Abstract
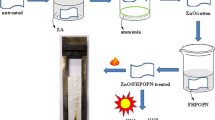
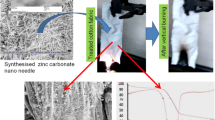
The easy burning of cotton fabrics, which have the widest usage area among natural fibers, is a serious problem. Thus, treatment with an environmental friend flame retardant material is essential for cotton fabrics. Zinc borates are multifunctional fire retardants. They can act as smoke suppressor, flame retardant and spark suppressor. Since they are non-toxic and environmental friend materials, they are ideal flame retardants for fabric treatment. In this study, nano-sized zinc borate (ZnO·3B2O3·7H2O) was synthesized and cotton fabric was treated with zinc borate powder with a novel method. Zinc borates are slightly soluble in water. They were dissolved with aid of ammonia as zinc ammonia borate complexes and were recrystalised on the cotton fabric fibers through the evaporation of ammonia. The burning resistance of treated cotton fabric was investigated. The hardness, hydrophobicity, smoke suppression and burning resistance of untreated and treated cotton fabrics were compared. Since zinc borates have smoke suppression feature, a more slight smoke was observed and a higher rate of carbonization occurred during combustion test of treated cotton fabric compared to the untreated cotton fabric. In addition, the burning rate was reduced from 2.26 cm/s to 1.26 cm/s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Ahmed, AUTEX 2009 World Textile Conference, Izmir, Turkey, Hybridization of Smart Textiles in Medical and Healthcare Management, https://danishchandna.files.wordpress.com/2009/12/paper-link.pdf (Accessed September 21, 2021).
N. Mao and M. Du in “Waterproof and Water Repellent Textiles and Clothing” (J. Williams Ed.), pp.233–265, Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, 2018.
J. Zhang, P. France, A. Radomyselskiy, S. Datta, J. Zhao, and W. V. Ooij, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 88, 1473 (2003).
H. J. Lee, S. Y. Yeo, and S. H. Jeong, J. Mater. Sci., 38, 2199 (2003).
F. Fang, B. Tong, T. Du, X. Zhang, Y. Meng, X. Liu, and X. Tian, Cellulose, 23, 3341 (2016).
A. Bashari, M. Shakeri, and A. R. Shirvan, “UV-protective textiles, The Impact and Prospects of Green Chemistry for Textile Technology”, pp.327–365, Woodhead Publishing, Sawston, 2019.
C. Jiang, W. Liu, M. Yang, C. Liu, S. He, Y. Xie, and Z. Wang, Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp., 559, 235 (2018).
Z. Mai, Z. Xiong, X. Shu, X. Liu, H. Zhang, X. Yin, Y. Zhou, M. Liu, M. Zhang, W. Xu, and D. Chen, Carbohydr. Polym., 199, 516 (2018).
Z. Omerogullari Basyigit and D. Kut, Text. Apparel, 28, 287 (2018).
Q. Zhang, W. Zhang, J. Huang, Y. Lai, T. Xing, G. Chen, W. Jin, H. Liu, and B. Sun, Mater. Des., 85, 796 (2015).
N. Yaman, Fiber. Polym., 10, 413 (2009).
M. Forouharshad, M. Montazer, M. B. Moghadam, and O. Saligheh, Thermochim. Acta, 516, 29 (2011).
Ş. Celep, MS Thesis, Çukurova University, Adana, 2007.
H. Dayioğlu and H. Canbaz Karakas, “Elyaf Bilgisi”, Teknik Fuarcilik, İstanbul, 2007.
N. Seventekin, “Tekstil Kimyasi”, 1st ed., Ege University Textile and Apparel Research Application Center, İzmir, 2004.
F. R. Abe, A. Á. S. De Oliveira R. V. Marino, T. C. R. Rialto, D. P. Oliveira, and D. J. Dorta, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 208, 111745 (2021).
W. Liu, R. Shi, X. Ge, H. Huang, X. Chen, and M. Mu, Prog. Org. Coat., 156, 106271 (2021).
W. Rao, J. Shi, C. Yu, H.-B. Zhao, and Y.-Z. Wang, Chem. Eng. J., 424, 130556 (2021).
A. Cayla, F. Rault, S. Giraud, F. Salaün, V. Fierro, and A. Celzard, Polymers, 8, 331 (2016).
M. Nakpathom and P. Phromphen, NU. Int. J. Sci., 4, 26 (2007).
P. Li, B. Wang, Y. J. Xu, Z. Jiang, C. Dong, Y. Liu, and P. Zhu, ACS Sust. Chem. Eng., 7, 19246 (2019).
J. Liu and C. Xiao, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 119, 1083 (2018).
Ö. Akgül, MS Thesis, Yildiz Technical University, Istanbul, 2010.
Y. Ipek, Turk. J. Chem., 44, 214 (2020).
A. S. Kipcak, F. T. Senberber, M. Yildirim, S. A. Yuksel, E. Moroydor Derun, and N. Tugrul, Chem., Main Group Met., 39, 59 (2016).
G. Ö. Çakal, B. Baltaci, G. Bayram, S. Özkar, and İ. Eroğlu, J. Cryst. Growth, 533, 125461 (2020).
Y. Fang, Q. Wang, C. Guo, Y. Song, and P. A. Cooper, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis, 100, 230 (2013).
H. Durrani, V. Sharma, D. Bamboria, A. Shukla, S. Basak, and W. Ali, Cellulose, 27, 9061 (2020).
S. Gordon and Y. L. Hsie, “Cotton: Science and Technology”, Woodhead Publishing Limited and CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2007.
Y. İpek and Ö. Ertekin, Fiber. Polym., 22, 2826 (2021).
M. Gönen, Ph.D. Dissertation, Izmir Institute of Technology, İzmir, 2009.
Q. Qin, R. H. Guo, E. H. Ren, X. X. Lai, C. Cui, H. Y. Xiao, M. Zhou, G. Yao, S. X. Jiang, and J. W. Lan, ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 8, 10335 (2020).
W. D. Schindler and P. J. Hauser, “Chemical Finishing of Textiles”, Elsevier, Woodhead Publishing, UK, 2004.
N. Tugrul, M. Bardakci, and E. Ozturk, Res. Chem. Intermed., 41, 4395 (2015).
N. Çakici, M. I. Aksu, and E. Erdemir, CYTA-J. Food, 13, 196 (2015).
R. Schubring, Arch. Lebensmittelhyg, 53, 34 (2002).
P. A. V. Freitas, R. R. A. Silva, T. V. de Oliveira, R. R. A. Soares, N. S. Junior, A. R. F. Moraes, A. C. dos S. Pires, and N. F. F. Soares, LWT, 132, 109780 (2020).
Acknowledgement
This study was financially supported by Munzur University (Project no: MFMUB017-05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest appears for the manuscript submission.
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESM)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İpek, Y. Eco-Friendly, Thermal Resistant Cotton Fabric Enhanced with Nano Zinc Borate Powder. Fibers Polym 23, 3435–3441 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4988-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4988-0