Abstract
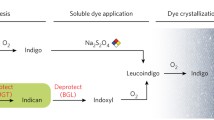
In this study, the reduction of indigo to leuco-indigo by glucose was improved by the use of enzymes, such as glucose oxidase (GOD) and laccase (LAC). In fact, indigo received electrons from the glucose oxidation reaction or the glucose degradation via intermediates resulting in production of leuco-indigo. For indigo reduction involving GOD or LAC, the redox centers of GOD and LAC act as electron carriers from the reduced glucose or transfer electrons directly to indigo molecules. Thus, the turnover rate of electron flow between glucose and indigo by means of these enzymes was increased and improved leuco-indigo production, by about 2–5 times the rate without enzymes. Enzymatically reduced indigo was applied to the dyeing of ramie fabric.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availabilty
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
R.S. Blackburn, T. Bechtold, P. John, Color. Technol. 125, 193 (2009)
A. Roessler, D. Crettenand, Dyes Pigment. 63, 29 (2004)
S. Komorsky-Lovrie, Chem 482, 222 (2000)
T. Bechtold, E. Burtscher, A. Turcanu, O. Bobleter, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143, 2411 (1996)
T. Bechtold, E. Burtscher, A. Turcanu, J. Electroanal. Chem. 465, 80 (1999)
T. Bechtold, E. Burtscher, A. Amann, O. Bobleter, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 89, 2451 (1993)
R.G. Compton, S.J. Perkin, D.P. Gamblin, J. Davis, F. Marken, A.N. Padden, P. John, New J. Chem. 24, 179 (2000)
C. Jung, D.I. Yoo, Y. Shin, Fiber Polym. 21, 2539 (2020)
S. Pricelius, C. Held, M. Murkovic, M. Bozic, V. Kokol, A. Cavaco-Paulo, G.M. Guebitz, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 77, 321 (2007)
M. Božič, S.S. Pricelius, G.M. Guebitz, V. Kokol, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 85, 563 (2010)
R.S. Blakburn, A. Harvey, Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4034 (2004)
A. Vuorema, P. John, M. Keskitalo, M.A. Kulandainathan, F. Marken, Dyes Pigment. 76, 542 (2008)
A. Vuorema, P. John, M. Keskitalo, M.F. Mahon, M.A. Kulandainathand, F. Marken, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 11, 1816 (2009)
L. Saikhao, J. Setthayanond, T. Karpkird, T. Bechtold, P. Suwanruji, J. Clean. Prod. 197, 106 (2018)
T. Tu, Y. Wang, H. Huang, Y. Wang, X. Jiang, Z. Wang, B. Yao, H. Luo, Food Chem. 281, 163 (2019)
G. Wohlfahrt, S. Witt, J. Hendle, D. Schomburg, H.M. Kalisz, H.J. Hecht, Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 55, 969 (1999)
F.N. Comba, M.R. Romero, F.S. Garay, A.M. Baruzzi, Anal. Biochem. 550, 34 (2018)
D.F. Malherbe, M. du Toit, R.R.C. Otero, P. van Rensburg, I.S. Pretorius, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 61, 502 (2003)
S.B. Bankar, M.V. Bule, R.S. Singhal, L. Ananthanarayan, Biotechnol. Adv. 27, 489 (2009)
C.F. Thurston, Microbiol. 140, 19 (1994)
S.V. Surwase, S.A. Patil, S. Srinivas, J.P. Jadhav, Enzyme Microb. Technol. 82, 110 (2016)
L.N. Nguyen, J.P. van de Merwe, F.I. Hai, F.D.L. Leusch, J. Kang, W.E. Price, F. Roddick, S.F. Magram, L.D. Nghiem, Bioresour. Technol. 200, 477 (2016)
M. Chivukula, V. Renganathan, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61, 4374 (1995)
K. Agrawal, V. Chaturvedi, P. Verma, Bioresour. Bioprocess. 5, 4 (2018)
C. Jung, J.I. Rhee, D.I. Yoo, Y. Shin, Fiber. Polym. 23, 127 (2022)
P.A. Shaffer, T.E. Friedemann, J. Biol. Chem. 86, 345 (1930)
B.Y. Yang, R. Montgomery, Carbohydr. Res. 280, 27 (1996)
Y. Degani, A. Heller, J. Phys. Chem. 91, 1285 (1987)
M. Božič, V. Kokol, G.M. Guebitz, Text. Res. J. 79, 895 (2009)
C. Vaz-Dominguez, S. Campuzano, O. Rudiger, M. Pita, M. Gorbacheva, S. Shleev, V.M. Fernadez, A.L. De Lacey, Biosens. Bioelectron. 24, 531 (2008)
S. Riva, TIBTECH 24, 219 (2006)
M.A. Kulandainathan, K. Patil, A. Muthukumaran, R.B. Chanvan, Color. Technol. 123, 143 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (NRF-2019R1I1A3A01057222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Duong, H.D., Rhee, J.I. Improving Indigo Reduction to Leuco-Indigo by Glucose by Means of Direct Electron Transfer and Electron Carriers of Enzymes. Fibers Polym 24, 361–371 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00037-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-023-00037-7