Abstract
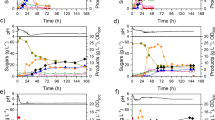
The present study was set to develop a robust and economic biorefinery process for continuous co-production of ethanol and xylitol from rice straw in a membrane bioreactor. Acid pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, detoxification, yeast strains selection, single and co-culture batch fermentation, and finally continuous co-fermentation were optimized. The combination of diluted acid pretreatment (3.5 %) and enzymatic conversion (1:10 enzyme (63 floating-point unit (FPU)/mL)/biomass ratio) resulted in the maximum sugar yield (81 % conversion). By concentrating the hydrolysates, sugars level increased by threefold while that of furfural reduced by 50 % (0.56 to 0.28 g/L). Combined application of active carbon and resin led to complete removal of furfural, hydroxyl methyl furfural, and acetic acid. The strains Saccharomyces cerevisiae NCIM 3090 with 66.4 g/L ethanol production and Candida tropicalis NCIM 3119 with 9.9 g/L xylitol production were selected. The maximum concentrations of ethanol and xylitol in the single cultures were recorded at 31.5 g/L (0.42 g/g yield) and 26.5 g/L (0.58 g/g yield), respectively. In the batch co-culture system, the ethanol and xylitol productions were 33.4 g/L (0.44 g/g yield) and 25.1 g/L (0.55 g/g yield), respectively. The maximum ethanol and xylitol volumetric productivity values in the batch co-culture system were 65 and 58 % after 25 and 60 h, but were improved in the continuous co-culture mode and reached 80 % (55 g/L) and 68 % (31 g/L) at the dilution rate of 0.03 L per hour, respectively. Hence, the continuous co-production strategy developed in this study could be recommended for producing value-added products from this hugely generated lignocellulosic waste.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SS, Khan M, Fagan B, Mullins E, Doohan FM (2012) Exploiting the inter-strain divergence of Fusarium oxysporum for microbial bioprocessing of lignocellulose to bioethanol. AMB Express, 15:2(1):16. doi: 10.1186/2191-0855-2-16
Amillastre E, Aceves-Lara CA, Uribelarrea JL, Alfenore S, Guillouet SE (2012) Dynamic model of temperature impact on cell viability and major product formation during fed-batch and continuous ethanolic fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 117:242–250
Avci A, Saha BC, Kennedy GJ, Cotta MA (2013) Dilute sulfuric acid pretreatment of corn stover for enzymatic hydrolysis and efficient ethanol production by recombinant Escherichia coli FBR5 without detoxification. Bioresour Technol 142:312–319
Balat M (2011) Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: a review. Energ Convers Manage 52:858–875
Biely P, Mislovičová D, Toman R (1985) Soluble chromogenic substrates for the assay of endo-1,4-β-xylanases and endo-1,4-β-glucanases. Anal Biochem 144:142–146
Binod P, Sindhu R, Singhania RR, Vikram S, Devi L, Nagalakshmi S, Kurien N, Sukumaran RK, Pandey A (2010) Bioethanol production from rice straw: an overview. Bioresour Technol 101:4767–4774
Chen Y (2011) Development and application of co-culture for ethanol production by co-fermentation of glucose and xylose: a systematic review. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(5):581–597
Chen C, Tang X, Xiao Z, Zhou Y, Jiang Y, Fu S (2012) Ethanol fermentation kinetics in a continuous and closed-circulating fermentation system with a pervaporation membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 114:707–710
Cheng JJ, Timilsina GR (2011) Status and barriers of advanced biofuel technologies: a review. Renew Energ 36:3541–3549
Cherubini F (2010) The biorefinery concept: using biomass instead of oil for producing energy and chemicals. Energ Convers Manage 51:1412–1421
Cherubini F, Ulgiati S (2010) Crop residues as raw materials for biorefinery systems—a LCA case study. Appl Energy 87:47–57
Colom X, Carrasco F, Pages P, Canavate J (2003) Effects of different treatments on the interface of HDPE/lignocellulosic fiber composites. Composites Sci Technol 63(2):161–169
da Cunha-Pereira F, Hickert LR, Sehnem NT, de Souza-Cruz PB, Rosa CA, Ayub MAZ (2011) Conversion of sugars present in rice hull hydrolysates into ethanol by “Spathaspora arborariae”, “Saccharomyces cerevisiae”, and their co-fermentations. Bioresour Technol 102:4218–4225
de Jong EA, Higson A, Walsh P, Wellisch M (2012) Product developments in the bio-based chemicals arena. Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 6:606–624
Dereli RK, van der Zee FP, Heffernan B, Grelot A, van Lier JB (2014) Effect of sludge retention time on the biological performance of anaerobic membrane bioreactors treating corn-to-ethanol thin stillage with high lipid content. Water Res 49:453–464
Ding WW, Wu YT, Tang XY, Yuan L, Xiao ZY (2011) Continuous ethanol fermentation in a closed-circulating system using an immobilized cell coupled with PDMS membrane pervaporation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:82–87
Edama NA, Sulaiman A, Rahim SNA (2014) Enzymatic saccharification of Tapioca processing wastes into biosugars through immobilization technology (Mini Review). Biofuel Res J 1(1):2–6
Emodi A (1978) Xylitol: its properties and food applications. Food Technol 32:28–32
Franceschin G, Sudiro M, Ingram T, Smirnova I, Brunner G, Bertucco A (2011) Conversion of rye straw into fuel and xylitol: a technical and economical assessment based on experimental data. Chem Eng Res Des 89:631–640
Galbe M, Zacchi G (2012) Pretreatment: the key to efficient utilization of lignocellulosic materials. Biomass Bioenerg 46:70–78
Granström TB, Izumori K, Leisola M (2007) A rare sugar xylitol. Part II: biotechnological production and future applications of xylitol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:273–276
Haghighi Mood S, Golfeshan AH, Tabatabaei M, Abbasalizadeh S, Ardjmand M, Salehi Jouzani G (2013a) Comparison of different ionic liquids pretreatment for corn stover enzymatic saccharification. Prep Biochem Biotech. doi:10.1080/10826068.2013.833112
Haghighi Mood S, Golfeshan AH, Tabatabaei M, Salehi Jouzani G, Najafi GH, Gholami M, Ardjmand M (2013b) Lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew Sust Energ Rev 27:77–93
Hendriks ATWM, Zeeman G (2009) Pretreatment to enhance the digestibility of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 100:10–18
Heredia-Olea E, Pérez-Carrillo E, Serna-Saldívar SO (2015) Effect of extrusion conditions and hydrolysis with fiber-degrading enzymes on the production of C5 and C6 sugars from brewers’ spent grain for bioethanol production. Biofuel Res J 2(1):203–208
Horiuchi J, Tada K, Kanno T (2010) Biorefinery for bioethanol, lactic acid, xylitol and astaxanthin production from corn cobs. J Biotech 150:171
Hsu TC, Guo GL, Chen WH, Hwang WS (2010) Effect of dilute acid pretreatment of rice straw on structural properties and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 101:4907–4913
Huang CF, Jiang YF, Guo GL, Hwang WS (2011) Development of a yeast strain for xylitol production without hydrolysate detoxification as part of the integration of co-product generation within the lignocellulosic ethanol process. Bioresour Technol 102:3322–3329
Iwamoto S, Nakagaito AN, Yano H, Nogi M (2005) Optically transparent composites reinforced with plant fiber-based nanofibers. Appl Physics A 81(6):1109–1112
Khongsay N, Laopaiboon L, Jaisil P, Laopaiboon P (2012) Optimization of agitation and aeration for very high gravity ethanol fermentation from sweet sorghum juice by Saccharomyces cerevisiae using an orthogonal array. Design Energies 5:561–576
Kim S, Dale BE (2004) Global potential bioethanol production from wasted crops and crop residues. Biomass Bioenerg 26:361–375
Kumar P, Barrett DM, Delwiche MJ, Stroeve P (2009) Methods for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for efficient hydrolysis and biofuel production. Ind Eng Chem Res 48:3713–3729
Kundiyana DK, Huhnke LR, Wilkins RM (2011) Effect of nutrient limitation and two-stage continuous fermentor design on productivities during “Clostridium ragsdalei” syngas fermentation. Bioresour Technol 102:6058–6064
Latif F, Rajoka MI (2001) Production of ethanol and xylitol from corn cobs by yeasts. Bioresour Technol 77(1):57–63
Li Q, Allen S, Ghosh S, Gorsich S (2009) Yeast genes identified in HMF tolerance screen suggest link to other lignocellulosic derived inhibitors including furfural and vanillin. The 31st Symposium on Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals (May 3-6, 2009)
Liu L, Sun J, Cai C, Wang S, Pei H, Zhang J (2009) Corn stover pretreatment by inorganic salts and its effects on hemicellulose and cellulose degradation. Bioresour Technol 100:5865–5871
Ma H, Liu WW, Chen X, Wu YJ, Yu ZL (2009) Enhanced enzymatic saccharification of rice straw by microwave pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 100:1279–1284
Martínez ML, Sánchez S, Bravo V (2012) Production of xylitol and ethanol by “Hansenula polymorpha” from hydrolysates of sunflower stalks with phosphoric acid. Ind Crop Prod 40:160–166
McMillan JD (1997) Bioethanol production: status and prospects. Renew Energ 10:295–302
Moon SK, Kim WS, Choi GW (2012) Simultaneous saccharification and continuous fermentation of sludge-containing mash for bioethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae CHFY0321. J Biotechnol 157:584–589
Morales-Rodriguez R, Gernaey KV, Meyer AS, Sin G (2011) A mathematical model for simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation (SSCF) of C6 and C5 sugars. Chin J Chem Eng 19(2):185–191
Ntihuga JN, Senn T, Gschwind P, Kohlus R (2012) Efficiency of Blenke cascade system for continuous bio-ethanol fermentation. Bioresour Technol 123:221–229
Palmqvist E, Hahn-Hägerdal B (2000) Fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysates. II: inhibitors and mechanisms of inhibition. Bioresour Technol 74:25–33
Pothiraj C, Arun A, Eyini M (2015) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of cassava waste for ethanol production. Biofuel Res J 2(1):196–202
Prakash G, Varma AJ, Prabhune A, Shouche Y, Rao M (2011) Microbial production of xylitol from D-xylose and sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose using newly isolated thermotolerant yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. Bioresour Technol 102:3304–3308
Radočaj O, Diosady LL (2014) Continuous ethanol fermentation in immersed, cross-flow microfiltration membrane bioreactor with cell retention. J Basic Appl Sci 10:543–553
Rinaldi R, Schüth F (2009) Acid hydrolysis of cellulose as the entry point into biorefinery schemes. Chem Sus Chem 2:1096–1107
Saha BC, Iten LB, Cotta MA, WuYV (2005) Dilute acid pretreatment, enzymatic saccharification and fermentation of wheat straw to ethanol. Process Biochem 40:3693–3700
Salehi Jouzani G, Taherzadeh MJ (2015) Advances in consolidated bioprocessing systems for bioethanol and butanol production from biomass: a comprehensive review. Biofuel Res J 2(1):152–195
Sanchez S, Bravo V, Garcıa JF, Cruz N, Cuevas M (2008) Fermentation of D-glucose and D-xylose mixtures by Candida tropicalis NBRC 0618 for xylitol production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:709–716
Sewalt VJH, Glasser WG, Beauchemin KA (1997) Lignin impact on fiber degradation. 3. Reversal of inhibition of enzymatic hydrolysis by chemical modification of lignin and by additives. J Agri Food Chem 45(5):1823–1828
Sharma S, Rangaiah GP (2012) Modeling and optimization of a fermentation process integrated with cell recycling and pervaporation for multiple objectives. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:5542–5551
Sharma S, Kumar R, Gaur R, Agrawal R, Gupta RP, Tuli DK, Das B (2015) Pilot scale study on steam explosion and mass balance for higher sugar recovery from rice straw. Bioresour Technol 175:350–357
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker D (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Technical Report NREL. TP-510-42618
Suriyachai N, Weerasaia K, Laosiripojana N, Champreda V, Unrean P (2013) Optimized simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of rice straw for ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Scheffersomyces stipitis co-culture using design of experiments. Bioresour Technol 142:171–178
Tang Y, Zhao D, Cristhian C, Jiang J (2011) Simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation of lignocellulosic residues from commercial furfural production and corn kernels using different nutrient media. Biotech Biofuel 4:1–10
Wahlbom CF, Hahn–Hägerdal B (2002) Furfural, 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, and acetoin act as external electron acceptors during anaerobic fermentation of xylose in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotech Bioeng 78:172–178
Wang L, Wang JG, Littlewood J, Cheng HB (2014) Co-production of biorefinery products from kraft paper sludge and agricultural residues: opportunities and challenges. Green Chem 16(3):1527–1533
Yadav KS, Naseeruddin S, Prashanthi GS, Sateesh L, Rao LV (2011) Bioethanol fermentation of concentrated Rice straw hydrolysate using co culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis. Bioresour Technol 102(11):6473–6478
Yin P, Yu Q, Lin Z, Kaewsarn P (2001) Biosorption and desorption of cadmium (II) by biomass of Laminaria japonica. Environ Technol 22(5):509–514
Ylitervo P, Akinbomi J, Taherzadeh MJ (2013) Membrane bioreactors’ potential for ethanol and biogas production: a review. Environ Technol 34(13-14):1711–1723
Ylitervo P, Franzén CJ, Taherzadeh MJ (2014) Continuous ethanol production with a membrane bioreactor at high acetic acid concentrations. Membranes 4(3):372–387
Zha J, Li BZ, Shen MH, Hu ML, Song H, Yuan YJ (2013) Optimization of CDT-1 and XYL1 expression for balanced co-production of ethanol and xylitol from cellobiose and xylose by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 8(7), e68317. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068317
Zhang J, Liu HJ, Liu DH (2005) Effect of different types of gas in gas stripping ethanol fermentation (GSEF). Chin J Process Eng 5:349–352
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by Agricultural Biotechnology Research Institute of Iran (Grant Number: 2-05-05-9009). We would like to thank all our colleagues in the Microbial Biotechnology and Biosafety Department of ABRII for their kind support and assistance during the course of this investigation.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahed, O., Jouzani, G.S., Abbasalizadeh, S. et al. Continuous co-production of ethanol and xylitol from rice straw hydrolysate in a membrane bioreactor. Folia Microbiol 61, 179–189 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0420-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0420-0