Abstract
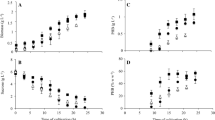
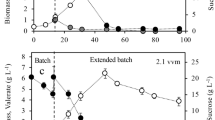
The PHB production by Cupriavidus necator H16 depends on the type and concentration of stress factors and on the time of stress application. Hydrogen peroxide and ethanol significantly enhanced PHB accumulation in C. necator cells. Improved yields (10.9 g/L PHB) were observed after exposure of bacterial culture to 0.5 mmol/L H2O2 at the beginning of cultivation and to additional peroxide stress (5 mmol/L H2O2) after 60 h of cultivation (beginning of the stationary phase). Production was then ≈28 % higher than in control (8.50 g/L PHB). The highest yields (11.2 g/L PHB) were observed when ethanol (0.5 %) was applied at the beginning of stationary phase. An application of exogenous stress could thus be used as a simple strategy for a significant improvement of PHB production in C. necator.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NB:
-
nutrient broth (agar, medium)
- MS:
-
mineral salt medium
- PHA:
-
polyhydroxyalkanoates
- PHB:
-
poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)
References
Ayub N.D., Pettinari M.J., Ruiz J.A., Lopez N.I.: A polyhydroxybutyrate-producing Pseudomonas sp. isolated from Antarctic environments with high stress resistance. Curr.Microbiol.49, 170–174 (2004).
Brandl H., Gross R.A., Lenz R.W., Fuller R.C.: Pseudomonas oleovorans as a source of poly(β-hydroxyalkanoates) for potential application as a biodegradable polyester. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.54, 1977–1982 (1988).
Breedveld M.W., Dijkema C., Zevenhuizen L.P.T.M., Zehner A.J.B.: Response of intracellular carbohydrates to NaCl shock in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar triforii TA-1 and Rhizobium meliloti SU-47. J.Gen.Microbiol.139, 3157–3163 (1993).
Deng S.P., Tabatabai M.A.: Colorimetric determination of reducing sugar in soils. Soil Biol.Biochem.26, 473–477 (1994)
Izawa S., Maeda K., Miki T., Mano J., Inoue Y., Kimura A.: Importance of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the adaptive response to hydrogen peroxide in Sacharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem.J.330, 811–817 (1998).
Kadouri D., Jurkevitch E., Okon Y.: Involvement of the reserve material poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in Azospirillum brasilense stress endurance and root colonization. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.69, 3244–3250 (2003).
Kamnev A.A., Tugarova A.V., Antonyuk L.P.: Endophytic and epiphytic strains of Azospirillum brasilense respond differently to heavy metal stress. Microbiology76, 809–811 (2007).
Kessler B., Wilholt B.: Poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates), pp. 2024–2040 in M.C. Flickinger, S.W. Drew (Eds): Encyclopedia of Bioprocess Technology — Fermentation, Biocatalysis, and Bioseparation, Vols 1–5. John Wiley & Sons, New York 1999.
Khanna S., Srivastava A.K.: Statistical media optimization studies for growth and PHB production by Ralstonia eutropha. Process Biochem.40, 2173–2182 (2005).
Kimura H., Ohura T., Matsumoto T., Ikaraski T.: Effective biosynthesis of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) with high 4-hydroxybutyrate fractions by Wautersia eutropha in the presence of α-amino acids. Polymer Internat. 57, 149–157 (2008).
Natarajan K., Kishore L., Babu C.R.: Sodium-chloride stress results in increased poly-β-hydroxybutyrate production in Rhizobium DDSS-69. Microbios82, 95–107 (1995).
Reddy C.S.K., Ghai R., Rashmi, Kalia V.C.: Polyhydroxyalkanoates: an overview. Biores.Technol.87, 137–146 (2003).
Ruiz J.A., Lopez N.I., Fernandez R.O., Mendez B.S.: Polyhydroxyalkanoate degradation is associated with nucleotide accumulation and enhances stress resistance and survival of Pseudomonas oleovorans in natural water microcosms. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.67, 225–230 (2001).
Sardesai N., Babu C.R.: Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate metabolism is affected by changes in respiratory enzymatic activities due to cold stress in two psychrotrophic strains of Rhizobium. Curr.Microbiol.42, 53–58 (2001).
Wang J., Yu H.Q.: Biosynthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) by Ralstonia eutropha ATCC 17699 in batch cultures. Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol.75, 871–878 (2007).
Zhang S.P., Norrlow O., Wawrzynczyk J., Dey E.S.: Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthesis in the biofilm of Alcaligenes eutrophus using glucose enzymatically released from pulp fiber sludge. Appl.Environ.Microbiol.70, 6776–6782 (2004).
Zhao Y.H., Li H.M., Qin L.F., Wang H.H., Chen G.Q.: Disruption of the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase gene in Aeromonas hydrophila reduces its survival ability under stress conditions. FEMS Microbiol.Lett.276, 34–41 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Obruca, S., Marova, I., Svoboda, Z. et al. Use of controlled exogenous stress for improvement of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production in Cupriavidus necator . Folia Microbiol 55, 17–22 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0003-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0003-z