Abstract
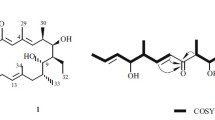
During the screening program for fungicides, one actinomycete strain ECO 00047 was isolated with the potential activity against fungus. According to the morphology and analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA gene (1500 bp) this isolate was identified as Streptomyces diastaticus. The active compounds were separated by silica gel column chromatography, Sephadex LH-20 gel filtration and then purified by flash chromatography on C18 (20–45 μm). The chemical structure of the bioactive compounds I and II were elucidated, based on the spectroscopic data of MS, IR, UV, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR and X-ray single crystal diffraction analysis. Compounds I and II were identical with oligomycins A and C, the macrolide antibiotics which have been known to be produced by Streptomyces diastatochromogenes, S. libani and S. avermitilis. The two compounds exhibited a strong activity against Aspergillus niger, Alternaria alternata, Botrytis cinerea and Phytophthora capsici but no activity toward bacteria. Although the two above antibiotics were known, their isolation has so far not been reported from S. diastaticus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schäffer A.A., Zhang J., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J.: Gapped blast and psi-blast: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl.Acids Res.25, 3389–3402 (1997).
Berdy J.: Bioactive microbial metabolites: a personal view. J.Antibiot.58, 1–26 (2005).
Carter G.T.: Structure determination of oligomycin A and C. J.Org.Chem.51, 4264–4271 (1986).
De Waard M.A., Georgopoulos S.G., Hollomon D.W., Ishii H., Leroux P., Ragsdale N.N., Schwinn F.J.: Chemical control of plant disease: problems and prospects. Ann.Rev.Phytopathol.31, 403–421 (1993).
El-Naggar M.Y.: Kosinostatin, a major secondary metabolite isolated from the culture filtrate of Streptomyces violaceusniger strain HAL64. J.Microbiol.45, 262–267 (2007).
El-Naggar M.Y., El-Aassar S.A., Abdul-Gawad S.M.: Meroparamycin production by newly isolated local Streptomyces sp. strain MAR01: taxonomy, fermentation, purification and structural elucidation. J.Microbiol.44, 432–438 (2006).
Enomoto Y., Shiomi K., Matsumoto A., Takahashi Y., Iwai Y., Harder A., Kölbl H., Woodruff H.B., ømura S.: Isolation of a new antibiotic oligomycin G produced by Streptomyces sp. WK-6150. J.Antibiot.54, 308–313 (2001).
Felsenstein J.: Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution39, 783–791 (1985).
Fourati-Ben Fguira L., Fotso S., Ben Ameur-Mehdi R., Mellouli L., Laatsch H.: Purification and structure elucidation of antifungal and antibacterial activities of newly isolated Streptomyces sp. strain US80. Res.Microbiol.156, 341–347 (2005).
von Gelehn M., Norrsetam R., Kierkegaard P., Maron L., Ernster L.: Three-dimensional structure of oligomycin B. FEBS Lett.20, 267–269 (1972).
Grammatikova N.E., Bibikova M.V., Spiridonova I.A., Kabanov A.E., Katlinskiy A.V.: Streptomyces griseolus no. 182 — a novel organism producing oligomycin antibiotics. Taxonomy, fermentation, and isolation. Antibiot.Khimioter.48, 11–15 (2003).
Higgins D.G., Bleasby A.J., Fuchs R.: Clustal V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput.Appl.Biosci.8, 189–191 (1992).
Holt J.G.: Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore 1994.
Hopwood D.A., Bibb M.J., Chater K.F., Kieser T., Bruton C.J., Kieser H.M., Lydiate D.J., Smith C.P., Ward J.M.: Preparation of chromosomal, plasmid and phage DNA, pp. 79–80 in D.A. Hopwood (Ed.): Genetic Manipulation of Streptomyces — a Laboratory Manual. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich (UK) 1985.
Kim H.S., Han S.B., Kim H.M., Kim Y.H., Lee J.J.: 41-Demethylhomooligomycin B, a new immunosuppresant antibiotic from Streptomyces ostreogriseus. J.Antibiot.49, 1275–1277 (1996).
Kim B.S., Moon S.S., Hwang B.K.: Isolation, identification, and antifungal activity of a macrolide antibiotic, oligomycin A, produced by Streptomyces libani. Can.J.Bot.77, 850–858 (1999).
Kim Y.S., Kim H.M., Chang C., Hwang I.C., Oh H., Ahn J.S., Kim K.D., Hwang B.K., Kim B.S.: Biological evaluation of neopeptins isolated from a Streptomyces strain. Pest.Manag.Sci.63, 1208–1214 (2007).
Kimura M.: A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J.Mol.Evol.16, 111–120 (1980).
Kimura M.: The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (UK) 1983.
Knight S.C., Anthony V.M., Brady A.M., Greenland A.J., Heaney S.P., Murray D.C., Powell K.A., Schulz M.A., Sinks C.A., Worthington P.A., Youle D.: Rationale and perspectives on the development of fungicides. Ann.Rev.Phytopathol.35, 349–372 (1997).
Kobayashi K., Nishino C., Ohta J., Sato S., Mikawa T., Shiobara Y., Kodama M., Nishimoto N.: Oligomycin E, a new antitumor antibiotic produced by Streptomyces sp. MCI-2225. J.Antibiot.40, 1053–1057 (1987).
Laatsch H., Kellner M., Wolf G., Lee Y.S., Hansske F., Konetschny-Rapp S., Pessara U., Scheuer W., Stockinger H.: Oligomycin F, a new immunosuppressive homologue of oligomycin A. J.Antibiot.46, 1334–1341 (1993).
Lange L., Lopez C.S.: Microorganisms as a source of biologically active secondary metabolite, pp. 1–26 in L.G. Copping (Ed.): Crop Protection Agents from Nature: Natural Products and Analogues. The Royal Society of Chemistry, London 1996.
Lechevalier H.A.: Production of the same antibiotics by members of different genera of microorganisms. Adv.Appl.Microbiol.19, 25–45 (1975).
Lee J.Y., Lee J.Y., Moon S.S., Hwang B.K.: Isolation and antifungal activity of 4-phenyl-3-butenoic acid from Streptomyces koyangensis strain VK-A60. J.Agric.Food Chem.53, 7696–7700 (2005).
Lin X., Wen Y., Li M., Chen Z., Guo J., Song Y., Li J.: A new strain of Streptomyces avermitilis produces high yield of oligomycin A with potent anti-tumor activity on human cancer cell lines in vitro. Appl.Microbiol.Biotechnol.81, 839–845 (2009).
Masamune S., Sehgal J.M., van Tamelen E.E., Strong F.M., Peterson W.H.: Separation and preliminary characterization of oligomycins A, B and C. J.Am.Chem.Soc.80, 6092–6095 (1958).
Miyadoh S.: Research on antibiotic screening in Japan over the last decade: a producing microorganisms approach. Actinomycetologica9, 100–106 (1993).
Morris G.A., Richards M.S.: Concerted use of two-dimensional NMR techniques in the ab initio assignment of oligomycin A. Magn. Reson.Chem.23, 676–683 (1985).
Park H.J., Lee J.Y., Hwang I.S., Yun B.S., Kim B.S., Hwang B.K.: Isolation and antifungal and actinomycete activities of staurosporine from Streptomyces roseoflavus strain LS-A24. J.Agric.Food Chem.54, 3041–3046 (2006).
Park C.N., Lee D., Kim W., Hong Y., Ahn J.S., Kim B.S.: Antifungal activity of salaceyin A against Colletotrichum orbiculare and Phytophthora capsici. J.Basic Microbiol.47, 332–339 (2007).
Porter N.: Physico-chemical and biophysical panel symposium biologically active secondary metabolites. Pestic.Sci.16, 422–427 (1985).
Saitou N., Nei M.: The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol.Biol.Evol.4, 406–425 (1987).
Shih H.D., Liu Y.C., Hsu F.L., Mulabagal V., Dodda R., Huang J.W.: Fungichromin: a substance from Streptomyces padanus with inhibitory effects on Rhizoctonia solani. J.Agric.Food Chem.51, 95–99 (2003).
Shirling E.B., Gottlieb D.: Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.16, 313–340 (1966).
Smith R.A., Peterson W.H., Mccoy E.: Oligomycin, a new antifungal antibiotic. Antibiot.Chemother.4, 962–970 (1954).
Stackebrandt E., Goebel B.M.: Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA re-association and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Internat.J.Syst.Bacteriol.10, 846–849 (1994).
Szilágyi L., Fehér K.: Oligomycins B and C: complete ab initio assignments of their 1H and 13C NMR spectra and a study of their conformations in solution. J.Mol.Struct.471, 195–207 (1998).
Tanaka Y.T., ømura S.: Agroactive compounds of microbial origin. Ann.Rev.Microbiol.47, 57–87 (1993).
Wagenaar M.M., Williamson R.T., Ho D.M., Carter G.T.: Structure and absolute stereochemistry of 21-hydroxyoligomycin A. J.Nat.Prod.70, 367–371 (2007).
Watve M.G., Tickoo R., Jog M.M., Bhole B.D.: How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces? Arch.Microbiol.157, 386–390 (2001).
Williams S.T., Goodfellow M., Alderson G., Wellington E.M.H., Sneath P.H.A., Sackin M.J.: Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J.Gen.Microbiol.129, 1743–1813 (1983).
William S.T., Goodfellow M., Wellington E.M.H., Vickers J.C., Alderson G., Sneath P.H.A., Sackin M.J., Mortimer A.M.: A probability matrix for identification of some Streptomycetes. J.Gen.Microbiol.129, 1815–1830 (1983).
Williams S.T., Sharpe M.E., Holt J.G., Murray R.G.E., Brener D.J., Kreig N.R., Mouldar J.W., Pfennig N., Sneath P.H.A., Staley J.T.: Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Williams & Willkins, Baltimore 1989.
Yamaguchi I.: Pesticides of microbial origin and applications of molecular biology, pp. 27–49 in L.G. Copping (Ed.): Crop Protection Agents from Nature: Natural Products and Analogues. The Royal Society of Chemistry, London 1996.
Yamazaki M., Yamashita T., Harada T., Nishikiori T., Saito S., Shimada N., Fujii A.: 44-Homooligomycins A and B, new antitumor antibiotics from Streptomyces bottropensis. Producing organism, fermentation, isolation, structure elucidation and biological properties. J.Antibiot.45, 171–179 (1992).
Zhang X., Ryu, K. Kim J., Cheon J., Kim B.: Changes in the sensitivity to metalaxyl, dimethomorph and ethaboxam of Phytophthora infestans in Korea. Plant Pathol.J.21, 33–38 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, P.W., Li, M.G., Zhao, J.Y. et al. Oligomycins A and C, major secondary metabolites isolated from the newly isolated strain Streptomyces diastaticus . Folia Microbiol 55, 10–16 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0002-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-010-0002-0