MF, Ben-Salah A (2011) Leishmania major infection among Psammomysobesus and Merionesshawi: reservoirs of zoonotic cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sidi Bouzid (centralTunisia). Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 11(12):1561–1568. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2011.0712
Gurel S, Ulukanlıgil M, Ozbilge H (2002) Cutaneous leishmaniasis in Sanliurfa: epidemiologic and clinical features of the last four years (1997-2000). Int J Dermatol 41(1):32–37. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0011-9059.2001.01396.x
Jose A (2010) Leishmaniasis in the World Health Organization Eastern Mediterranean Region. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36:62–65
Koltas IS, Eroğlu F, Alabaz D, Uzun S (2014) The emergence of Leishmania major and Leishmania donovani in southern Turkey. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 108(3):154–158. https://doi.org/10.1093/trstmh/trt119
Mahmoudzadeh-Niknam H, Ajdary S, Riazi-Rad F, Mirzadegan E, Rezaeian A, Khaze V, Djadid DN, Alimohammadian HM (2012) Molecular epidemiology of cutaneous leishmaniasis and heterogeneity of Leishmania major strains in Iran. Trop Med Int Health 17(11):1335–1344
Ozbel Y, Turgay N, Ozensoy S, Ozbilgin A, Alkan MZ, Ozcel MA, Jaffe CL, Schnur L, Oskam L, Abranches P (1995) Epidemiology, diagnosis and control of Leishmaniasis in the Mediterranean region. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 89(1):89–93
Ozbilgin A, Çulha G, Zeyrek F, Kurt O, Töz S, Gündüz C, Akyar I, Ostan I, Kocagöz T, Çavus I, Ozbel Y (2013) Leishmaniasis in Turkey: is Leishmania major present in Turkey?. European society of clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Parasit Dis Protozoans. 12:30–13:30
Ozcel MA, Ozbel Y, Ozensoy S, Turgay N, Daldal N, Alkan MZ (1999) The current status of Leishmaniasis in Turkey. In: Matsumoto Y (ed) Epidemiology and control of Leishmania is in Central Eurasia. Research report series no.1. International Press Editing Centre Incorporation, Tokyo, pp 27–30
Ozensoy Toz S, Nasereddin A, Ozbel Y, Ertabaklar H, Culha G, Sevil N, Alkan MZ, Jaffe CL (2009) Leishmaniasis in Turkey: molecular characterization of Leishmania from human and canine clinical samples. Trop Med Int Health 14(11):1401–1406. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3156.2009.02384.x
Ozensoy Toz S, Culha G, Yıldız Zeyrek F, Ertabaklar H, Alkan MZ, Tetik Vardarlı A, Gunduz C, Ozbel Y (2013) A real-time ITS1-PCR based method in the diagnosis and species identification of Leishmania parasite from human and dog clinical samples in Turkey. PLOS Negl Trop Dis 7(5):e2205. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002205
Postigo JA (2010) Leishmaniasis in the World Health Organization astern mediterranean region. Int J Antimicrob Agents 36:62–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.06.023.
Reithinger R, Mohsen M, Leslie T (2010) Risk factors for anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis at the household level in Kabul, Afghanistan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4(3):e639. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0000639
Rostami MN, Saghafipour A, Vesali E (2013) A newly emerged cutaneous leishmaniasis focus in central Iran. Int J Infect Dis 17(12):e1198–e1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2013.07.003.
Schonian G, Kuhls K (2009) Manual molecular procedures. Leishmaniasis epidemiology network South America. Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janerio
Schonian G, Schnur L, El Fari M et al (2001) Genetic heterogeneity in the species Leishmania tropica revealed by different PCR-based methods. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 95(2):217–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0035-9203(01)90173-7
Schonian G, Nasereddin A, Dinse N et al (2003) PCR diagnosis and characterization of Leishmania in local and imported clinical samples. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 47:349–358
Schonian G, Kuhls K, Mauricio IL (2011) Molecular approaches for a better understanding of the epidemiology and population genetics of Leishmania. Parasitology 138(4):405–425. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182010001538
Ser O, Çetin H (2013) Cutaneous leishmaniasis and its status in Antalya, Turkey. Turk Parasitol 37(2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.5152/tpd.2013.21
Serin MS, Daglioglu K, Bagirova M, Allahverdiyev A, Uzun S, Vural Z, Kayar B, Tezcan S, Yetkin M, Aslan G, Emekdas G, Koksal F (2005) Rapid diagnosis and genotyping of Leishmania isolates from cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis by microcapillary cultivation and polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism of miniexon region. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 53(3):209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2005.05.007
Svobodová M, Sádlová J, Chang KP, Volf P (2003) Shortreport: distribution and feding preference of the sandflies Phlebotomus sergenti and P. papatasi in a cutaneous leishmaniasis focus in Sanliurfa, Turkey. Am J Trop Med Hyg 68(1):6–9
Toprak S, Ozer N (2005) Sandfly species of Sanliurfa province in Turkey. Med Vet Entomol 19(1):107–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0269-283X.2005.00545.x
Uzun S, Uslular C, Yücel A, Acar MA, Özpoyraz M, Memişoğlu HR (1999) Cutaneous leishmaniasis: evaluation of 3074 cases in the Çukurova region of Turkey. Br J Dermatol 140(2):347–350. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02673.x
Volf P, Ozbel Y, Akkafa F, Svobodová M, Votýpka J, Chang KP (2002) Sandflies (Diptera: Phlebotominae) in Sanliurfa, Turkey: relationship of Phlebotomus sergenti with the epidemic of anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis. J Med Entomol 39(1):12–15. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-2585-39.1.12
WHO, Leishmaniasis (2014) http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/en/. Accessed 20 Jul 2014
WHO, Leishmaniasis, Iran ( 2014) http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/resources/IRAN.pdf. Accessed 10 Aug 2014
WHO, Leishmaniasis, Syrian Arab Republic (2014) http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/resources/SYRIAN_ARAB_REPUBLIC.pdf. Accessed 10 Aug 2014
World Health Organization Tech Rep Ser 2010:949. Control of the Leishmaniasis. Report of a meeting of the WHO Expert Committee on the Control of Leishmaniases, Geneva, 22–26 March 2010
Yehia L, AdibHoureih M, Raslan WF, Kibbi A, Loya A, Firooz A, Satti M, El-Sabban M, Khalifeh I (2012) Molecular diagnosis of cutaneous leishmaniasis and species identification: analysis of 122 biopsies with varied parasite index. J Cutan Pathol 39(3):347–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0560.2011.01861.x
Yıldız Zeyrek F, Korkmaz M, Ozbel Y (2007) Serodiagnosis of Anthroponotic cutaneous Leishmaniasis (ACL) caused by Leishmania tropica in Sanliurfa province, Turkey, where ACL is highly endemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol 14(11):1409–1415
Yıldız Zeyrek F, Dirim Erdoğan D, Uluca N, Tümer S, Korkmaz M (2012) Kutanöz Leishmaniasis tanısında serolojinin yeri (The Role of Serology in The Diagnosis of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis). Kafkas Univ Vet Fak 18(suppl A):121–124. https://doi.org/10.9775/kvfd.2011.6083
Funding
This study was supported by Gaziantep University Scientific Research Fund with project number FED.13.16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurses, G., Ozaslan, M., Zeyrek, F.Y. et al. Molecular identification of Leishmania spp. isolates causes cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) in Sanliurfa Province, Turkey, where CL is highly endemic. Folia Microbiol 63, 353–359 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0556-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-017-0556-1