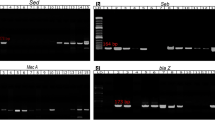
Abstract
Mastitis caused by microbial infections in dairy goats reduces milk yield, modifies milk composition, and potentially contributes to morbidity in herds and consumers of dairy products. Microorganisms associated with mastitis in dairy goats are commonly controlled with antibiotics, but it is known that continued use of these chemical agents promotes antibiotic resistance among bacterial populations. Recently, it has been shown that bacteriocins of Bacillus thuringiensis inhibit growth of food-borne pathogens and also bacteria associated with bovine mastitis. However, there is no report on their ability to inhibit microorganisms linked to mastitis in dairy goats. In this study, using 16S rDNA and ITS regions of rDNA, we identified nine bacterial isolates and an encapsulated yeast associated with mastitis in dairy goats. Enterococcus durans, Brevibacillus sp., and Staphylococcus epidermidis 2 were resistant to, respectively, 75, ~67, ~42, and ~42 % of the antibiotics screened. In addition, 60 % of the bacterial isolates were resistant to penicillin, ampicillin, vancomycin, and dicloxacillin. Importantly, 60 % of the isolates were inhibited by the bacteriocins, but S. epidermidis 1, Enterobacter sp., Escherichia vulneris, and Cryptococcus neoformans were not susceptible to these antimicrobial peptides. Using Brevibacillus sp. and Staphylococcus chromogenes as indicator bacteria, we show that peptides of ~10 kDa that correspond to the molecular mass of bacteriocins used in this study are responsible for the inhibitory activity. Our results demonstrate that multiple antibiotic-resistant bacteria associated with subclinical mastitis in dairy goats from Guanajuato, Mexico, are susceptible to bacteriocins produced by B. thuringiensis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barboza-Corona JE, Vazquez-Acosta H, Bideshi DK, Salcedo-Hernández R (2007) Bacteriocin-like inhibitor substances produced by Mexican strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Arch Microbiol 187:117–126
Barboza-Corona JE, de la Fuente-Salcido N, Alva-Murillo N, Ochoa-Zarsoza A, Lopez-Meza JE (2009) Activity of bacteriocins synthesized by Bacillus thuringiensis against Staphylococcus aureus isolates associated to bovine mastitis. Vet Microbiol 138:179–183
Barron-Bravo OG, Gutierrez-Chavez AJ, Angel-Sahagun CA, Montaldo HH, Shepard L, Valencia-Posadas M (2013) Losses in milk yield, fat and protein contents according to different levels of somatic cell count in dairy goats. Small Rumin Res 113:421–431
Bernacka H (2006) Cytological quality of goat milk on the basis of the somatic cell count. J Cent Eur Agr 7:773–778
Bose T, Reese AJ, Ory JJ, Janbon G, Doerin TL (2003) A yeast under cover: the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans. Eukaryot Cell 2:655–663
Bottone EJ (1980) Cryptococcus neoformans: pitfalls in diagnosis through evaluation of gram-stained smears of purulent exudates. J Clin Microbiol 12:790–791
Bourabah A, Ayad A, Boukraa L, Hammoudi SM, Benbarek H (2013) Prevalence and etiology of subclinical mastitis in goats of the Tiaret region, Algeria. Global Vet 11:604–608
Castañeda-Ramirez C, Cortes-Rodriguez V, de la Fuente-Salcido N, Bideshi DK, Barboza-Corona JE (2011) Isolation of Salmonella spp. from lettuce and evaluation of its susceptibility to novel bacteriocins synthesized by Bacillus thuringiensis and antibiotics. J Food Prot 74:274–278
Chu C, Yu C, Lee L, Su Y (2012) Genetically divergent methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and sec-dependent mastitis of dairy goats in Taiwan. BMC Vet Res 8:39
Cladera-Oliva F, Caron GR, Brandelli A (2004) Bacteriocin-like substance production by Bacillus licheniformis strain P40. Lett Appl Microbiol 38:251–256
Cotter PD, Ross RP, Hill C (2013) Bacteriocins—a viable alternative to antibiotics? Nature Rev Microbiol 11:95–105
de la Fuente-Salcido N, Alanis-Guzman MG, Bideshi DK, Salcedo-Hernandez R, Bautista-Justo M, Barboza-Corona JE (2008) Enhanced synthesis and antimicrobial activities of bacteriocins produced by Mexican strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Arch Microbiol 190:633–640
de la Fuente-Salcido NM, Barboza-Corona JE, Espino-Monzon AN, Pacheco-Cano RD, Balagurusamy N, Bideshi DK, Salcedo-Hernandez R (2012) Expanding the use of a fluorogenic method to determine activity and mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis bacteriocins against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Sci World J 2012:503269
Delgado A, Brito D, Fevereiro P, Tenreiro R, Peres C (2005) Bioactivity quantification of crude bacteriocins solutions. J Microbiol Meth 62:121–124
Escareño L, Salinas-Gonzalez H, Wirzinger M, Iñiguez L, Sölkner J, Meza-Herrera C (2013) Dairy goat production systems: status quo, perspectives and challenges. Trop Anim Health Prod 45:17–34
Federici BA (2005) Insecticidal bacteria: an overwhelming success for invertebrate pathology. J Invertebr Pathol 89:30–38
Fujita SI, Senda Y, Nakaguchi S, Hashimoto T (2001) Multiplex PCR using internal transcribed spacer 1 and 2 regions for rapid detection and identification of yeast strains. J Clin Microbiol 39:3617–3622
Haenlein GFW (2002) Relationship of somatic cell counts in goat milk to mastitis and productivity. Small Rumin Res 45:163–178
Islam A, Samad A, Rahman AKMA (2012) Prevalence of subclinical caprine mastitis in Bangladesh based on parallel interpretation of three screening tests. Inter J Anim Vet Adv 4:225–228
Leitner G, Merin U, Silanikove N (2004) Changes in milk composition as affected by subclinical mastitis in goats. J Dairy Sci 87:1719–1726
León-Galván MF, Carbajal N, Frickey T, Santos L (2009) Microbial identification of the Nichupte-Bojorquez coastal lagoon in Cancun, Mexico. Aquatic Ecol 43:197–205
León-Galván MF, Barboza-Corona JE, Lechuga-Arana AA, Valencia-Posadas M, Aguayo DD, Cedillo-Pelaez C, Martínez-Ortega EA, Gutierrez-Chavez AJ (2015) Molecular detection and sensitivity to antibiotics and bacteriocins of pathogens isolates from bovine mastitis in family dairy herds of central Mexico. BioMed Res Int 2015:615153
Moroni P, Pisoni G, Antonini M, Ruffo G, Carli S, Varisco G, Boettcher P (2005) Subclinical mastitis and antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococcus caprae and Staphylococcus epidermis isolated from two Italian goat herds. J Dairy Sci 88:1694–1704
Ndegwa EN, Mulei CM, Munyua SJ (2001) Prevalence of microorganisms associated with udder infection in Dairy goats on small scale farms in Kenyae. J S Afr Vet Assoc 72:97–98
Paik HD, Bae SS, Park H, Pan JG (1997) Identification and partial characterization of tochicin, a bacteriocin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. tochigiensis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19:294–298
Pal M, Randhawa HS (1976) Caprine mastitis due to Cryptococcus neoformans. Sabouraudia 14:261–263
Persson Y, Olofsson I (2011) Direct and indirect measurement of somatic cell count as indicator of intramammary infection in dairy goats. Acta Vet Scand 53:15
Pieterse R, Todorov SD, Dicks LM (2008) Bacteriocin ST91KM, produced by Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. macedonicus ST91KM, is a narrow-spectrum peptide active against bacteria associated with mastitis in dairy cattle. Can J Microbiol 54:525–531
Raynal-Ljutovac K, Pirisi A, de Cremoux R, Gonzalo C (2007) Somatic cells of goat and sheep milk: analytical, sanitary, productive and technological aspects. Small Rumin Res 68:126–144
Ryan MP, Meaney WJ, Ross RP, Hill C (1998) Evaluation of lacticin 3147 and a teat seal containing this bacteriocin for inhibition of mastitis pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2287–2290
Thomas P (2006) Isolation an ethanol-tolerant endospore-forming gram-negative Brevibacillus sp. as a convert contaminant in grape tissue cultures. J Appl Microbiol 101:764–774
Twomey DP, Wheelock AI, Flynn J, Meaney WJ, Hill C, Ross RP (2000) Protection against Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in dairy cows using a bismuth-based teat seal containing the bacteriocin, lacticin 3147. J Dairy Sci 83:1981–1988
Ukuku DO, Shelef LA (1997) Sensitivity of six strains of Listeria monocytogenes to nisin. J Food Prot 60:867–869
Varella-Coelho ML, Santos-Nascimento JD, Fagundes PC, Madureira DJ, Oliveira SS, de Paiva V, Brito MA, Freire Bastos Mdo C (2007) Activity of staphylococcal bacteriocins against Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus agalactiae involved in bovine mastitis. Res Microbiol 158:625–630
Viguier C, Arora S, Gilmartin N, Welbeck K, O’Kennedy R (2009) Mastitis detection: current trends and future perspectives. Trends Biotechnol 27:486–493
Yount NY, Yeaman MR (2005) Immunocontinuum: perspectives in antimicrobial peptides mechanisms of action and resistance. Protein Pept Lett 12:49–67
Yount NY, Yeaman MR (2013) Peptide antimicrobials: cell wall as a bacterial target. Ann NY Acad Sci 1277:127–138
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grants from the Universidad de Guanajuato (project 24/2011) and Fundación Guanajuato Produce A.C. Mexico (project FGP 583/12) to J. E. Barboza-Corona and M. Valencia-Posadas, respectively. E.A. Martínez-Ortega is an undergraduate student supported by the Universidad de Guanajuato. We thank Dr. Luz Edith Casados-Vázquez and Jaime J. Badajoz-Martínez from Universidad de Guanajuato for their technical support during this study. We appreciate the facilities provided by the producers for this study as well.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez-Chávez, A.J., Martínez-Ortega, E.A., Valencia-Posadas, M. et al. Potential use of Bacillus thuringiensis bacteriocins to control antibiotic-resistant bacteria associated with mastitis in dairy goats. Folia Microbiol 61, 11–19 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0404-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-015-0404-0