Abstract
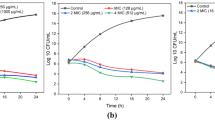
In order to determine the existence of synergism of the bacteriostatic action of flavonoids against G+ bacteria between a clinically interesting conventional antibiotic and a flavonoid, combinations of oxacillin (OXC) and 2,4-dihydroxychalcone (DCH) as enhancer were assayed against methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29 213 and methicillin-resistant S. aureus ATCC 43 300. Using a kinetic-turbidimetric method, growth kinetics was monitored in a broth containing variable amounts of OXC alone and combinations of variable OXC-constant DCH. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of OXC alone and in combination with DCH were evaluated. For the 29 213 strain, OXC MIC was 25 μg/mL, while combinations of 2–8 μg/mL OXC with 10 μg/mL of DCH totally inhibited growth and showed synergism. The resistance of the 43 300 strain in the presence of OXC was verified; OXC-DCH combinations decreased bacterial growth by 35 %. DCH augments the action of OXC against methicillin-susceptible S. aureus and therefore constitutes a good bacteriostatic agent for methicillin-resistant S. aureus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DCH:
-
2,4-dihydroxychalcone
- MIC:
-
minimum inhibitory concentration
- MRSA:
-
methicillin-resistant (S. aureus)
- MSSA:
-
methicillin-sensitive (S. aureus)
- OXC:
-
oxacillin
- PRSP:
-
penicillin-resistant (S. pneumoniae)
- VRE:
-
vancomycin-resistant enterococci
References
Alvarez M.A., Zarelli V.E., Pappano N.B., Debattista N.B.: Bacteriostatic action of synthetic polyhydroxylated chalcones against Escherichia coli ATCC 25 922. Biocell28, 31–34 (2004).
Alvarez M.A., Pappano N.B., Debattista N.B.: Synergism of flavonoids with bacteriostatic action against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25 923 and Escherichia coli ATCC 25 922. Biocell30, 39–42 (2006).
Alvarez M.A., Debattista N.B., Pappano N.B.: Antimicrobial activity and synergism of some substituted flavonoids. Folia Microbiol.53, 23–28 (2008).
Basri D.F., Zin N.M., Bakar N.S., Rahmat F., Mohtar M.: Synergistic effects of phytochemical and oxacillin on laboratory passage-derived vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus strain. J.Med.Sci.8, 131–136 (2008).
Brickner S.J., Hutchinson D.K., Barbachyn M.R., Manninen P.R., Ulanowicz D.A., Garmon S.A., Grega K.C., Hendges S.K., Toops D.S., Ford C.W., Zurenko G.E.: Synthesis and antibacterial activity of U-100592 and U-100766, two oxazolidinone antibacterial agents for the potential treatment of multidrug-resistant Gram-positive bacterial infections. J.Med.Chem.39, 673–679 (1996).
Cushnie T.T.P., Lamb A.J.: Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Internat.J.Antimicrob.Agents26, 343–356 (2005).
Dhar D.N.: The Chemistry of Chalcones and Related Compounds, pp. 5–9. John Wiley & Sons, New York 1981.
Enright M.C., Robinson D.A., Randle G., Feil E.J., Grundmann H., Spratt B.G.: The evolutionary history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Proc.Nat.Acad.Sci.USA99, 7687–7692 (2002).
Fridkin S.K., Hageman J.C., Morrison M., Sanza L.T., Comosabetti K., Jernigan J.A., Harriman K., Harrison L.H., Lynfield R., Farley M.M..: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N.Engl.J.Med.352, 1436–1444 (2005).
Fukai T., Marumo A., Kaitou K., Kanda T., Terada S., Nomura T.: Antimicrobial activity of licorice flavonoids against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Fitoterapia73, 536–539 (2002).
Haraguchi H., Tanimoto K., Tamura Y., Mizutani K., Kinoshita T.: Mode of antibacterial action of retrochalcones from Glycyrrhiza inflata. Phytochemistry48, 125–129 (1998).
Havsteen B.: Flavonoids, a class of natural products of high pharmacological potency. Biochem.Pharmacol. 32, 1141–1148 (1983).
Middleton E. Jr., Kandaswami C., Theoharides T.C.: The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol.Rev.52, 673–751 (2000).
Mori A., Nishino C., Enoki N., Tawata S.: Antibacterial activity and mode of action of plant flavonoids against Proteus vulgaris and Staphylococcus aureus. Phytochemistry26, 2231–2234 (1987).
Nakatsu T., Lupo A., Chinn J., Kang R.: Biological activity of essential oils and their constituents. Stud.Natur.Prod.Chem.21, 571 (2000).
NCCLS (National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards): Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 7th ed.; NCCLS Document M2-A8. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne (PA) 2004a.
NCCLS:Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 14th Informational Suppl.; NCCLS Document M100-S14. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne (PA) 2004b.
NCCLS:Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 5th ed. NCCLS Document M7-A6. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne (PA) 2004c.
Nguyen D.M., Mascola L., Brancoft E.: Recurring methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in a football team. Emerg.Infect.Dis.11, 526–532 (2005).
Pan E.S., Diep B.A., Charlebois E.D., Auerswald C., Carleton H.A., Sensabaugh G.F., Perdreau-remington F.: Population dynamics of nasal strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and their relation to community-associated disease activity. J.Infect.Dis.192, 811–818 (2005).
Pappano N.B., Centorbi O.P., Ferretti F.H.: Determinación de la concentración mÍnima inhibitoria a partir de parámetros cinéticos de crecimiento. Rev.Microbiol.21, 183–188 (1990).
Pappano N.B., Centorbi O.P., Ferretti F.H.: Determination of the responsible molecular zone for the chalcones bacteriostatic activity. Rev.Microbiol.25, 168–174 (1994).
Radulović N., Miíć M., Aleksić J., Đoković D., Palić R., Stojanović G.: Antimicrobial synergism and antagonism of salicylaldehyde in Filipendula vulgaris essential oil. Fitoterapia78, 565–570 (2007).
Saiman L., O’Keefe M., Graham P.L. III, Wu F., Said-Salim B., Kreiswirth B., Lasala A., Schlievert P.M., Della-Latta P.: Hospital transmission of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus among postpartum women. Clin. Infect.Dis.37, 313–1319 (2003).
Saravolatz L.D., Pohlod D.J, Arking L.M.: Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a new source for nosocomial outbreaks. Ann.Intern.Med.97, 325–329 (1982).
Stapleton P.D., Shah S., Anderson J.C., Hara Y., Hamilton-miller J.M.T., Taylor P.W.: Modulation of β-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by catechins and gallates. Internat.J.Antimicrob.Agents23, 462–467 (2004).
Tsuchiya H., Iinuma M.: Reduction of membrane fluidity by antibacterial sophoraflavanone G isolated from Sophora exigua. Phytomedicine7, 161–165 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talia, J.M., Alvarez, M.A., Debattista, N.B. et al. Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus strains toward combinations of oxacillin-2,4-dihydroxychalcone. Folia Microbiol 54, 516–520 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0074-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-009-0074-x